Abstract
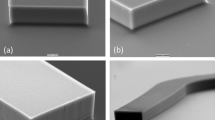
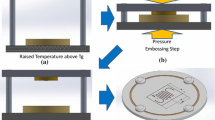
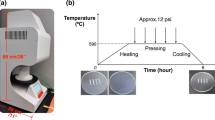
Benzocyclobutene (BCB) is a thermosetting polymer that can form microfluidics and bond top and bottom layers of the microfluidics at the same time, and yields high repeatability and high bonding strength. This paper reports using photosensitive BCB to fabricate microfluidics and to bond with a thermal press for 4 in. wafers. By optimizing the parameters for pattern development and using a three-stage temperature and pressure increment BCB bonding, we realize the whole wafer glass–Si or glass–glass bonding in thermal press without any crack. The wafer-level bonding shows a bonding percentage above 70%, a tensile stress above 4.94 MPa, and a bonding repeatability over 95%. Furthermore, the bonding is compatible with thick electrode integration, that microfluidics with 380 nm thick electrodes underneath can be well-bonded. Our bonding method much reduces the cost compared with bonding BCB in a wafer bonding machine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boehm S, Dilger K, Hesselbach J et al (2006) Micro bonding with non-viscous adhesives. Microsyst Technol 12:676–679. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0101-7
Hwang TJ, Popa D, Sin JS et al (2004) BCB wafer bonding for microfluidics. Proc SPIE 5342:182–191. doi:10.1117/12.524621
Jourdain A, Ziad H, De Moor P et al (2003) Wafer-scale 0-level packaging of (RF-) MEMS devices using BCB. Symposium on design, test, integration and packaging of MEMS/MOEMS, pp 239–244
Jourdain A, De Moor P, Baert K (2005) Mechanical and electrical characterization of BCB as a bond and seal material for cavities housing (RF-)MEMS devices. J Micromech Microeng 15:S89–S96. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/7/013
Kim HS, Najafi K (2003) Wafer bonding using parylene and wafer-level transfer of free-standing parylene membranes. 12th international conference on solid-state sensors, actuators and microsystems, transducers, vol 1, pp 790–793
Lee KK, He JP, Clement R et al (2004) Biocompatible benzocyclobutene (BCB)-based neural implants with micro-fluidic channel. Biosens Bioelectron 20:404–407. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2004.02.005
Liang ZH, Cheng YT, Hsu WY et al (2006) A wafer-level hermetic encapsulation for MEMS manufacture application. IEEE T Adv Packaging 29:513–519. doi:10.1109/TADVP.2006.875092
Lu JQ, Jindal A, Persans PD et al (2003) Wafer-level assembly of heterogeneous technologies. Proceedings of 2003 international conference on compound semiconductor manufacturing technology, GaAs MANTECH, pp 91–94
Ng SH, Wang ZF, Shi ZF et al (2006) Realization of a microelectrofluidic platform. International MEMS Conference. J Phys Conf Ser 34:373–378. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/34/1/061
Niklaus F, Enoksson P, Kälvesten E et al (2000) Void free full wafer adhesive bonding. 13th IEEE international conference on microelectromechanical sytems (MEMS’00), Miyazaci, Japan, pp 247–252
Niklaus F, Enoksson P, Griss P et al (2001a) Low-temperature wafer-level transfer bonding. J Microelectromech Syst 10:525–531. doi:10.1109/84.967375
Niklaus F, Enoksson P, Griss P et al (2001b) Low-temperature full wafer adhesive bonding. J Micromech Microeng 11:100–107. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/11/2/303
Niklaus F, Andersson H, Enoksson P et al (2001c) Low temperature full wafer adhesive bonding of structured wafers. Sens Actuators A Phys 92:235–241. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(01)00568-4
Niklaus F, Stemme G, Lu JQ et al (2006) Adhesive wafer bonding. J Appl Phys 99:31–101. doi:10.1063/1.2168512
Oberhammer J, Niklaus F, Stemme G (2003) Selective wafer-level adhesive bonding with benzocyclobutene for fabrication of cavities. Sens Actuators A Phys 105:297–304. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(03)00202-4
Oberhammer J, Niklaus F, Stemme G (2004) Sealing of adhesive bonded devices on wafer level. Sens Actuators A Phys 110:407–412. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2003.06.003
Pascual DN (2004) Effects of softbake parameters on a Benzocyclobutene (BCB) adhesive wafer bond. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 782:187–192
Plecis A, Chen Y (2007) Fabrication of microfluidic devices based on glass–PDMS–glass technology. Microelectron Eng 84:1265–1269. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2007.01.276
Polyakov A, Bartek M, Burghartz JN (2005) Area-selective adhesive bonding using photosensitive BCB for WL CSP applications. J Electron Packaging 127:7–11. doi:10.1115/1.1846059
Seok S, Rolland N, Rolland PA (2006) Packaging methodology for RF devices using a BCB membrane transfer technique. J Micromech Microeng 16:2384–2388. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/11/019
Tanigawa T, Onishi T, Nagai S et al (2006) 12.5-Gbps operation of 850-nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers with reduced parasitic capacitance by BCB planarization technique. IEEE J Quantum Electron 42:785–790. doi:10.1109/JQE.2006.878186
The Dow Chemical Company (2008) Processing procedures for CYCLOTENE 4000 series photo BCB resins (puddle develop), online manual available via DIALOG http://www.dow.com/cyclotene/prod/402646.htm of subordinate document. Accessed 26 Aug 2008
Turmezei P, Polyakov A, Mollinger JR et al (2003) Low-cost microfilter for red blood cell membrane stiffness measurement using photosensitive BCB. 12th international conference on transducers, solid-state sensors, actuators and microsystems, vol 1, pp 107–110
Venditti R, Xuan XC, Li DQ (2006) Experimental characterization of the temperature dependence of zeta potential and its effect on electroosmotic flow velocity in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:493–499. doi:10.1007/s10404-006-0100-0
Zhang J, Bloomfield MO, Lu JQ et al (2005) Thermal stresses in 3D IC inter-wafer interconnects. Microelectron Eng 82:534–547. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2005.07.053
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the A*STAR project IMRE/06-1R0320. We acknowledge Sharon Oh for taking some of the pictures and giving beneficial discussions, and colleagues in SERC nanofabrication and characterisation facility (SNFC) in the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE) for providing the fabrication convenience.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Virasawmy, S. & Quan, C. Wafer-level BCB bonding using a thermal press for microfluidics. Microsyst Technol 15, 573–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0712-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-008-0712-2