Abstract
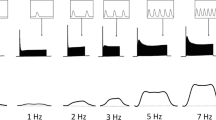
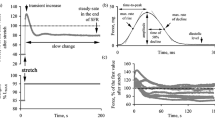
Using 22 isolated rat ventricular muscle preparations, we investigated whether or not the increase in preload and/or contraction frequency may counteract the negative inotropy of both isoflurane (2.0%) and halothane (1.0%). Increases in preload from 94% of Lmax (the length where muscles produce the maximal tension) to Lmax did not alter significantly the percent decrements in tension development caused by either isoflurane or halothane. The increases in contraction frequency from 0.1 to 0.6 Hz augmented the depressant effect of isoflurane significantly (P<0.001), while the depressant effect of halothane was not altered at these contraction frequencies. Small but significant counteraction occurred in the depressant effects of halothane at 0.8 and 1.6 Hz (P=0.002). These changes in intracellular mechanism(s), resulted from the increase in contraction frequency, interacted with the two anesthetics on tension development, while these may not be the case for the increase in preload.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimosato S: Anesthesia and Cardiac Performance in Health and disease. Springfield, Charles C Thomas, 1981, pp. 5–47
Lynch C III: Differential depression of myocardial contractility by halothane and isoflurane in vitro. Anesthesiology 64:620–631, 1986
Komai H, Rusy BF: Negative inotropic effects of isoflurane and halothane in rabbit papillary muscles. Anesth Analg 66:29–33, 1987
Wolf WJ, Neal MB, Mathew BP, Bee DE: Comparison of the in vitro myocardial depressant effects of isoflurane and halothane anesthesia. Anesthesiology 69:660–666, 1988
Stephenson DG, Wendt IR: Length dependence of changes in sarcoplasmic calcium concentration and myofibrillar calcium sensitivity in striated muscle fibers. J Muse Res Cell Motility 5:243–272, 1984
Kurihara S, Allen DG: Intracellular Ca++ transients and relaxation in mammalian cardiac muscle. Jpn Circ J 46:39–43, 1982
Pinto JG, Price JM, Fung YC, Mead EH: A device for testing mechanical properties of biological materials —the “Biodyne”. J Appl Physiol 39:863–867, 1975
Sutko JL, Willerson JT, Templeton GH, Jones LR, Besch HR, Jr Ryanodine: Its alterations of cat papillary muscle contractile state and responsiveness to inotropic interventions and a suggested mechanism of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 209:37–47, 1979
Winer BJ: Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. New York, McGraw-Hill, 1971, pp. 149–260
Allen DG, Kurihara S: The effects of muscle length on intracellular calcium transients in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol (London) 327:79–94, 1982
Stemmer P, Akera T: Concealed positive force-frequency relationships in rat and mouse cardiac muscle revealed by ryanodine. Am J Physiol 25l:H1106-H1110, 1986
Sutko JL, Willerson JT: Ryanodine alteration of contractile state of rat ventricular myocardium. Comparison with dog, cat, and rabbit ventricular tissues. Circ Res 46:332–343, 1980
Orchard CH, Lakkata EG: Intracellular calcium transients and developed tension in rat heart muscle. A mechanism for the negative interval-strength relationships. J Gen Physiol 86:637–651, 1985
Allen DG, Jewell BR, Wood EH: Studies of the contractility of mammalian myocardium at low rates of stimulation. J Physiol (London) 254:1–17, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Saeki, S., Shimosato, S. & Kosaka, F. Frequency- and length-dependent tension development in rat heart muscles exposed to isoflurane and halothane. J Anesth 5, 338–343 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054010050338
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s0054010050338