Abstract
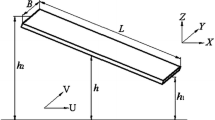
This paper discusses the effect of varying the shock pulse width on the shock response of small form factor hard disk drives. We develop a new shock simulator for hard disk drives which simulates the structural as well as the air bearing dynamics of the disk drive simultaneously. We observe that the response of the disk to the shock pulse is of critical importance and depends strongly on the pulse width of the shock pulse. We also find that if a suspension bending frequency is close to the first umbrella frequency of the disk, there can be failure of the head–disk interface due to resonance.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava P, Bogy DB (2005) Numerical simulation of load/unload in small form factor hard disk drives. Technical Report 2005-011, CML, University of California, Berkeley
Bhargava P, Bogy DB (2007) Numerical simulation of operational-shock in small form factor hard disk drives. ASME J Tribol 129:153–160
Edwards JR (1999) Finite element analysis of the shock response and head slap behavior of a hard disk drive. IEEE Trans Magn 35:863–867
Guyan RJ (1965) Reduction of stiffness and mass matrices. AIAA J 3:310
Harrison JC, Mundt MD (2000) Flying height response to mechanical shock during operation of a magnetic hard drive. ASME J Tribol 122:260–263
Jayson EM, Murphy J, Smith PW, Talke FE (2003) Shock modeling of the head–media interface in an operational hard disk drive. IEEE Trans Magn 39:2429–2432
Jiang ZW, Takashima K, Chonan S (1995) Shock proff design of head disk assembly subjected to impulsive excitation. JSME Int J 38:411–419
Kouhei T, Yamada T, Keroba Y, Aruga K (1995) A study of head–disk interface shock resistance. IEEE Trans Magn 31:3006–3008
Kumar S, Khanna V, Sri-Jayantha M (1994) A study of the head disk interface shock failure. In: The 6th MMM-Intermag conference
Lu S (1997) Numerical simulation of slider air bearings. PhD thesis, University of California
Zeng Q, Bogy DB (2000) Numerical simulation of shock response of disk-suspension-slider air bearing systems in hard disk drives. Microsyst Tech 8:289–296
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Seagate Corporation and the Computer Mechanics Laboratory (CML) at the University of California, Berkeley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhargava, P., Bogy, D.B. Effect of shock pulse width on the shock response of small form factor disk drives. Microsyst Technol 13, 1107–1115 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0328-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0328-3