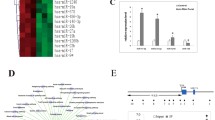
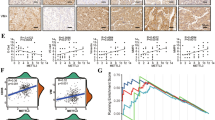
Abstract
Background
Currently, the molecular mechanism of the interaction between lncRNAs and microRNAs (miRNAs) and the target of miRNAs in tumor vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation have not been clarified. Our aim is to study the interaction between lncRNA n339260 and miRNA30e-5p in the formation of VM.
Methods
Animal xenografts were established, 104 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients’ frozen tissues were obtained and HCC cells in vitro were used to observe the role of n339260 in HCC progression.
Results
In vivo experiment showed lncRNA n339260 promoted tumor growth and VM formation. LncRNA n339260 and miRNA30e-5p were found to be associated with VM formation, metastasis and survival time in HCC patients. In vitro experiment showed that LncRNA n339260 could inhibit miRNA30e-5p expression and TP53INP1 was found to be the downstream targets of miRNA30e-5p. Snail, MMP2, MMP9, VE-cadherin, vimentin and N-cadherin overexpression and the downregulation of TP53INP1 and E-cadherin were observed in HCCLM3 and HepG2 cells overexpressing lncRNA n339260 or in cells with decreased expression of miRNA30e-5p.
Conclusion
LncRNA n339260 promotes the development of VM, and lncRNA n339260 may enhance Snail expression by decreasing the expression of miRNA30e-5p, thereby reducing TP53INP1 expression. Therefore, a potential lncRNA n339260- miRNA30e-5p- TP53INP1 regulatory axis was associated with HCC progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemical
- lncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- VM:
-
Vasculogenic mimicry
References
Wang Y, Zhou XY, Lu XY, et al. Involvement of the circular RNA/microRNA/glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase axis in the pathological mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2021;20:530–4.
Folberg R, Hendrix MJ, Maniotis AJ. Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:361–81.
Sun T, Sun BC, Zhao XL, et al. Promotion of tumor cell metastasis and vasculogenic mimicry by way of transcription coactivation by Bcl-2 and Twist1: a study of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;54:1690–706.
Sun T, Zhao N, Zhao XL, et al. Expression and functional significance of Twist1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: its role in vasculogenic mimicry. Hepatology. 2010;51:545–56.
Guzman G, Cotler SJ, Lin AY, et al. A pilot study of vasculogenic mimicry immunohistochemical expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1776–81.
Shao B, Zhao X, Liu T, et al. LOXL2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry and tumour aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:1363–74.
Li X, Sun B, Zhao X, et al. Function of BMP4 in the Formation of vasculogenic mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2020;11:2560–71.
Engreitz JM, Pandya-Jones A, McDonel P, et al. The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science. 2013;341:1237973.
Kanduri C. Long noncoding RNAs: lessons from genomic imprinting. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2016;1859:102–11.
Ard R, Tong P, Allshire RC. Long non-coding RNA-mediated transcriptional interference of a permease gene confers drug tolerance in fission yeast. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5576.
Li Y, Wang Z, Shi H, et al. HBXIP and LSD1 Scaffolded by lncrna hotair mediate transcriptional activation by c-myc. Can Res. 2016;76:293–304.
Sun M, Nie F, Wang Y, et al. LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by scaffolding the chromatin modification factors prc2, lsd1, and dnmt1. Can Res. 2016;76:6299–310.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–58.
Huan L, Liang LH, He XH. Role of microRNAs in inflammation-associated liver cancer. Cancer Biol Med. 2016;13:407–25.
Hu W, Wang T, Yang Y, et al. CPuORF correlates with miRNA responsive elements on protein evolutionary rates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;452:66–71.
Xiao M, Li J, Li W, et al. MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1326–34.
Uva P, Cossu-Rocca P, Loi F, et al. miRNA-135b contributes to triple negative breast cancer molecular heterogeneity: different expression profile in basal-like versus non-basal-like phenotypes. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15:536–48.
Huang V, Place RF, Portnoy V, et al. Upregulation of cyclin B1 by miRNA and its implications in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:1695–707.
Chen S, Deng X, Sheng H, et al. Noncoding RNAs in pediatric brain tumors: molecular functions and pathological implications. Mol ther Nucl acids. 2021;26:417–31.
Zhou H, Jia X, Yang F, et al. Long noncoding RNA SATB1-AS1 contributes to the chemotherapy resistance through the microRNA-580/ 2’-5’-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Bioengineered. 2021;12:6403–17.
Yin Y, Yang W, Zhang L, et al. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL and its target microRNAs (microRNA-34a, microRNA-125a and microRNA-186) relate to risk stratification and prognosis in multiple myeloma. Hematology. 2021;26:160–9.
Jiang G, Yu H, Li Z, et al. lncRNA cytoskeleton regulator reduces nonsmall cell lung cancer radiosensitivity by downregulating miRNA206 and activating prothymosin alpha. Int J Oncol. 2021;59:88.
