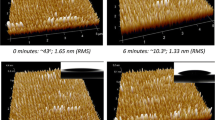
Abstract
It was experimentally demonstrated that bonding strength strongly depends on the total SiO2 thickness near the bonding interface for a given O2 plasma surface activation. Systematic experiments of Si/SiO2 and SiO2/SiO2 wafer bonding are performed for analyzing the evolution of the bonding surface energy with the interfacial oxide thickness. Optimum plasma exposure time increases with the interfacial SiO2 thickness to achieve the maximum bonding strength in SiO2/SiO2 or SiO2/Si. An optimal process option for plasma activated SiO2/SiO2 wafer bonding is proposed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirfeiz P, Bengtsson S, Bergh M, Zanghellini E, Börjesson L (2000) Formation of silicon structures by plasma activated wafer bonding. J Electrochem Soc 147:2693–2698
Banerjee K, Souri SJ, Kapur P, Saraswat KC (2001) 3-D ICs: a novel chip design for improving deep-submicrometer interconnect performance and systems-on-chip integration. Proc IEEE 89:602–633
Bertholet Y, Iker F, Raskin JP and Pardoen T (2004) Steady-state measurement and modeling of wafer bonding failure resistance. Sens Actuators A 110:157–163
Bruel M (1995) Silicon on insulator material technology. Electron Lett 31:1201–1202
Choi K, Ghosh S, Lim J, Lee CM (2003) Removal efficiency of organic contaminants on Si wafer by dry cleaning using UV/O3 and ECR plasma. Appl Surf Sci 206:355–364
Dessein K, Anil Kumar PS, Németh S, Delaey L, Borghs G and De Boeck J (2001) The vacuum wafer bonding technique as an alternative method for the fabrication of metal/semiconductor heterostructures. J Cryst Growth 227–228:906–910
Goustouridis D, Minoglou K, Kolliopoulou S, Chatzandroulis S, Morfouli P, Normand P, Tsoukalas D (2004) Low temperature wafer bonding for thin film layer transfer. Sens Actuators A 110:401–406
Hahn PO, Lampet I, Schnegg A (1988) In: Pantelides ST, Lucovsky G (eds) SiO2 and its interfaces: symposium, materials research society, 30 November–5 December 1987, Pittsburgh, pp 247–252
Henttinen K, Suni I, Lau SS (2000) Mechanically induced Si layer transfer in hydrogen-implanted Si wafers. Appl Phys Lett 76:2370–2372
Hurley RE and Gamble HS (2003) Thin film sputtered silicon for silicon wafer bonding applications. Vacuum 70(2–3):131–140
Kräuter G, Schumacher A, Gösele U (1998) Low temperature silicon direct bonding for application in micromechanics: bonding energies for different combinations of oxides. Sens Actuators A70:271–275
Lai SI, Lin HY, Hu CT (2004) Effect of surface treatment on wafer direct bonding process. Mater Chem Phys 83:265–272
Pasquariello D, Lindeberg M, Hedlund C, Hojrt K (2000) Surface energy as a function of self-bias voltage in oxygen plasma wafer bonding. Sens Actuators 82:239–244
Pasquariello D, Hedlund C and Hjort K (2000) Oxidation and induced damage in oxygen plasma in situ wafer bonding. J Electrochem Soc 147(7):2699–2703
Suni T, Henttinen K, Suni I, Mäkinen J (2002) Effects of plasma activation on hydrophilic bonding of Si and SiO2. J Electrochem Soc 149:G348–G351
Tong G, Cha QY, Gafiteanu R, Gösele U (1994) Low temperature wafer direct bonding. J Microelectromech Syst 3:29–35
Tong QY, Kim WJ, Lee TH, Gösele U (1998) Low vacuum wafer bonding, Electrochem. Solid State Lett 1(1):52–53
Wei BY, Cher MT, Su SD, Sharon MLN (2004) Influence of applied load on vacuum wafer bonding at low temperature. Sens Actuators A 115:67–72
Williams JS, Short KT, Petravic M, Svensson BG (1997) Oxidation of silicon by low energy oxygen ions. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 121:24–29
Zhang X, Raskin JP (2004) Investigation on the uniformity of surface energy is silicon direct bonding technique. J Electrochem Soc 151(9):G568–G573
Zhang X, Raskin JP (2004) Low-temperature wafer bonding optimal O2 plasma surface pretreatment time. Electrochem Solid State Lett 7:G172–G174
Zhang X, Raskin JP (2005) Low temperature wafer bonding: a study of void formation and influence on bonding strength. J Microelectromech Syst (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olbrechts, B., Zhang, X., Bertholet, Y. et al. Effect of interfacial SiO2 thickness for low temperature O2 plasma activated wafer bonding. Microsyst Technol 12, 383–390 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0038-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0038-2