Abstract
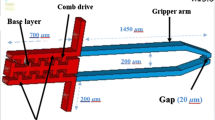
This paper presents design and simulation of a novel electrostatic microelectromechanical systems gripper with an integrated capacitive contact sensor. Moreover, this microgripper is able to employ vibration to release micro objects (cells) actively. Lateral comb drive system is used to close the gap between the gripper arms and hold the objects while the transverse comb differential capacitances act as a contact sensor to prevent damaging the fragile micron-sized particles specifically biological cells. In addition, the capability of the microgripper in generating vibration at the end-effectors electrostatically is an advantage to facilitate releasing process by overbalancing the adhesion forces between the particle and the gripper arm. Finite element analysis based simulations are carried out to estimate the behavior of the microgripper while the standard SOI-MUMPs micromachining process is proposed for fabrication of the microgripper.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar C, Shkel A (2009) MEMS vibratory gyroscopes: structural approaches to improve robustness. Springer, New York
Arai F, Andou D, Fukuda T (1996) Adhesion forces reduction for micro manipulation based on micro physics. In: Paper presented at the IEEE conference, San Diego, 1996
Bazaz SA, Khan F, Shakoor RI (2011) Design, simulation and testing of electrostatic SOI MUMPs based microgripper integrated with capacitive contact sensor. Sens Actuators A Phys 167:44–53
Beyeler F, Neild A, Oberti S, Bell DJ, Sun Y, Dual J, Nelson BJ (2007) Monolithically fabricated microgripper with integrated force sensor for manipulating microobjects and biological cells aligned in an ultrasonic field. J Microelectromech Syst 16:7–15
Chen BK, Zhang Y, Sun Y (2009) Active release of microobjects using a MEMS microgripper to overcome adhesion forces. J Microelectromech Syst 18:652–659
Chen T, Chen L, Sun L, Rong W, Yang Q (2010a) Micro manipulation based on adhesion control with compound vibration. In: Paper presented at the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, October 18–22, 2010
Chen T, Sun L, Chen L, Rong W, Li X (2010b) A hybrid-type electrostatically driven microgripper with an integrated vacuum tool. Sens Actuators A Phys 158:320–327
Chronis N, Lee LP (2005) Electrothermally activated SU-8 microgripper for single cell manipulation in solution. J Microelectromech Syst 14:857–863
Demaghsi H, Mirzajani H, Ghavifekr HB (2013) Design and simulation of a novel metallic microgripper using vibration to release nano objects actively. J Microsys Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-013-1888-7
Duc TC, Lau GK, Creemer JF, Sarro PM (2008) Electrothermal microgripper with large jaw displacement and integrated force sensors. J Microelectromech Syst 17:1546–1555
Fang Y, Tan X (2006) A dynamic JKR model with application to vibrational release in micromanipulation. Paper presented at the Intelligent Robots and Systems Beijing, 9–15 Oct 2006
Fuchiwaki O, Ito A, Misaki D, Aoyama H (2008) Multi-axial micromanipulation organized by versatile micro robots and micro tweezers. In: Paper presented at IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2008, Pasadena, CA, USA
Goldfarb M, Celanovic N (1999) A flexure-based gripper for small-scale manipulation. Robotica 17:181–187
Kim CJ, Pisano AP, Muller RS, Lim MG (1992) Polysilicon microgripper. Sens Actuators A Phys 33:221–227
Kim K, Nilsen E, Huang T, Kim A, Ellis M, Skidmore G, Lee JB (2004) Metallic microgripper with SU-8 adaptor as end-effectors for heterogeneous micro/nano assembly applications. Microsys Technol 10:689–693. doi:10.1007/s00542-004-0367-6
Kohl M, Krevet B, Just E (2002) SMA microgripper system. Sens Actuators A Phys 97:646–652
Kyung JH, Ko BG, Ha YH, Chung GJ (2008) Design of a microgripper for micromanipulation of microcomponents using SMA wires and flexible hinges. Sens Actuators A Phys 141:144–150
Mackay RE, Le HR, Clark S, Williams JA (2013) Polymer micro-grippers with an integrated force sensor for biological manipulation. J Micromech Microeng 23:015005
Millet O, Bernardoni P, Régnier S, Bidaud P, Tsitsiris E, Collard D, Buchaillot L (2004) Electrostatic actuated micro gripper using an amplification mechanism. Sens Actuators A Phys 114:371–378
Molhave K (2004) Tools for in-situ manipulation and characterization of nanostructures. Dissertation, MIC-Department of Micro and Nanotechnology Technical University of Denmark
Park J, Moon W (2005) The systematic design and fabrication of a three-chopstick microgripper. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:251–261
Petrin AA (2009) Processing of sensor information in micro and nano manipulation. Automat Doc Math Ling 43:355–362
Raghavendra MRA, Kumar AS, Jagdish BN (2010) Design and analysis of flexure-hinge parameter in microgripper. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:1185–1193. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2478-9
Riaz K, Bazaz SA, Saleem MM, Shakoor RI (2011) Design, damping estimation and experimental characterization of decoupled 3-DoF robust MEMS gyroscope. Sens Actuators A Phys 172:523–532
Sinan Haliyo D, Régnier S, Bidaud P (2003) Manipulation of micro-objects using adhesion forces and dynamical effects. J Exp Robatics VIII 382–391
Stavrov V, Tomerov E, Hardalov C et al (2010) Low voltage thermo-mechanically driven monolithic microgripper with piezoresistive feedback. In: Ratchev S (ed) Precision Assembly Technologies and Systems. Springer, New York
Tang WC, Nguyen TCH, Howe RT (1989) Laterally driven polysilicon resonant microstructures. Sens Actuator 20:25–32
Varona J, Saenz E, Fiscal-Woodhouse S, Hamoui AA (2009) Design and fabrication of a novel microgripper based on electrostatic actuation. In: Paper presented at IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS’09). 827–832
Voicu R, Esinenco D, Müller R, Eftime L, Tibeica C (2007) Method for overcoming the unwanted displacements of an electro-thermally actuated microgripper. J Young 1
Volland BE, Heerlein H, Rangelow IW (2002) Electrostatically driven microgripper. Microelectron Eng 61:1015–1023
Volland BE, Ivanova K, Ivanov T et al (2007) Duo-action electro thermal micro gripper. Microelectron Eng 84:1329–1332
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demaghsi, H., Mirzajani, H. & Ghavifekr, H.B. A novel electrostatic based microgripper (cellgripper) integrated with contact sensor and equipped with vibrating system to release particles actively. Microsyst Technol 20, 2191–2202 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1989-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1989-3