Abstract
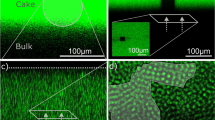
The performance of the microfiltration process is controlled by the filter fouling due to the accumulation of solid matter forming a cake layer on the membrane surface. The objective of this work is to study the cake build up and growth at the particle level and to establish correlations with microfiltration performance measured at the process scale. A theoretical model coupling Navier–Stokes equation, convective/diffusion particle transport and deposit formation is developed to simulate a sequence of microfiltration in a confined geometry (Comsol Multyphysics®). This model is used to make predictive simulations of cake growth during the filtration of diluted particles in the range of size of microorganism (5 μm). In the same time a specific filtration micro-system including an optical chamber and a microsieve (Aquamarijn®) filtration membrane is designed in order to perform an experimental approach allowing in situ 3D-visualization of a deposit of model particles (polystyrene fluorescent microspheres) using Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Based on image analysis, the cake building and properties (particle arrangement, thickness) are analyzed. These experimental data will be further used to improve the filtration model in order to obtain a predictive tool for process optimization.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaufort S, Alfenore S, Lafforgue C (2011) Use of fluorescent microorganisms to perform in vivo and in situ local characterization of microbial deposits. J Membr Sci 369:30–39
Brans G, Kromkamp J, Pek N, Gielen J, Heck J, van Rijn CJM, van der Sman RG, Schroën CGPH, Boom RM (2006) Evaluation of microsieve membrane design. J Membr Sci 278:344–348
Brans G, van Dinther A, Odum B, Schroën CGPH, Boom RM (2007) Transmission and fractionation of micro-sized particle suspensions. J Membr Sci 290:230–240
Dullien FAL (1991) Porous media: fluid transport and pore structure, 2nd edn. Academic Press
Foley G (2006) A review of factors affecting filter cake properties in dead-end microfiltration of microbial suspensions. J Membr Sci 274:38–46
Gómez M, de la Rua A, Garralón G, Plaza F, Hontoria E, Gómez MA (2006) Urban wastewater disinfection by filtration technologies. Desalination 190:16–28
Günther J, Schmitz P, Albasi C, Lafforgue C (2010) A numerical approach to study the impact of packing density on fluid flow distribution in hollow fiber module. J Membr Sci 348:277–286
Günther J, Hobbs D, Albasi C, Lafforgue C, Cockx A, Schmitz P (2012) Modeling the effect of packing density on filtration performances in hollow fiber microfiltration module: a spatial study of cake growth. J Membr Sci 389:126–136
Hughes D, Tirlapur UK, Field R, Cui Z (2006) In situ 3D characterization of membrane fouling by yeast suspensions using two-photon femtosecond near infrared non-linear optical imaging. J Membr Sci 280:124–133
Kromkamp J, Bastiaanse A, Swarts J, Brans G, van der Sman RGM, Boom RM (2005) A suspension flow model for hydrodynamics and concentration polarisation in crossflow microfiltration. J Membr Sci 253:67–79
Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG (2006) Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 284:17–53
Mendret J, Guigui C, Cabassud C, Schmitz P (2010) Numerical investigations of the effect of non-uniform membrane permeability on deposit formation and filtration process. Desalination 263:122–132
Zhang Y, Fane A, Law A (2006) Critical flux and particle deposition of bidisperse suspensions during crossflow microfiltration. J Membr Sci 282:189–197
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Paul Duru from the Fluid Mechanic Institute of Toulouse (IMFT) and Aurélie Le Ru from FR3450 confocal platform (Auzeville France) for their technical support. The financial support from “Franco-Tunisian Integrated Action of French Foreign and European office and Tunisian Higher Education and Scientific Research office” is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Hassan, I., Lafforgue, C., Ellero, C. et al. Coupling of local visualization and numerical approach for particle microfiltration optimization. Microsyst Technol 21, 509–517 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1906-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1906-9