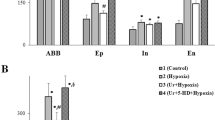
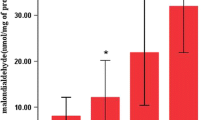
Abstract
Morphological alterations in the lungs of rats deficient in either or both of vitamin E and essential fatty acids were investigated after exposure to hyperoxia for 48 h. In rats deficient in both vitamin E and essential fatty acids, there was damage to type-2 alveolar cells observed as swollen mitochondria and bleb formation in the cytoplasm. None of these changes was found in rats deficient in only one of these substances. Hyperoxia in rats deficient in both substance also caused destruction of the capillary endothelial cells and edema in the interstitium. The lungs of rats deficient in only one of the substances showed some edema in the capillary endothelial cells, but not destruction, and less interstitial edema. These findings suggest that simultaneous deficiency in vitamin E and essential fatty acids facilitates lung damage in rats exposed to hyperoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Obara H, Sekimoto M, Iwai S: Alterations to the bronchial and brochiolar surfaces of adult mice after exposure to high concentrations of oxygen. Thorax 34:479–485, 1979
Obara H, Pappas CT, Northway WH, Bensch KG: Comparison of the effect of two and six week exposure to 80% and 100% oxygen on the newborn mouse: A quantitative SEM and TEM correlative study. Int Radiation Oncology Biol Phys 11:285–298, 1985
Pappas CT, Obara H, Bensch KG, Northway WH: Effect of prolonged exposure to 80% oxygen on the lung of the newborn mouse. Lab Invest 48:735–748, 1983
Poland RL: Effect of Vitamin E deficiency in pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Pediat Res 11:577A, 1977
Kann HE: Oxygen toxicity and vitamin E. Aerosp Med 35:840–844, 1964
Taylor DW: The effect of vitamin E deficiency on oxygen oxicity in the rat. J Physiol 121:49–53, 1953
Galdwell MD, Jonsson HT, Otherson HB: Essential fatty acid deficiency in an infant receiving prolonged parenteral alimentation. J Pediatr Surg 81:894–898, 1972
White HB, Tuner MD, Tuner AG, Miller RG: Blood lipid alterations in the infants receiving intravenous fat free alimentation. J Pediatr Surg 83:305–313, 1973
Gutcher GR, Raynor WJ, Farrell PM: An evaluation of vitamin E status in premature infants. AM J Clin Nutr 40:1078–1089, 1984
Abe K, Kusube K, Mukasa K, Ichiguro Y, Sato T, Ichikawa S, Hoshida H: Determination of vitamin A, E and K and ubiqninones in plasma by high speed liquid chromatography. Jap Soci Anal Chem 33:309–314, 1984
Paulsrud JK, Pensler L, Whitten CF, Stewart S, Holmen RT: Essential fatty acid deficiency in infants induced by fat-free intravenous feeding. Am J Clin Nutr 25:897–904, 1972
Holman RT, Caster WO, Wiese HF: The essential fatty acid requirement of infants and the assessment of their dietary intake of linoleate by serum fatty acid analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 14:70–75, 1964
Kisler JD, Caldwell PRS, Weibel ER: Development of fine structural damage to alveolar and capillary lining cells in oxygenpoisoned rat lungs. J Cell Biol 32:605–628, 1967
Harrison GA: Ultrastructural changes in rat lung during long-term exposure to oxygen. Exp Med Surg 29:96–100, 1971
Kapanci Y, Weibel ER, Kaplan HP: Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest 20:101–118, 1969
Ludwin SK, Northway WH, Bensch KG: Oxygen toxicity in the newborn: necrotizing bronchiolitis in mice exposed to 100 per cent oxygen. Lab Invest 31:425–435, 1974
Wender DF, Thulin GE, Walker SGJ, Wardhaw JB: Vitamin E affects lung biochemical and morphologic response to hyperoxia in the newborn rabbit. Pediatr Res 15:262–268, 1981
Tappel AI: Vitamin E as the biological lipid antioxidant. Vitam Horm 20:493–497, 1962
Ward JA, Roberts RJ: Vitamin E inhibition of the effects of hyperoxia on the pulmonary surfactant system of the newborn rabbits. Pediatr Res 18:329–334, 1984
Bucher JR, Robert RJ: Effects of α-tochopherol treatment on newborn rat lung development and injury in hyperoxia. Pediatr Pharmacol 2:1–9, 1982
Friedman Z, Danon Z, Stahlman MT, Oates JA: Rapid onset of essential fatty acid deficiency in the newborn. Pediatrics 58:640–649, 1976
Edmonds RH, Beeler DA, Treble DH, Kyriakids EG, Burnell J, Balint JA: Morphological alterations in type-II alveolar cells in essential fatty acid deficiency. Exper Mol Path 23:276–283, 1975
Kehrer JP, Autor AP: The effect of dietary fatty acid on the composition of adult rat lung lipid. Relationship to oxygen toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 44:423–430, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, R., Obara, H., Momota, T. et al. The effect of hyperoxia on the lungs of rats deficient in essential fatty acids. J Anesth 3, 149–154 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054090030149
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054090030149