Abstract
Background
Liver fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis and hepatic carcinoma without treatment. CircDCBLD2 was found to be downregulated in liver fibrosis. However, the precise underlying mechanism requires further investigation.
Methods
qRT-PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry assays were used to detect the related molecule levels. HE, Masson’s trichrome, and Sirius Red staining were used to assess the pathological changes in mice’s liver tissues. Flow cytometric analysis and commercial kit were used to assess the levels of lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS), malonaldehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), and iron. Cell viability was assessed by MTT. Immunoprecipitation was used to study the ubiquitination of PARK7. Mitophagy was determined by immunostaining and confocal imaging. RIP and Co-IP assays were used to assess the interactions of circDCBLD2/HuR, HuR/STUB1, and STUB1/PARK7. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunofluorescence staining were used to assess the co-localization of circDCBLD2 and HuR.
Results
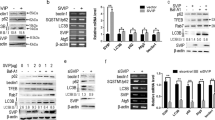
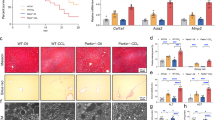
CircDCBLD2 was downregulated, whereas PARK7 was upregulated in liver fibrosis. Ferroptosis activators increased circDCBLD2 while decreasing PARK7 in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and mice with liver fibrosis. CircDCBLD2 overexpression reduced cell viability and GSH, PARK7, and GPX4 expression in erastin-treated HSCs while increasing MDA and iron levels, whereas circDCBLD2 knockdown had the opposite effect. CircDCBLD2 overexpression increased STUB1-mediated PARK7 ubiquitination by promoting HuR-STUB1 binding and thus increasing STUB1 mRNA stability. PARK7 overexpression or HuR knockdown reversed the effects of circDCBLD2 overexpression on HSC activation and ferroptosis. CircDCBLD2 reduced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting PARK7.
Conclusion
CircDCBLD2 overexpression increased PARK7 ubiquitination degradation by upregulating STUB1 through its interaction with HuR, inhibiting HSC activation and promoting HSC ferroptosis, ultimately enhancing liver fibrosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSCs:
-
Hepatic stellate cells
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GPX4:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- PARK7:
-
Parkinson disease 7
- STUB1:
-
STIP1 homology and U-Box containing protein 1
- circRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- act-D:
-
Actinomycin D
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- RIP:
-
RNA immunoprecipitation
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- CCl4 :
-
Carbon tetrachloride
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- HYP:
-
Hydroxyproline
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- IRP2:
-
Iron-regulatory protein 2
References
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–18.
Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018.
Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:125–72.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:369–79.
Ursini F, Maiorino M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175–85.
Zhang Z, Yao Z, Wang L, et al. Activation of ferritinophagy is required for the RNA-binding protein ELAVL1/HuR to regulate ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy. 2018;14:2083–103.
Martinat C, Shendelman S, Jonason A, et al. Sensitivity to oxidative stress in DJ-1-deficient dopamine neurons: an ES- derived cell model of primary Parkinsonism. PLoS Biol. 2004;2:e327.
Cao J, Chen X, Jiang L, et al. DJ-1 suppresses ferroptosis through preserving the activity of S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1251.
Chen L, Luo M, Sun X, et al. DJ-1 deficiency attenuates expansion of liver progenitor cells through modulating the inflammatory and fibrogenic niches. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2257.
Li Y, Jin C, Shen M, et al. Iron regulatory protein 2 is required for artemether -mediated anti-hepatic fibrosis through ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:845–59.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Vo JN, Cieslik M, Zhang Y, et al. The landscape of circular RNA in cancer. Cell. 2019;176(4):869-81 e13.
Wang W, Dong R, Guo Y, et al. CircMTO1 inhibits liver fibrosis via regulation of miR-17-5p and Smad7. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:5486–96.
Yang YR, Hu S, Bu FT, et al. Circular RNA CREBBP suppresses hepatic fibrosis via targeting the hsa-miR-1291/LEFTY2 Axis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:741151.
Srikantan S, Gorospe M. HuR function in disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012;17:189–205.
Mederacke I, Dapito DH, Affo S, et al. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc. 2015;10:305–15.
Wang P, Huang Z, Peng Y, et al. Circular RNA circBNC2 inhibits epithelial cell G2-M arrest to prevent fibrotic maladaptive repair. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6502.
Shrestha N, Chand L, Han MK, et al. Glutamine inhibits CCl4 induced liver fibrosis in mice and TGF-beta1 mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016;93:129–37.
Zhou Y, Lv X, Qu H, et al. Differential expression of circular RNAs in hepatic tissue in a model of liver fibrosis and functional analysis of their target genes. Hepatol Res. 2019;49:324–34.
Dong S, Chen QL, Song YN, et al. Mechanisms of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis with combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. J Toxicol Sci. 2016;41:561–72.
Yang Y, Liu T, Hu C, et al. Ferroptosis inducer erastin downregulates androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.7976.
Kim KM, Cho SS, Ki SH. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in liver pathophysiology. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43:985–96.
Daher B, Parks SK, Durivault J, et al. Genetic ablation of the cystine transporter xCT in PDAC cells inhibits mTORC1, growth, survival, and tumor formation via nutrient and oxidative stresses. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3877–90.
Bao Y, Pang Y, Tang S, et al. 12N-Substituted Matrinol Derivatives Inhibited the Expression of Fibrogenic Genes via Repressing Integrin/FAK/PI3K/Akt Pathway in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Molecules. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203748.
