Abstract
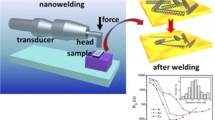
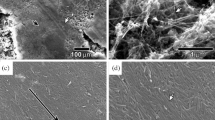
A novel batch welding of aligned carbon nanotubes (CNTs) onto metallic electrodes is developed by radio frequency induction heating. The experiments had achieved optimum contact between CNTs and metal electrodes, two hundred samples had the same trend of reduction of contact resistance after heating process, and this reduction was irreversible, which demonstrated good reproducibility of induction heating for CNT welding. Because of its non-contact and selective heating, induction heating provide a potential approach to reproducible large-scale fabrication and wide applications of CNTs devices.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachtold A, Hadley P, Nakanishi T, Dekker C (2001) Logic circuits with carbon nanotube transistors. Science 294:1317–1320
Chen CX, Zhang YF (2006) Ultrasonic nanowelding of carbon nanotubes to metal electrodes. Nanotechnology 17:2192–2197
Chen Z, Appenzeller J, Knoch J, Lin YM, Avouris P (2005) The role of metal-nanotube contacts in the performance of carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nano Lett 5:1497–1502
Chen MX, Liu WM, Xi YY (2010) Wafer level bonding using localized radio-frequency induction heating. Sci China Tech Sci 53:1252–1257
Dong LF, Youkey S, Bush J, Jiao J (2007) Effects of local Joule heating on the reduction of contact resistance between carbon nanotubes and metal electrodes. J Appl Phys 101:024320
Javey A, Guo J, Wang Q, Lundstrom M, Dai HJ (2003) Ballistic carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Nature 424:654–657
Madsen DN, Mølhave K, Mateiu R et al (2003) Soldering of nanotubes onto microelectrodes. Nano Lett 3:47–49
Monthioux M (2002) Filling single-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 40:1809–1823
Shankar G, Sood AK, Kumar N (2003) Carbon nanotube flow sensors. Science 299:1042–1043
Vijayaraghavan A, Blatt S, Weissenberger D et al (2007) Ultra-large-scale directed assembly of single-walled carbon nanotube devices. Nano Lett 7:1556–1560
Wei L, Charles ML (2007) Nanoelectronics from the bottom up. Nat Mater 6:841–850
Wei BQ, Vajtai R, Ajayan PM (2001) Reliability and current carrying capacity of carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 79:1172–1174
Woo Y, Duesberg GS, Roth S (2007) Reduced contact resistance between an individual single-walled carbon nanotube and a metal electrode by a local point annealing. Nanotechnology 18:095203
Yang H, Wu MC, Fang W (2005) Localized induction heating solder bonding for wafer level MEMS packaging. J Micromech Microeng 15:394–399
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant numbers 50875012 & 51075171.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Song, X., Liu, S. et al. Batch welding of aligned carbon nanotube onto metal electrodes. Microsyst Technol 18, 679–682 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1494-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1494-0