Abstract
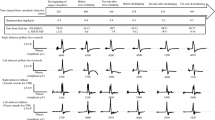
No postoperative paraplegia occurred in a patient whose leg myogenic motor evoked potentials (mMEPs) disappeared during thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. A 69-year-old man underwent resection and repair of a type III (Crawford classification) thoracoabdominal aneurysm. An epidural catheter was placed into the epidural space for epidural cooling, and a Swan-Ganz catheter was placed into the subarachnoid space for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage. Continuous CSF pressure and temperature measurement was carried out the day before surgery. The mMEPs gradually disappeared 10 min after proximal double aortic clamping and complete aortic transection. Selective perfusion of intercostal arteries was started about 20 min after the loss of the mMEPs, but the mMEPs were not restored. Possibly, spinal cord hyperemia, induced by selective perfusion of the intercostal vessels, narrowed the subarachnoid space so that CSF could not be satisfactorily drained during surgery. The spinal cord hyperemia may have decreased spinal function and suppressed the leg mMEPs. The persistence of the loss of mMEPs was undeniably due to the influence of the anesthetic agent or a perfusion disorder in the lower-extremity muscles. Of note, moderate spinal cord hypothermia and postoperative CSF drainage probably resulted in improved lower-limb motor function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SM Frank SD Parker P Roc RB Gorman S Kelly C Beattie GM Williams (1994) ArticleTitleModerate hypothermia with partial bypass and segmental sequential repair for thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm J Vasc Surg 19 687–697 Occurrence Handle8164285 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB3MjitVw%3D
HJ Safi KR Hess M Randel DC Iliopoulos JC Baldwin RK Mootha SS Shenaq R Sheinau T Green (1996) ArticleTitleCerebrospinal drainage and distal aortic perfusion: reducing neurologic complications in repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm types I and II J Vasc Surg 23 223–229 Occurrence Handle8637099 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC1Mrhs1w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0741-5214(96)70266-5
RP Cambria JK Davison S Zannetti G L'Italian DC Brewster JP Gertler AC Moncure GM LaMuraglia (1997) ArticleTitleClinical experience with epidural cooling for spinal cord protection during thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair J Vasc Surg 25 234–243 Occurrence Handle9052558 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3crgsFU%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0741-5214(97)70360-4
NT Kouchoukos BB Daily CK Rokkas SF Murphy S Bauer N Abbound (1994) ArticleTitleHypothermic bypass and circulatory arrest for operations on the descending thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm Ann Thorac Surg 60 67–77
RP Cambria JK Davison C Christopher DC Brewster Y Chung KA Clark S Atamian (2000) ArticleTitleEpidural cooling for spinal cord protection during thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair: a 5-year experience J Vasc Surg 31 1093–1102 Occurrence Handle10842145 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czgt12ntw%3D%3D
MJHM Jacobs SA Meylaerts P de Haan BA De Mol CJ Kalkman (1999) ArticleTitleStrategies to prevent neurologic deficit based on motor-evoked potentials in type I and II thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair J Vasc Surg 29 48–59 Occurrence Handle9882789 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7gt1aktg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0741-5214(99)70349-6
K Grabitz W Sandmann K Stühmeirer B Mainzer E Godehardt B Ohle U Hartwich (1996) ArticleTitleThe risk of ischemic spinal cord injury in patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms J Vasc Surg 23 230–240 Occurrence Handle8637100 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC1Mrhs10%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0741-5214(96)70267-7
CCJ Dong DB MacDonald MT Janusz (2002) ArticleTitleIntraoperative spinal cord monitoring during descending thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysm surgery Ann Thorac Surg 74 S1873–1876 Occurrence Handle12440684 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0003-4975(02)04137-1
CJ Kalkman JC Drummond AA Ribberink PM Patel T Sano RG Bickford (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of propofol, etomidate, midazolam, and fentanyl on motor evoked responses to transcranial electrical or magnetic stimulation in humans Anesthesiology 76 502–509 Occurrence Handle1550274 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xit1yjur8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000542-199204000-00003
BP Keller SS Haghighi JJ Oro GWN Eggers (1992) ArticleTitleThe effects of propofol anesthesia on transcranial electric evoked potentials in the rat Neurosurgery 30 557–560 Occurrence Handle1374852 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B287nvFc%3D
M Kawaguchi T Sakamoto S Inoue M Kakimoto H Furuya T Morimoto T Sakaki (2000) ArticleTitleLow dose propofol as a supplement to ketamine-based anesthesia during intraoperative monitoring of motor-evoked potentials Spine 25 974–979 Occurrence Handle10767811 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3jt1SgtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00007632-200004150-00013
SA Meylaerts P DeHaan CJ Kalkman J Lips BA DeMol MJ Jacobs (1999) ArticleTitleThe influence of regional spinal cord hypothermia on transcranial myogenic motor-evoked potential monitoring and the efficacy of spinal cord ischemia detection J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 118 1038–1045 Occurrence Handle10595976 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2Fmtlyjsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-5223(99)70099-1
T Sakamoto M Kawaguchi M Kakimoto S Inoue M Takahashi H Furuya (2003) ArticleTitleThe effect of hypothermia on myogenic motor-evoked potentials to electrical stimulation with a single pulse and a train of pulses under propofol/ketamine/fentanyl anesthesia in rabbits Anesth Analg 96 1692–1697 Occurrence Handle12760998 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXltFGhu74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1213/01.ANE.0000064202.24119.07
K Tsutsumi T Ueda H Shimizu K Hashizume Y Iino S Kawada (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of post-ischemic hypothermia on spinal cord damage induced by transient ischemic insult in rabbits Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 50 359–365 Occurrence Handle12382401 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02913184
LH Hollier SR Money TC Naslund CD Proctor SuffixSr WC Buhrman RJ Marino DE Harmon FJ Kazmier (1992) ArticleTitleRisk of spinal cord dysfunction in patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic replacement Am J Surg 164 210–214 Occurrence Handle1415916 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD3snhvF0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(05)81072-4
A Hill P Kalman K Johnston H Vosu (1994) ArticleTitleReversal of delayed-onset paraplegia after thoracic aortic surgery with cerebrospinal fluid drainage J Vasc Surg 20 315–317 Occurrence Handle8040958 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuA3MrmvFw%3D
JS Coselli SA LeMaire ZC Schmittling Köksoy (2000) ArticleTitleCerebrospinal fluid drainage in thoracoabdominal aortic surgery Semin Vasc Surg 13 308–314 Occurrence Handle11156059 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3gtFCntQ%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Denda, S., Taneoka, M., Honda, H. et al. Prolonged loss of leg myogenic motor evoked potentials during thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair, without postoperative paraplegia. J Anesth 20, 314–318 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0439-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0439-0