Abstract
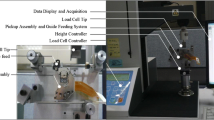
The position error signal (PES) in current hard disk drives is generated from the embedded servo data and used as the input for the track following controller. The servo pattern design and the decoding are both quite complicated in terms of the servo writing and servo detection, but they are important for the system dynamics study and track following controller design. In this paper, a novel scheme based on discrete fourier transformation (DFT) to decode the servo signal from a special magnetic servo pattern and generate the PES is proposed. In the scheme adjacent magnetic tracks with different frequencies are recorded to the disk and used as servo tracks to encode the position information. Simulation results show that the amplitudes at the two writing frequencies in the readback spectrum depend on the magnetic head position. The quadrature PES defined by the difference of the amplitudes is almost linear between the two adjacent tracks The simulation and off-line experimental results analysis agree with each other and prove the feasibility of this scheme. A real-time signal acquiring and processing system with a commercial field programmable gate array (FPGA) and ADC/DAC chips was built, and the proposed scheme was implemented in the FPGA to do the high-speed signal analysis. The magnetic head position information is extracted from the readback spectrum in the FPGA and transferred to a PC host for real-time graphic display using a labview interface. The system demonstrates an ability to generate the PES at 25 K samples per second with a resolution around 3 nm. The sampling rate can be enhanced further to 125 kHz if more servo sectors are written to the disk. This system provides a re-configurable research stage for studying the dynamic behavior of hard disk drives and for developing the control algorithm for track following.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mamun A, Lee TH, and Tay GH (2001) Efficient position encoding in hard disk drive using dual frequency servo bursts, Proc 27th Annu Conf IEEE Ind. Electronics Society, pp. 609–614
Ehrlich RM, Lin J, Jeppson DB, Oki K (2003) Hard disk drive having self-written servo burst patterns. US Patent 6519107B1
Guo L, Chen Y-J (2001) Disk flutter and its impact on HDD servo performance. IEEE Trans Magn 37(2):866–870
Guzik N, Stein AB, Talalai A (2004) Multi-frequency servo bursts in magnetic disc memory system. US Patent 6785085
Kazemi M (2008) Analysis of the slider off-track vibration caused by the aerodynamic loads associated with different components of a head stack assembly in a disk drive. IEEE Trans Magn 44(5):633–639
Kiely J, Hsia Y-T (2008) Slider dynamic motion during writer-induced head-disk contact. Microsyst Technol 14:403–409
Wong WE, Feng L, He Z, Liu J, Kan CM, Guo G (2005) PC-based position error signal generation and servo system for a spinstand. IEEE Trans Magn 41:4315–4322
Li Y, Horowitz R (2002) Design and testing of track-following controllers for dual-stage servo systems with PZT actuated suspensions. Microsyst Technol 8:194–205
Yamada T, Fukushi M, Suzuki H, Takaishi K (2006) Servo track writing technology. Fujitsu Sci Tech J 42(1):93–102
Yuan Y, Du H, Wang S (2010) A miniature in-plane piezoresistive MEMS accelerometer for detection of slider off-track motion in hard disk drives. Microsyst Technol 16:931–940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, S., Bogy, D. Position error signal generation in hard disk drives based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA). Microsyst Technol 19, 1307–1311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1786-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1786-z