Abstract
Purpose
Remimazolam, a newly synthesized ultrashort-acting benzodiazepine, has not been previously compared with sevoflurane with regard to postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). The aim of this study is to investigate the incidence of PONV between remimazolam and sevoflurane among patients undergoing artificial joint replacement surgery.
Methods
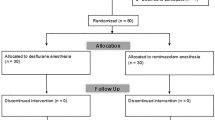
We conducted a retrospective analysis of the electronic medical records of patients who underwent artificial joint replacement surgery at Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital from 2020 to 2022, with a focus on comparing the incidence of PONV among those who received sevoflurane versus remimazolam anesthesia. To control for confounding factors, we employed a propensity score-matching technique to pair patients who received sevoflurane anesthesia with those who received remimazolam anesthesia.
Results
The records of 292 patients receiving general anesthesia for artificial joint replacement surgery were collected and categorized into group sevoflurane (n = 241) or group remimazolam (n = 51). Before propensity score matching, age and ASA-PS exhibited significant differences between two groups. There was no significant difference in the incidence of PONV between them (p = 0.461). After matching, there were 51 patients in each group. However, there is no significant difference in the incidence of PONV between the two matched cohorts (p = 0.243).
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that there was no difference in the prevalence of PONV between remimazolam and sevoflurane anesthesia in patients undergoing artificial joint replacement surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, KY. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions e.g. their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Cohen MM, Duncan PG, DeBoer DP, Tweed WA. The postoperative interview: assessing risk factors for nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg. 1994;78:7–16.
Apfel CC, Läärä E, Koivuranta M, Greim CA, Roewer N. A simplified risk score for predicting postoperative nausea and vomiting: conclusions from cross-validations between two centers. Anesthesiology. 1999;91:693–700.
Koivuranta M, Läärä E, Snåre L, Alahuhta S. A survey of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anaesthesia. 1997;52:443–9.
Kranke P, Eberhart LH, Toker H, Roewer N, Wulf H, Kiefer P. A prospective evaluation of the POVOC score for the prediction of postoperative vomiting in children. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:1592–7.
Macario A, Weinger M, Carney S, Kim A. Which clinical anesthesia outcomes are important to avoid? The perspective of patients. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:652–8.
Fortier J, Chung F, Su J. Unanticipated admission after ambulatory surgery–a prospective study. Can J Anaesth. 1998;45:612–9.
Hill RP, Lubarsky DA, Phillips-Bute B, Fortney JT, Creed MR, Glass PS, Gan TJ. Cost-effectiveness of prophylactic antiemetic therapy with ondansetron, droperidol, or placebo. Anesthesiology. 2000;92:958–67.
Masui K. Remimazolam besilate, a benzodiazepine, has been approved for general anesthesia!! J Anesth. 2020;34:479–82.
Hari Y, Satomi S, Murakami C, Narasaki S, Morio A, Kato T, Tsutsumi YM, Kakuta N, Tanaka K. Remimazolam decreased the incidence of early postoperative nausea and vomiting compared to desflurane after laparoscopic gynecological surgery. J Anesth. 2022;36:265–9.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:452–8.
Sneyd JR. Remimazolam: new beginnings or just a me-too? Anesth Analg. 2012;115:217–9.
Wiltshire HR, Kilpatrick GJ, Tilbrook GS, Borkett KM. A placebo- and midazolam-controlled phase I single ascending-dose study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of remimazolam (CNS 7056): Part II. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:284–96.
Kilpatrick GJ. Remimazolam: non-clinical and clinical profile of a new sedative/anesthetic agent. Front Pharmacol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.690875.
Song SW, Jang YN, Yoon MW, Jeon YG. Quality of recovery in patients administered remimazolam versus those administered an inhalant agent for the maintenance of general anesthesia: a randomized control trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022;22:226.
Suzuki Y, Kawashima S, Makino H, Doi M, Nakajima Y. A comparison of remimazolam and propofol for postoperative nausea and vomiting: a propensity score-matched, observational, single-center cohort study. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.4097/kja.22441.
Mao Y, Guo J, Yuan J, Zhao E, Yang J. Quality of recovery after general anesthesia with remimazolam in patients’ undergoing urologic surgery: a randomized controlled trial comparing remimazolam with propofol. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:1199–209.
Choi JY, Lee HS, Kim JY, Han DW, Yang JY, Kim MJ, Song Y. Comparison of remimazolam-based and propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia on postoperative quality of recovery: a randomized non-inferiority trial. J Clin Anesth. 2022;82: 110955.
Lee Y, Wang JJ, Yang YL, Chen A, Lai HY. Midazolam vs ondansetron for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting: a andomized controlled trial. Anaesthesia. 2007;62:18–22.
Ahn EJ, Kang H, Choi GJ, Baek CW, Jung YH, Woo YC. The effectiveness of midazolam for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2016;122:664–76.
Gan TJ, Diemunsch P, Habib AS, Kovac A, Kranke P, Meyer TA, Watcha M, Chung F, Angus S, Apfel CC, Bergese SD, Candiotti KA, Chan MT, Davis PJ, Hooper VD, Lagoo-Deenadayalan S, Myles P, Nezat G, Philip BK, Tramèr MR, Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia. Consensus guidelines for the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg. 2014;118:85–113.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yunoki, K., Mima, H. Postoperative nausea and vomiting after artificial joint replacement surgery: comparison between remimazolam and sevoflurane, a propensity score analysis. J Anesth 37, 666–671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-023-03214-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-023-03214-3