Abstract
Background
The virological efficacy and safety of the direct-acting antiviral (DAA) regimen consisting of daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir (DCV/ASV/BCV) for patients chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1 have not been previously evaluated in Japanese real-world settings.
Methods
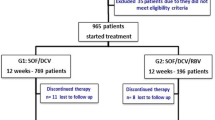
In a Japanese nationwide multicenter study, the rate of sustained virologic response (SVR) and safety were analyzed in 91 patients who started the DCV/ASV/BCV regimen between November 2016 and July 2017. SVR rates were compared based on baseline patient characteristics.
Results
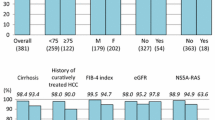
More than 60% of patients had a history of failure to achieve SVR with interferon (IFN)-free DAA therapy. Overall, 50 of 91 patients (54.9%) achieved SVR. Multivariate analysis identified a history of failure with IFN-free DAA therapy and pretreatment HCV RNA levels as factors significantly associated with treatment failure. Whereas the SVR rate in patients without a history of IFN-free DAA therapy was 91.7% (33 of 36 patients), it was only 30.9% (17 of 55 patients) among patients with a history of IFN-free DAA therapy. The rate of discontinuation due to an adverse event was 4.4%.
Conclusions
Many patients treated with the DCV/ASV/BCV regimen have a history of a failure to achieve SVR with previous IFN-free DAA therapy. SVR rate was not as high as that in pre-approval clinical trial of this regimen in IFN-free DAA-naïve patients. In addition, most patients with a history of failure with IFN-free DAA therapy, particularly the DCV/ASV regimen, showed resistance to this regimen.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chayama K, Hayes CN. HCV drug resistance challenges in Japan: the role of pre-existing variants and emerging resistant strains in direct acting antiviral therapy. Viruses. 2015;7:5328–42.
Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Ikeda K, et al. Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. Hepatology. 2014;59:2083–91.
Fujii H, Umemura A, Nishikawa T, et al. Real-world efficacy of daclatasvir and asunaprevir with respect to resistance-associated substitutions. World J Hepatol. 2017;9:1064–72.
Sezaki H, Suzuki F, Hosaka T, et al. The efficacy and safety of dual oral therapy with daclatasvir and asunaprevir for genotype 1b in Japanese real-life settings. Liver Int. 2017;37:1325–33.
Iio E, Shimada N, Abe H, et al. Efficacy of daclatasvir/asunaprevir according to resistance-associated variants in chronic hepatitis C with genotype 1. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:94–103.
Mizokami M, Yokosuka O, Takehara T, et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin for 12 weeks in treatment-naive and previously treated Japanese patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:645–53.
Kumada H, Chayama K, Rodrigues L Jr, et al. Randomized phase 3 trial of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir for HCV genotype 1b-infected Japanese patients with or without cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2015;62:1037–46.
Kumada H, Suzuki Y, Karino Y, et al. The combination of elbasvir and grazoprevir for the treatment of chronic HCV infection in Japanese patients: a randomized phase II/III study. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:520–33.
Toyota J, Karino Y, Suzuki F, et al. Daclatasvir/asunaprevir/beclabuvir fixed-dose combination in Japanese patients with HCV genotype 1 infection. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:385–95.
Ohno O, Mizokami M, Wu RR, et al. New hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotyping system that allows for identification of HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4, 5a, and 6a. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:201–7.
Uchida Y, Kouyama J, Naiki K, et al. A novel simple assay system to quantify the percent HCV RNA levels of NS5A Y93H mutant strains and Y93 wild-type strains relative to the total HCV-RNA levels to determine the indication for antiviral therapy with NS5A inhibitors. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e112647.
Sterling RK, Lissen E, Clumeck N, et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology. 2006;43:1317–25.
The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1994;20:15–20.
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, et al. FIB-4: an inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and FibroTest. Hepatology. 2007;46:32–6.
Kozuka R, Hai H, Motoyama H, et al. The presence of multiple NS5A RASs is associated with the outcome of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy in NS5A inhibitor-naïve patients with chronic HCV genotype 1b infection in a real-world cohort. J Viral Hepat (in press).
Toyoda H, Atsukawa M, Takaguchi K, et al. Real-world virological efficacy and safety of elbasvir and grazoprevir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection in Japan. J Gastroenterol (in press).
Everson GT, Sims KO, Rodriguez-Torres M, et al. Efficacy of an interferon- and ribavirin-free regimen of daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and BMS-791325 in treatment naïve patients with HCV genotype 1 infection. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:420–9.
Muir AJ, Poordad F, Lalezari J, et al. Daclatasvir in combination with asunaprevir and beclabuvir for hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection with compensated cirrhosis. JAMA. 2015;313:1736–44.
Kao JH, Yu ML, Peng CY, et al. Daclatasvir/asunaprevir/beclabuvir, all-oral, fixed-dose combination for patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:1998–2005.
Itakura J, Kurosaki M, Hasebe C, et al. Complex pattern of resistance-associated substitutions of hepatitis C virus after daclatasvir/asunaprevir treatment failure. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0165339.
Kumada H, Watanabe T, Suzuki F, et al. Efficacy and safety of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in HCV-infected Japanese patients with prior DAA experience, severe renal impairment, or genotype 3 infection. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:566–75.
Teraoka Y, Uchida T, Imamura M, et al. Limitations of daclatasvir/asunaprevir plus beclabuvir treatment in cases of NS5A inhibitor treatment failure. J Gen Virol. 2018;99:1058–65.
Hassanein T, Sims KD, Bennett M, et al. A randomized trial of daclatasvir in combination with asunaprevir and beclabuvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 4 infection. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1204–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takaguchi, K., Toyoda, H., Tsutsui, A. et al. Real-world virological efficacy and safety of daclatasvir/asunaprevir/beclabuvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection in Japan. J Gastroenterol 54, 742–751 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01568-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01568-8