Okholm TLH, Sathe S, Park SS, et al. Transcriptome-wide profiles of circular RNA and RNA-binding protein interactions reveal effects on circular RNA biogenesis and cancer pathway expression. Genome Med. 2020;12:112.
Ding Q, Xie XL, Wang MM, et al. The role of the apoptosis-related protein BCL-B in the regulation of mitophagy in hepatic stellate cells during the regression of liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1–13.
Dou SD, Zhang JN, Xie XL, et al. MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy. Open Med (Wars). 2021;16:1718–27.
Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, et al. Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S15-24.
Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M, Hussen BM, et al. Function of circular RNAs in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;140: 111721.
Rengganaten V, Huang CJ, Tsai PH, et al. Mapping a circular RNA-microRNA-mRNA-signaling regulatory axis that modulates stemness properties of cancer stem cell populations in colorectal cancer spheroid cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217864.
Li H, Zhao Y, Shen Q, et al. Multiple circRNAs regulated by QKI5 conjointly spongemiR-214-3p to antagonize bisphenol A-inducedspermatocyte toxicity. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022;54:1090–9.
Ma L, Yang X, Wei R, et al. MicroRNA-214 promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing Sufu expression. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:718.
Pan Q, Luo Y, Xia Q, et al. Ferroptosis and liver fibrosis. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18:3361–6.
Aldrovandi M, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: the Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Cell Res. 2020;30:1061–2.
Zhang Z, Wang X, Wang Z, et al. Dihydroartemisinin alleviates hepatic fibrosis through inducing ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. BioFactors. 2021;47:801–18.
Zhu Y, Zhang C, Huang M, et al. TRIM26 induces ferroptosis to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation and mitigate liver fibrosis through mediating SLC7A11 ubiquitination. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:644901.
Cho SS, Yang JH, Lee JH, et al. Ferroptosis contribute to hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;193:620–37.
Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98:87–97.
Huang A, Zheng H, Wu Z, et al. Circular RNA-protein interactions: functions, mechanisms, and identification. Theranostics. 2020;10:3503–17.
Li S, Song F, Lei X, et al. hsa_circ_0004018 suppresses the progression of liver fibrosis through regulating the hsa-miR-660-3p/TEP1 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:11517–29.
Liu Z, Wang Q, Wang X, et al. Circular RNA cIARS regulates ferroptosis in HCC cells through interacting with RNA binding protein ALKBH5. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:72.
Yiakouvaki A, Dimitriou M, Karakasiliotis I, et al. Myeloid cell expression of the RNA-binding protein HuR protects mice from pathologic inflammation and colorectal carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:48–61.
Badawi A, Hehlgans S, Pfeilschifter J, et al. Silencing of the mRNA-binding protein HuR increases the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to ionizing radiation through upregulation of caspase-2. Cancer Lett. 2017;393:103–12.
Abdelmohsen K, Panda AC, Munk R, et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017;14:361–9.
Tang DE, Dai Y, Lin LW, et al. STUB1 suppresseses tumorigenesis and chemoresistance through antagonizing YAP1 signaling. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:3145–56.
Zhang S, Zhang X, Bie Y, et al. STUB1 regulates antiviral RNAi through inducing ubiquitination and degradation of Dicer and AGO2 in mammals. Virol Sin. 2022;37:569–80.
Tsubouchi K, Araya J, Minagawa S, et al. Azithromycin attenuates myofibroblast differentiation and lung fibrosis development through proteasomal degradation of NOX4. Autophagy. 2017;13:1420–34.
Chen SC, Liu CM, Hsieh PL, et al. E3 ligase carboxyl-terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP) suppresses fibrotic properties in oral mucosa. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020;119:595–600.
Xin H, Xu X, Li L, et al. CHIP controls the sensitivity of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by modulating the basal level of Smad3 through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20842–50.
Seo J, Lee EW, Sung H, et al. CHIP controls necroptosis through ubiquitylation- and lysosome-dependent degradation of RIPK3. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18:291–302.
Vavougios GD, Solenov EI, Hatzoglou C, et al. Computational genomic analysis of PARK7 interactome reveals high BBS1 gene expression as a prognostic factor favoring survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;309:L677–86.
Yu Y, Sun X, Gu J, et al. Deficiency of DJ-1 ameliorates liver fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic ROS production and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:1225–35.
Chen S, Xia H, Sheng L. WTAP-mediated m6A modification on circCMTM3 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma ferroptosis by recruiting IGF2BP1 to increase PARK7 stability. Dig Liver Dis. 2023;55:967–81.
Liao T, Xu X, Ye X, et al. DJ-1 upregulates the Nrf2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit trophoblast ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2022;12:2934.
Schriever SC, Zimprich A, Pfuhlmann K, et al. Alterations in neuronal control of body weight and anxiety behavior by glutathione peroxidase 4 deficiency. Neuroscience. 2017;357:241–54.
Xu M, Hang H, Huang M, et al. DJ-1 deficiency in hepatocytes improves liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by enhancing mitophagy. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12:567–84.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82170639), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund (No. 82200671), and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2022JJ70068, 2022JJ70070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW: conceptualization; methodology; HZ: visualization; supervision; LC: validation; formal analysis; KF: investigation; resources; YY: data curation; writing–original draft; ZL: writing—review and editing; project administration; funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no competing financial interest exists.
Ethics approval
The Animal Care and Use Committee of Central South University’s Third Xiangya Hospital approved all mouse-related experiments.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Chen, L. et al. CircDCBLD2 alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating ferroptosis via facilitating STUB1-mediated PARK7 ubiquitination degradation. J Gastroenterol 59, 229–249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-023-02068-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-023-02068-6