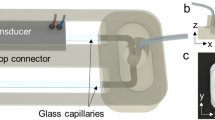
Abstract
Digital microfluidics combines the advantages of a low consumption of reagents with a high flexibility of processing fluid samples. For applications in life sciences not only the processing but also the characterization of fluids is crucial. In this contribution, a microfluidic platform, combining the actuation principle of electrowetting on dielectrics for droplet manipulations and the sensor principle of impedance spectroscopy for the characterization of the fluid composition and condition, is presented. The fabrication process of the microfluidic platform comprises physical vapor deposition and structuring of the metal electrodes onto a substrate, the deposition of a dielectric isolator and a hydrophobic top coating. The key advantage of this microfluidic chip is the common electric nature of the sensor and the actuation principle. This allows for fabricating digital microfluidic devices with a minimal number of process steps. Multiple measurements on fluids of different composition (including rigid particles) and of different conditions (temperature, sedimentation) were performed and process parameters were monitored online. These sample applications demonstrate the versatile applications of this combined technology.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthier J, Dubois P, Clementz P, Claustre P, Peponnet C, Fouillet Y (2007) Actuation potentials and capillary forces in electrowetting based microsystems. Sens Actuators A 134(2):471–479
Chatterjee D, Hetayothin B, Wheeler AR, King DJ, Garrel RL (2006) Droplet-based microfluidics with nonaqueous solvents and solutions. Lab Chip 6:199–206
Cho SK, Moon H, Kim C-J (2003) Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits. J Microelectromech Syst 12(1):70–80
Clara S (2010) Anwendung und Analyse der Impedanzspektroskopie in electrowetting-lab-on-chip Systemen. Master thesis, Johannes Kepler University Linz
Evans R, Luan L, Jokerst N, Fair R (2007) Optical detection heterogeneously integrated with a coplanar digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip platform. Proc IEEE Sens 2007:423–426
Hammouche A, Karden E, Doncker RWD (2004) Monitoring state-of-charge of ni-mh and ni-cd batteries using impedance spectroscopy. J Power Sources 127(1–2):105–111
Hirschorn B, Orazem ME, Tribollet B, Vivier V, Frateur I, Musianid M (2010) Constant-Phase-Element Behavior Caused by Resistivity Distributions in Films. J Electrochem Soc 157(12):C452–C457
Lapierre F, Piret G, Drobrecq H, Melnyk O, Coffinier Y, Thomy V and Boukherroub R (2010) Ewod lab on chip for mass spectrometry and fluorescence analysis. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on microsystems for chemistry and life science, microTAS 2010, pp 647–649
Lederer T, Stehrer BP, Bauer S, Jakoby B, Hilber W (2011) Utilizing a high fundamental frequency quartz crystal resonator as a biosensor in a digital microfluidic platform. Sens Actuators A 172(1):161–168
Li Y, Parkes W, Haworth L, Stokes A, Muir K, Li P, Collin A, Hutcheon N, Henderson R, Rae B, Walton A (2008) Anodic Ta2O5 for cmos compatible low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric device fabrication. Solid State Electron 52(9):1382–1387
Lippmann G (1875) Relations entre les phenomenes electriques et capillaries. Ann Chim Phys 5:494–548
Lu H-W, Bottausci F, Fowler JD, Bertozzi AL, Meinhart C, Kim C-J (2008) A study of EWOD-driven droplets by PIV investigation. Lab Chip 8:456–461
Luan L, Evans R, Jokerst N, Fair R (2008) Integrated optical sensor in a digital microfluidic platform. IEEE Sens J 8(5):628–635
Macdonald JR (2005) Impedance spectroscopy theory, experiment, and applications. Wiley, New York
Moon H, Wheeler AR, Garrell RL, Loo JA, Kim C-J (2006) An integrated digital micro fluidic chip for multiplexed proteomic sample preparation and analysis by MALDI-MS. Lab Chip 6:1213–1219
Nelson W, Kavehpour P and Kim C-J (2010) A Micro Extensional Filament Rheometer Enabled by EWOD. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), pp 75–78
Paik P, Pamula VK, Fair RB (2003) Rapid droplet mixers for digital microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 3:253–259
Randles JEB (1947) Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions. Discuss Farady Soc 1(1):11–19
Seo S-W, Cho S-Y, Jokerst N (2005) A thin-film laser, polymer waveguide, and thin-film photodetector cointegrated onto a silicon substrate. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 17(10):2197–2199
Tlili C, Reybier K, Geloen A, Ponsonnet L, Martelet C, Ouada HB, Lagarde M, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2003) Fibroblast Cells: A Sensing Bioelement for Glucose Detection by Impedance Spectroscopy. Anal Chem 75(14):3340–3344
Vallet M, Berge B, Vovelle L (1996) Electrowetting of water and aqueous solutions on poly(ethylene terephthalate) insulating films. Polymer 37(12):2465–2470
Wu J, Ben Y, Chang H-C (2005) Particle detection by electrical impedance spectroscopy with asymmetric-polarization AC electroosmotic trapping. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:161–167
Acknowledgments
This work was co-financed by the Austrian Science Fund FWF under contract no. L442-N14 and the Austrian Center of Competence in Mechatronics ACCM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lederer, T., Clara, S., Jakoby, B. et al. Integration of impedance spectroscopy sensors in a digital microfluidic platform. Microsyst Technol 18, 1163–1180 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1464-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1464-6