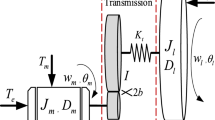
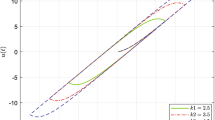
Abstract
In feedback control systems, the anti-resonant zeros cannot be arbitrarily placed, hence degrading tracking performance as well as input disturbance and noise rejection capabilities due to reduced gain at the frequencies of the zeros. In this paper, an online adaptive inverse control with saturation (OAICS) algorithm is proposed for compensating the minimum phase resonant poles and anti-resonant zeros of a PZT active suspension using measured position error signal. Experimental results on a Φ-shaped PZT active suspension using laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) shows the proposed OAICS is effective in cancelling the first two dominant minimum phase pole-zero pairs to achieve high servo bandwidth and low sensitivity servo system with small overshoot during set-point tracking.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åström KJ, Hagander P, Sternby J (1984) Zeros of sampled systems. Automatica 20(1):31–38
Bjarnason E (1995) Analysis of the filtered-X LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 3:504–514
Chen BM, Lee TH, Peng K, Venkataramanan V (2006) Hard disk drive servo systems, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Chow JT, Lawrence DA (2001) Adaptive equalization for disk drives. In: Proceedings of the 2001 American control conference. Arlington, VA, pp 3836–3842
Du C, Zhang J, Guo G (2002) Vibration analysis and control design comparison of fluid bearing and ball bearing HDDs. In: Proceedings of the 2002 American control conference. Anchorage, AK, USA, pp 1380–1385
Eriksson LJ, Allie MC, Greiner RA (1987) The selection and application of an IIR adaptive filter for use in active sound attenuation. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process. ASSP-35(4):433–437
Farhang-Boroujeny B (1998) Adaptive filters: theory and applications. Wiley, New York
Feintuch PL (1976) An adaptive recursive LMS filter. Proc IEEE 64:1622–1624
Kang C-I, Kim C-H (2005) An adaptive notch filter for suppressing mechanical resonance in high track density disk drives. Microsyst Technol 11(8–10):638–652
Ljung L (1977) Analysis of recursive stochastic algortihms. IEEE Trans Automat Control AC-22(4):551–575
Mosquera C, Gómez JA, Pérez F, Sobreira M (1999) Adaptive IIR filters for active noise control. In: Proceedings of sixth international congress on sound and vibration. Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 1571–1582
NHK Spring: Precision Springs and Components Division. http://info-sec.nhkspg.co.jp/eng/prod/disk.html (Online)
Pang CK, Wu D, Guo G, Chong TC, Wang Y (2005) Suppressing sensitivity hump in HDD dual-stage servo systems. Microsyst Technol 11(8–10):653–662
Pang CK, Guo G, Chen BM, Lee TH (2006) Self-sensing actuation for nanopositioning and active-mode damping in dual-stage HDDs. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 11(3):328–338
Pang CK, Lewis FL, Ge SS, Guo G, Chen BM, Lee TH (2007a) Singular perturbation control for vibration rejection using the PZT active suspension as fast subsystem observer. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(3):1375–1386
Pang CK, Wong WE, Guo G, Chen BM, Lee TH (2007b) Nonrepeatable run-out rejection using online iterative control for high-density data storage. IEEE Trans Magn 43(5):2029–2037
Wang AK, Ren W (1999) Convergence analysis of the filtered-U algorithm for active noise control. Signal Processing 73:255–266
Widrow B, Walach E (1996) Adaptive inverse control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Wu D, Guo G, Chong TC (2000) Adaptive compensation of microactuator resonance in hard disk drives. IEEE Trans Magn 36(5):2247–2250
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank S. S. Ge of Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore, for his constructive comments and valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, C.K., Tam, S.C., Guo, G. et al. Improved disturbance rejection with online adaptive pole-zero compensation on a Φ-shaped PZT active suspension. Microsyst Technol 15, 1499–1508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0796-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0796-3