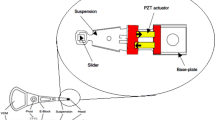
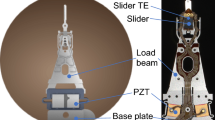
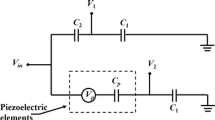
Abstract
The increase in aerial storage capacities of future magnetic hard disk drives has fostered the use of dual-stage actuators for high track density data recording. In a hard disk drive with a dual-stage actuator the standard rotary actuation of the voice coil motor is combined with an additional micro or milli actuation to accomplish high-bandwidth and highly accurate track following. In order to guarantee error less data transfer, the track following servo controller needs to perform robustly under different operating conditions, that include changes in flying height and product manufacturing tolerance of the dual-stage actuator. Essential in the controller design is to characterize these uncertain conditions and design a robust track following servo accordingly. In this paper we present an experiment based methodology to characterize the varying servo conditions in the form of an uncertainty model. The uncertainty model can be used for analysis and synthesis of robust servo controllers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åström KJ (1970) Introduction to stochastic control theory. Academic, New York
Böling JM, Mäkilä PM (1998) On control relevant criteria in H ∞ identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 43(5):694–700
de Callafon RA, Roover D, Van den Hof PMJ (1996) Multivariable least squares frequency domain identification using polynomial matrix fraction descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 35th IEEE conference on decision and control, Kobe, Japan, pp 2030–2035
de Callafon RA, Harper DHF, Skelton RE, Talke FE (1999) Experimental modeling and feedback control of a piezo-based milliactuator. J Inform Storage Process Syst 1(3):217–224
Chen J, Farell JA, Nett CN, Zhou K (1996) H ∞ identification of multivariable systems by tangential interpolation methods. IEEE Trans Autom Control 41(12):1822–1828
Fan LS, Ottesen HH, Reiley TC, Wood RW (1995) Magnetic recording head positioning at very high track densities using a microaactuator-based, two-stage servo system. IEEE Trans Indus Electron 42(3):222–223
Gaikwad SV, Rivera DE (1997) Multivariable frequency-response curve fitting with application to control-relevant parameter estimation. Automatica 33(6):1169–1174
Hernandez D, Park S, Horowitz R, Packard A (1999) Dual-stage track-following servo design for hard disk drives. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, San Diego, pp 4116–4121
Li Y, Horowitz R (2002) Design and testing of track-following controllers for dual-stage servo systems with pzt actuated suspensions. Microsyst Technol 8:194–205
Li Y, Horowitz R, Evans R (2003) Vibration control of a pzt actuated suspension dual-stage servo system using a pzt sensor. IEEE Trans Magn 39:932–937
Ljung L (1999) System identification: theory for the user, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Partington JR (1991) Robust identification and interpolation in H ∞. Int J Control 54:1281–1290
Pena S, Snaizer RS (1995) Robust identification with mixed time/frequency experiments: consistency and interpolation algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 34th IEEE conference on decision and control, New Orleans, pp 234–236
Rotunno M, de Callafon RA (2000) Fixed order H ∞ control design for dual-stage hard disk drives. In: Proceedings of the 39th IEEE conference on decision and control, vol 4, Sydney, Australia, pp 3118–3119
Scheid RE, Bayard DS (1995) A globally convergent minimax solution for spectral overbounding and factorization. IEEE Trans Autom Control 40(4):712–716
Scheid RE, Bayard DS, Yam Y (1991) A linear programming approach to characterizing norm bounded uncertainty from experimental data. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, Boston, pp 1956–1958
Skogestad S, Postlethwaite I (1996) Multivariable feedback control. Wiley, Chichester
Teerjuis AP, Cools SJM, de Callafon RA (2003) Reduction of flow induced suspension vibrations in a hard disk drive by dual-stage suspension control. IEEE Trans Magn 39(5):2237–2239
Van den Hof PMJ, van Donkelaar ET, Dötsch HGM, de Callafon RA (1997) Control-relevant uncertainty modelling directed towards performance robustness. In: Proceedings of the 13th IFAC world congress, San Francisco, pp 103–108
Zhou K, Doyle JC (1998) Essentials of robust control. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Zhou K, Doyle JC, Glover K (1996) Robust and optimal control. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rotunno, M., Oboe, R. & de Callafon, R.A. Modeling product variations in hard disk drive micro-actuator suspensions. Microsyst Technol 12, 803–813 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0207-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-006-0207-y