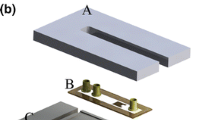
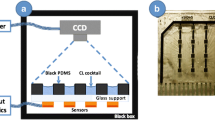
Abstract
Silicon–glass microchips were designed and fabricated for on-chip solid phase extraction (SPE) and zone electrophoresis studies. The solvent channels for extraction and the separation channels for analyses were fabricated sequentially on the silicon device. Electrical contacts were integrated in a fused silica glass lid. Amorphous silicon thin film electrodes were fabricated for high voltage and conductivity detection. A chip installation rack with electrical and fluidic contacts was constructed to facilitate the experiments. Simulation was used to elucidate both the liquid flow and the electric field distribution. The operational performance of the microchips was demonstrated by using a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled testosterone derivative as the model analyte and fluorescein as both the negative control and the calibration compounds. In SPE an immunosorbent, based on recombinant anti-testosterone Fab-fragments, was immobilized to activated Sepharose gel. Simultaneous monitoring of the movement of FITC-testosterone from SPE cavity through the channel to the detection point was performed with a laser-induced fluorescence detector. The observed limit of detection for FITC-testosterone was 2 μM.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amundsen LK, Sirén H (2007) Clinical and pharmaceutical analysis of body fluids using affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) based on antibody-antigen interactions. Electrophoresis 28:99–113. doi:10.1002/elps.200500962
Amundsen LK, Nevanen TK, Takkinen K, Rovio S, Sirén H (2007) Microscale immunoaffinity SPE and MEKC in fast determination of testosterone in male urine. Electrophoresis 28:3232–3241. doi:10.1002/elps.200700037
Anderson H, Wijngaart W, Enoksson P, Stemme G (2000) Micromachined flow-through filter-chamber for chemical reactions on beads. Sens Actuators B Chem 67:203–208. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00413-5
Chan YC, Carles M, Sucher NJ, Wong M, Zohar Y (2003) Design and fabrication of an integrated microsystem for microcapillary electrophoresis. J Micromech Microeng 13:914–921. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/6/314
Chan YC, Lee Y-K, Zohar Y (2006) High-throughput design and fabrication of an integrated microsystem with high aspect-ratio sub-micron pillar arrays for free-solution micro capillary electrophoresis. J Micromech Microeng 16:699–707. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/4/005
Dalluge JJ, Sander LC (1998) Precolumn affinity capillary electrophoresis for the identification of clinically relevant proteins in human serum: application to human cardiac troponin I. Anal Chem 70:5339–5343. doi:10.1021/ac980773u
Delaunay-Bertoncini N, Hennion M-C (2004) Immunoaffinity solid-phase extraction for pharmaceutical and biomedical trace-analysis—coupling with HPLC and CE—perspectives. J Pharm Biomed Anal 34:717–736. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(03)00559-4
Graß B, Siepe D, Neyer A, Hergenröder R (2001) Comparison of different conductivity detector geometries on an isotachophoresis PMMA-microchip. Fresenius J Anal Chem 371:228–233. doi:10.1007/s002160100965
Guzman NA (2000) Determination of immunoreactive gonadotropin-releasing hormone in serum and urine by on-line immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 749:197–213. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00410-2
Guzman NA (2003) Improved solid-phase microextraction device for use in on-line immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 24:3718–3727. doi:10.1002/elps.200305647
Guzman NA (2004) Immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis applications of clinical and pharmaceutical relevance. Anal Bioanal Chem 378(1):37–39. doi:10.1007/s00216-003-2326-y
Guzman NA, Phillips T (2005) Immunoaffinity CE for proteomics studies. Anal Chem 77(3):60A–67A
Hale JE (1995) Irreversible, oriented immobilization of antibodies to cobalt-iminodiacetate resin for use as immunoaffinity media. Anal Biochem 231:46–49. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.1501
Kriikku P, Graß B, Hokkanen A, Stuns I, Sirén H (2004) Isotachophoresis of ß-blockers in a capillary and on a poly(methyl methacrylate) chip. Electrophoresis 35(10–11):1687–1694. doi:10.1002/elps.200305872
Nevanen T, Söderholm L, Kukkonen K, Suortti T, Teerinen T, Linder M, Söderlund H, Teeri TT (2001) Efficient enantioselective separation of drug enantiomers by immobilised antibody fragments. J Chromatogr A 925:89–97. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01021-4
Phillips TM (1998) Determination of in situ tissue neuropeptides by capillary immunoelectrophoresis. Anal Chim Acta 372:209–218. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00342-0
Phillips TM (2004) Rapid analysis of inflammatory cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid using chip-based immunoaffinity electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 25:1652–1659. doi:10.1002/elps.200305873
Phillips TM, Dickens F (1998) Analysis of recombinant cytokines in human body fluids by immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 19(16–17):2991–2996. doi:10.1002/elps.1150191632
Phillips TM, Wellner E (2006) Measurement of neuropeptides in clinical samples using chip-based immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1111:106–111. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.102
Phillips TM, Kennedy LM, De Fabo EC (1997) Microdialysis-immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis studies on neuropeptide-induced lymphocyte secretion. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 697:101–109. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00132-1
Sikanen T, Heikkila L, Tuomikoski S, Ketola RA, Kostiainen R, Franssila S, Kotiaho T (2007) Performance of SU-8. Microchips as separation devices and comparison with glass microchips. Anal Chem 79(16):6255–6263. doi:10.1021/ac0703956
Suni T (2006) Direct wafer bonding for MEMS and microelectronics. Doctoral thesis, VTT Publications 609, Espoo
Tuomikoski S, Franssila S (2004) Wafer-level bonding of MEMS structures with SU-8 epoxy photoresist. Phys Scr T 114:223–226. doi:10.1088/0031-8949/2004/T114/056
Tuomikoski S, Franssila S (2005) Free-standing SU-8 microfluidic chips by adhesive bonding and release etching. Sens Actuators A Phys 120:408–415. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2005.01.012
Tuomikoski S, Rovio S, Hokkanen A, Sirén H, Franssila S (2005) Design and fabrication of integrated SPE-CE device for testosterone detection. In: 18th international conference on microscale bioseparations MSB 2005, New Orleans, LA, USA, February 2005, p 198
Tuomikoski S, Virkkala N, Rovio S, Hokkanen A, Sirén H, Franssila S (2006) Design and fabrication of integrated solid-phase extraction-zone electrophoresis microchip. J Chromatogr A 1111(2):258–266. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.10.021
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by TEKES Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and (project no. 40339 IN 2002–2005). The Academy of Finland is acknowledged for support (project no. 43326) to H.S. L. K. A. is grateful to the National Graduate School in Informational and Structural Biology for financial support. Authors also express their gratitude to Joona Koponen (VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland) for conductivity electrode modelling, Arto Laitinen (VTT) for microfluidic measurement equipment fabrication and Armi Boman (VTT) for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hokkanen, A., Sirén, H., Amundsen, L.K. et al. Silicon–glass instrumented solid-phase extraction–zone electrophoresis microchip with thin amorphous silicon film electrodes: performance in immunoaffinity analysis. Microsyst Technol 15, 611–619 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0746-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0746-5