Abstract
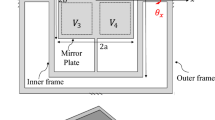
In this paper dynamic characteristics of a capacitive torsional micromirror under electrostatic forces and mechanical shocks have been investigated. A 2DOF model considering the torsion and bending stiffness of the micromirror structure has been presented. A set of nonlinear equations have been derived and solved by Runge–Kutta method. The Static pull-in voltage has been calculated by frequency analyzing method, and the dynamic pull-in voltage of the micromirror imposed to a step DC voltage has been derived for different damping ratios. It has been shown that by increasing the damping ratio the dynamic pull-in voltage converges to static one. The effects of linear and torsional shock forces on the mechanical behavior of the electrostatically deflected and undeflected micromirror have been studied. The results have shown that the combined effect of a shock load and an electrostatic actuation makes the instability threshold much lower than the threshold predicted, considering the effect of shock force or electrostatic actuation alone. It has been shown that the torsional shock force has negligible influence on dynamic response of the micromirror in comparison with the linear one. The results have been calculated for linear shocks with different durations, amplitudes, and input times.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthasuresh GK, Gupta RK, Senturia SD (1996) An approach to macromodeling of MEMS for nonlinear dynamic simulation. In: Proceedings of ASME international conference of mechanical engineering congress and exposition (MEMS), vol 40. Atlanta, GA, pp 1–7
Brown TG (2003) Harsh military environments and microelectromechanical (MEMS) devices. Proc IEEE Sens 2(7):53–60
Coster JD, Tilmans HCM, van Beek JT, Rijks TGSM, Puers R (2004) The influence of mechanical shock on the operation of electrostatically driven RF-MEMS switches. J Micromech Microeng 14(S):49–54
Dickensheets DL, Kino GS (1998) Silicon-micromachined scanning confocal optical microscope. J Microelectromech Syst 7:38–47. doi:10.1109/84.661382
Guo JG, Zhao Ya-Pu (2004) Influence of van der Waals and Casimir forces on electrostatic torsional actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 13(6):1027–1035. doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2004.838390
Hornbeck LJ (1983) 128 128 deformable mirror devices. IEEE Trans Electron Dev ED-30(5):539–545. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1983.21163
Hornbeck LJ (1989) Deformable-mirror spatial light modulators spatial light modulators and applications III. SPIE Crit 1150:86–102
Huang JM, Liu AQ, Deng ZL, Zhang QX, Ahn J, Asundi A (2004) An approach to the coupling effect between torsion and bending for electrostatic torsional micromirrors. Sens Actuators A 115:159–167. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2004.04.032
Jaecklin VP, Linder C, De Rooij NF, Moret JM, Vuilleumier R (1993) Optical microshutters and torsional micromirror for light modulator arrays. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Micro Electro Mech. Systems Workshop, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, pp 124–127
Krylov S, Maimon R (2003) Pull-in dynamics of an elastic beam actuated by distributed electrostatic force. In: Proceedings of the 19th biennial conference in mechanical vibration and noise (VIB), (Chicago, IL) DETC/VIB-48518
Lin T-H (1994) Implementation and characterization of a flexure-beam micromechanical spatial light modulator. Opt Eng 33(11):3643–3648. doi:10.1117/12.181578
Lin W-H, Zhao Y-P (2005) Nonlinear behavior for nanoscale electrostatic actuators with Casimir force. J Chaos Solitons Fractals 23(5):1777–1785
Muller RS, Lau KY (1998) Surface-micromachined microoptical elements and systems. Proc IEEE 86(8):1705–1720. doi:10.1109/5.704276
Petersen KE (1980) Silicon torsional scanning mirror. IBM J Res Dev 24(5):631–637
Rezazadeh Gh, Tahmasebi AA, Zubtsov M (2006) Application of piezoelectric layers in electrostatic mem actuators: controlling of pull-in voltage. J Microsyst Technol 12(12):1163–1170
Rezazadeh Gh, Khatami F, Tahmasebi AA (2007) Investigation of the torsion and bending effects on static stability of electrostatic torsional micromirrors. J. Microsyst Technol 13:715–722. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0362-1
Shi F, Ramesh P, Mukherjee A (1996) Dynamic analysis of micro-electromechanical systems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39:4119–4139. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19961230)39:24<4119::AID-NME42>3.0.CO;2-4
Timoshenko SP, Goodier JN (1970) Theory of elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Toshiyoshi H, Fujita H (1996) Electrostatic micro torsion mirrors for an optical switch matrix. J Microelectromech Syst 5:231–237. doi:10.1109/84.546402
Van Kessel PF, Hornbeck LJ, Meier RE, Douglass MR (1998) MEMS-based projection display. Proc IEEE 86(8):1687–1704. doi:10.1109/5.704274
Wagner U, Franz J, Schweiker M, Bernhard W, Muller-Fiedler R, Michel B, Paul O (2001) Mechanical reliability of MEMS-structures under shock load. Microelectron Reliab 41(16):57–62
Younis MI, Miles R, Jordy D (2006) Investigation of the response of microstructures under the combined effect of mechanical shock and electrostatic forces. J Micromech Microeng 16:2463–2474. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/11/030
Yu H, Chen H (2006) Development of a novel micromirror based on surface micromachining technology. J Sens Actuators 125(A):458–462
Zavracky PM, Majumder S, McGruer NE (1997) Micromechanical switches fabricated using nickel surface micromaching. J Microelectromech Syst 6:3–9. doi:10.1109/84.557524
Zhao JP, Chen HL, Huang JM, Liu AQ (2005) A study of dynamic characteristics and simulation of MEMS torsional micromirrors. Sens Actuators 120(A):199–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatami, F., Rezazadeh, G. Dynamic response of a torsional micromirror to electrostatic force and mechanical shock. Microsyst Technol 15, 535–545 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0738-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0738-5