Raei N, Safaralizadeh R, Hesseinpourfeizi M, et al. Crosstalk between lncRNAs and miRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer drug resistance. Life Sci. 2021;284: 119933.
Babaei G, Raei N, Toofani Milani A, et al. The emerging role of miR-200 family in metastasis: focus on EMT, CSCs, angiogenesis, and anoikis. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48:6935–47.
Mirzaei S, Saebfar H, Gholami MH, et al. MicroRNAs regulating SOX2 in cancer progression and therapy response. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2021;23: e13.
Crudele F, Bianchi N, Astolfi A, et al. The Molecular Networks of microRNAs and their targets in the drug resistance of colon carcinoma. Cancers. 2021;13:4355.
Zhao X, Sun B, Liu T, et al. Long noncoding RNA n339260 promotes vasculogenic mimicry and cancer stem cell development in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:3197–208.
Wang Y, Sun H, Zhang D, et al. TP53INP1 inhibits hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry formation via the ROS/snail signalling axis in breast cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:3475–88.
Sun B, Zhang D, Zhao N, et al. Epithelial-to-endothelial transition and cancer stem cells: two cornerstones of vasculogenic mimicry in malignant tumors. Oncotarget. 2017;8:30502–10.
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Meltzer PS, et al. Expression and functional significance of VE-cadherin in aggressive human melanoma cells: role in vasculogenic mimicry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:8018–23.
Li W, Zong S, Shi Q, et al. Hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry formation in human colorectal cancer cells: Involvement of HIF-1a, Claudin-4, and E-cadherin and Vimentin. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37534.
Bai J, Yeh S, Qiu X, et al. TR4 nuclear receptor promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and metastasis via altering the miR490-3p/vimentin signals. Oncogene. 2018;37:5901–12.
Bassiouni W, Ali MAM, Schulz R. Multifunctional intracellular matrix metalloproteinases: implications in disease. FEBS J. 2021;288:7162–82.
Qin X, Li C, Guo T, et al. Upregulation of DARS2 by HBV promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through the miR-30e-5p/MAPK/NFAT5 pathway. J exp clin cancer res:CR. 2017;36:148.
Jiang F, Liu T, He Y, et al. MiR-125b promotes proliferation and migration of type II endometrial carcinoma cells through targeting TP53INP1 tumor suppressor in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:425.
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, et al. Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:79–89.
Mali AV, Joshi AA, Hegde MV, et al. Enterolactone modulates the ERK/NF-kappaB/Snail signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 to revert the TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol Med. 2018;15:137–56.
Liu Q, Qiao L, Liang N, et al. The relationship between vasculogenic mimicry and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20:1761–9.
Zheng N, Zhang S, Wu W, et al. Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of vasculogenic mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol Res. 2021;166: 105507.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the following grants: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81572872).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
535_2022_1901_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1. (A) The wound healing experiment of lncRNA n339260 upregulated (n339260) and downregulated (n339260-SH) HCC cells. (B) The wound healing experiment of miRNA30e-5p upregulated (30e-5p) and downregulated (inhibitor) HCC cells. (TIF 12459 KB)
535_2022_1901_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Figure S2. (A) The wound healing experiment of TP53INP1 upregulated (TP53INP1) and downregulated (TP53INP1-SH) HCC cells. (B) The wound healing experiment of n339260 and miRNA30e-5p co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (TIF 3682 KB)
535_2022_1901_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Figure S3. (A) The wound healing experiment of n339260 and miRNA30e-5p co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (B) The migration experiment, invasion experiment and three-dimensional VM tubules of n339260 and miRNA30e-5p co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (C) Western blots of TP53INP1, VM marker (MMP2, MMP9 and VE-cadherin) and EMT indexes (snail, E-cadherin and vimentin) expression in lncRNA n339260 and miRNA30e-5p co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (D) Luciferase reporter gene experiment of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 in 293T cells. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (TIF 1117 KB)
535_2022_1901_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Figure S4. (A) The migration experiment, invasion experiment and three-dimensional VM tubules of n339260 and miRNA30e-5p co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (B) The wound healing experiment of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (TIF 3548 KB)
535_2022_1901_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Figure S5. (A) The wound healing experiment of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (B) The migration experiment, invasion experiment and three-dimensional VM tubules of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (C) Western blots of VM marker (MMP2, MMP9 and VE-cadherin) and EMT indexes (snail, E-cadherin and vimentin) expression of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (TIF 4104 KB)
535_2022_1901_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Figure S6. (A) The migration experiment, invasion experiment and three-dimensional VM tubules of miRNA30e-5p and TP53INP1 co-transfected HCC cells in rescue experiment. (TIF 5428 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Liao, S., Mo, J. et al. LncRNA n339260 functions in hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of miRNA30e-5p/TP53INP1 expression. J Gastroenterol 57, 784–797 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-022-01901-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-022-01901-8