Abstract
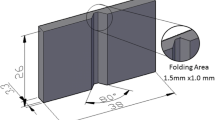
In order to reduce the output errors of micromechanisms, our study has suggested the use of new micro-hinges with a rigidity that has been made suitable enough to decrease the differences between the hinge end locus and the circular locus. Based on this, we have conducted theoretical analyses, while at the same time creating micro-hinge models using a semiconductor minute processing technique (RIE, etc.) for our experiments. Afterwards, we will discuss and study the effectiveness of the use of the suggested micro-hinges, through comparisons with conventional shaped micro-hinges. The results clarified that the suggested hinge models could reduce errors with the circular locus. This ultimately confirms the effectiveness of our newly reinforced micro-hinge.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is partly supported by the Scientific Research Grant-in-Aid No. 13450064 from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture.
This paper was presented at the Fourth International Workshop on High Aspect Ratio Microstructure Technology HARMST 2001 in June 2001.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horie, M., Torii, S. & Kamiya, D. Micro-hinges changed flexural rigidity intermittently for micromechanism joints. Microsystem Technologies 9, 381–385 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-002-0219-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-002-0219-1