Abstract
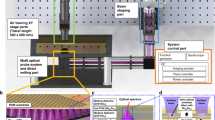
P-beam writing (proton beam writing) is a unique direct write 3D nano-lithographic technique which has been developed at the Centre for Ion Beam Applications (CIBA), in the Physics Department of the National University of Singapore. This technique employs a focused MeV proton beam which is scanned in a predetermined pattern over a resist (e.g. PMMA, SU-8 or HSQ), which is subsequently chemically developed. In e-beam writing as well as p-beam writing the energy loss of the primary beam is dominated by energy transfer to substrate electrons. Unlike the high energy secondary electrons generated during e-beam writing the secondary electrons induced by the primary proton beam have low energies (typically less than 100 eV) and therefore a limited range, resulting in minimal proximity effects. The low proximity effects exhibited by p-beam writing coupled with the straight trajectory and high penetration of the proton beam enables the production of high aspect ratio, high density 3D micro- and nano-structures with well defined smooth side walls to be directly written into resist materials. These structures can be used as templates to electroplate metallic nanowires.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari K, van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Watt F (2004) Fabrication of high aspect ratio 100 nm metallic stamps for nanoimprint lithography using proton beam writing. Appl Phys Lett 85:476–478
Baibich MN, Broto JM, Fert A, Nguyen VDF, Petroff F, Etienne P, Creuzt G, Friederich A, Chazelas J (1988) Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr magnetic superlattices. Phys Rev Lett 61:2472–2475
Biersack J, Haggmark LG (1980) A Monte Carlo computer program for the transport of energetic ions in amorphous targets. Nucl Instr Meth 174:257–269
Breese MBH, Grime GW, Linford W, Harold M (1999) An extended magnetic quadrupole lens for a high-resolution nuclear microprobe. Nucl Instr Meth B158:48–52
Chen J, Klaumünzer S, Lux-Steiner MC, Könenkamp R (2004) Vertical nanowire transistors with low leakage current. Appl Phys Lett 85:1401–1403
Kruglyak VV, Hicken RJ, Kuchko AN, Gorobets VYu (2005) Spin waves in a periodically layered magnetic nanowire. J Appl Phys 98:014304-1–014304-4
Liu H-R, Ren T-L, Qu B-J, Liu L-T, Ku W-J, Li W (2003) The optimization of Ta buffer layer in magnetron sputtering IrMn top spinvalve. Thin Solid Films 441:111–114
Martin CR, Baker LA (2005) Expanding the molecular electronics toolbox. Science 309:67–68
Namatsu H, Takahashi Y, Yamazaki K, Yamaguchi T, Nagase M, Kurihara K (1998) Three-dimensional siloxane resist for the formation of nanopatterns with minimum linewidth fluctuations. J Vac Sci Technol B16:69–76
Pramanik S, Stefanita C-G, Bandyopadhyay S (2006) Spin transport in self assembled all-metal nanowire spin valves: a study of the pure Elliott–Yafet mechanism. J Nano Sci Tech 6:1973–1978
Qin L, Park S, Huang L, Mirkin CH (2005) On-wire lithography. Science 309:113–115
Springham SV, Osipowicz T, Sanchez JL, Gan LH, Watt F (1997) Micromachining using deep ion beam lithography. Nucl Instr Meth B130:155–159
Szymanski R, Jamieson DN (1997) Ion source brightness and nuclear microprobe applications. Nucl Instr Meth B130:80–85
Thelander C, Agarwal P, Brongersma S, Eymery J, Feiner LF, Forchel A, Scheffler M, Riess W, Ohlsson BJ, Gösele U, Samuelson L (2006) Nanowire-based one-dimensional electronics. Materialstoday 9:28–35
Udalagama CNB, Bettiol AA, van Kan JA, Teo EJ, Breese MBH, Watt F (2007) The rapid secondary electron imaging system of the proton beam writer at CIBA. Nucl Instr Meth B260:390–395
van Kan JA, Sum TC, Osipowicz T, Watt F (2000) Sub 100 nm proton beam micromachining: theoretical calculations on resolution limits. Nucl Instr Meth B161–163:366–370
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Wee BS, Sum TC, Tang SM, Watt F (2001) Proton beam micromachining: a new tool for precision 3D microstructures. Sens Actuators A92:370–374
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Watt F (2003a) Three-dimensional nanolithography using proton beam writing. Appl Phys Lett 83:1629–1631
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Watt F (2003b) Proton beam nano-machining: end station design and testing. Mat Res Soc Symp Proc 777:T2.1.1
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Ansari K, Shao PG, Watt F (2004a) Improvement in proton beam writing at the nano scale. Proc IEEE MEMS 673–676
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Ansari K, Teo EJ, Sum TC, Watt F (2004b) Proton beam writing: a progress review. Int J Nanotechnol 1(4):464–479
van Kan JA, Shao PG, Molter P, Saumer M, Bettiol AA, Osipowicz T, Watt F (2005) Fabrication of a free standing resolution standard for focusing MeV ion beams to sub 30 nm dimensions. Nucl Instr Meth B231:170–175
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Watt F (2006) Proton beam writing of three-dimensional nanostructures in hydrogen silsesquioxane. Nano Lett 6:579–583
van Kan JA, Bettiol AA, Chiam SY, Saifullah MSM, Subramanian KRV, Welland ME, Watt F (2007) New resists for proton beam writing. Nucl Instr Meth B260:460–463
Waligorski MPR, Hamm RN, Katz R (1986) The radial distribution of dose around the path of a heavy ion in liquid water. Nucl Tracks Radiat Meas 11:309–319
Watt F, van Kan JA, Rajta I, Bettiol AA, Choo TF, Breese MBH, Osipowicz T (2003) The national university of singapore high energy ion nano probe facility performance tests. Nucl Instr Meth B210:14–20
Zhang F, van Kan JA, Chiam SY, Watt F (2007) Fabrication of free standing resolution standards using proton beam writing. Nucl Instr Meth B260:474–478
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge financial support from ASTAR Singapore, the MOE Academic Research Fund as well as the AOARD (Asian Office of Aerospace Research & Development).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Kan, J.A., Zhang, F., Chiam, S.Y. et al. Proton beam writing: a platform technology for nanowire production. Microsyst Technol 14, 1343–1348 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-007-0514-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-007-0514-y