Abstract
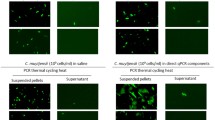
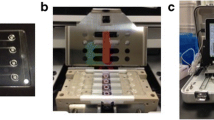
Thermalcycler was extensively used machine for amplify DNA sample. One of the major problems in the working time was that it spent most of time for cooling and heating. In order to improve the efficient, the study presented a novel method for amplify DNA sample. For this concept, the DNA sample in the silicon chamber which was pushed by a tappet through the three temperature regions around a center and then the DNA segments could be amplified rapidly after 30 cycles. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) platform was composed of the thin-film heaters, Cu plates, DC powers, and temperature controllers. The photolithography and bulk etching technologies were utilized to construct the thin-film heater and DNA reaction chambers. Finally, 1 μl 100 bp DNA segment of Escherichia coli K12 was amplified successfully within 36 min on this PCR platform.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chien CH, Yu HM (2005) Miniaturized PCR-chip for DNA amplification with an external peristaltic pump. J Mech Med Biol 5:1–7
Chou CF, Changrani R, Roberts P, Sadler D, Burdon J, Zenhausern F, Lin S, Mulholland A, Swami N, Terbrueggen R (2002) A miniaturized cyclic PCR device-modeling and experiments. Microelectron Eng 61–62:921–925
El-Ali J, Perch-Nielsen IR, Poulsen CR, Bang DD, Telleman P, Wolff A (2004) Simulation and experimental validation of a SU-8 based PCR thermocycler chip with integrated heaters and temperature sensor. Sens Actuators A 110:3–10
Fukuba T, Yamamoto T, Naganuma T (2004) Microfabricated flow-through device for DNA amplification-toward in situ gene analysis. Chem Eng J 101:151–156
Kopp MU, de Mello AJ, Manz A (1998) Chemical amplification: continuous-flow PCR on a chip. Science 280:1046–1048
Lin YC, Huang MY, Young KC, Chang TT, Wu CY (2000) A rapid micro-polymerase chain reaction system for hepatitis C virus amplification. Sens Actuators B 71:2–8
Schneegaβ I, Köhler JM (2001) Flow-through polymerase chain reactions in chip thermocyclers. Rev Mol Biotechnol 82:101–121
Shoffner MA, Cheng J, Hvichi GE, Krick J, Wilding P (1996) Chip PCR. Part I. Surface passivation of microfabricated silicon-glass chips for PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24(2):375–379
Sun K, Yamaguchi A, Ishida Y, Matsuo S, Misawa H (2002) A heater-integrated transparent micro channel chip for continuous-flow PCR. Sens Actuators 84:283–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, CH., Yu, HM. The design and fabrication of polymerase chain reaction platform. Microsyst Technol 13, 1523–1527 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0266-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0266-0