Abstract
Background
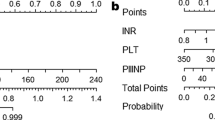
The FIB4 index is clinically useful, but because its formula includes age, the appropriate cutoff point may differ by age group. Here, new FIB4 index cutoff points were validated using cohort data from 14 hepatology centers in Japan.
Methods
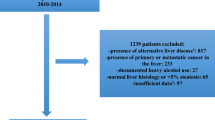
The FIB4 index was determined in biopsy-confirmed NAFLD patients (n = 1050) who were divided into four groups: ≤ 49, 50–59, 60–69, and ≥ 70 years. ROC analysis predicted advanced fibrosis in each age group; low and high cutoff points were defined by a sensitivity and specificity of 90%. The new and conventional cutoffs were compared for detecting advanced fibrosis.
Results
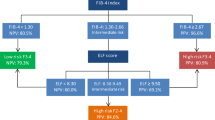
The modified low and high cutoff points were 1.05 and 1.21 in ≤ 49 years, 1.24 and 1.96 in 50–59 years, 1.88 and 3.24 in 60–69 years, and 1.95 and 4.56 in ≥ 70 years. In ≥ 60 years, the false-negative rate was increased using the modified high cutoff point, and the high cutoff point was better with the conventional cutoff point. The new proposed low and high cutoff points are 1.05 and 1.21 in ≤ 49 years, 1.24 and 1.96 in 50–59 years, 1.88 and 2.67 in 60–69 years, and 1.95 and 2.67 in ≥ 70 years; these cutoff points improved the accuracy of advanced fibrosis diagnosis.
Conclusions
FIB4 index cutoff points for predicting advanced fibrosis in NAFLD increased with age. Cutoff points modified by age improved the diagnostic accuracy of estimations of advanced liver fibrosis using the FIB4 index.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 May 2018
The coauthor Masashi Yoneda’s affiliation has been incorrectly published in the original publication of the article. The correct affiliation is provided in this correction.
References
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84.
Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:1413–9.
Rafiq N, Bai C, Fang Y, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(2):234–8.
Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:389–97.
Ekstedt M, Hagström H, Nasr P, et al. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. 2015;61:1547–54.
Myers RP, Fong A, Shaheen AA. Utilization rates, complications and costs of percutaneous liver biopsy: a population-based study including 4275 biopsies. Liver Int. 2008;28:705–12.
McPherson S, Stewart SF, Henderson E, et al. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2010;59:1265–9.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45:846–54.
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328–57.
Sumida Y, Yoneda M, Hyogo H, et al. Validation of the FIB4 index in a Japanese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:2.
Sterling RK, Lissen E, Clumeck N, et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology. 2006;43:1317–25.
Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, et al. Nash Clinical Research Network. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1104–12.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–21.
Japanese Society for the Study of Obesity. New criteria of obesity in Japanese. J Jpn Soc Study Obes. 2000;6:18–28.
American Diabetes Association. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:1183–97.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2467–74.
Sumida Y, Nakajima A, Itoh Y. Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:475–85.
Angulo P, Bugianesi E, Bjornsson ES, et al. Simple noninvasive systems predict long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:782–9.
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388–402.
Nagai Y, Metter EJ, Earley CJ, et al. Increased carotid artery intimal- medial thickness in asymptomatic older subjects with exercise-induced myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 1998;98:1504–9.
McPherson S, Hardy T, Dufour JF, et al. Age as a confounding factor for the accurate non-invasive diagnosis of advanced NAFLD fibrosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:740–51.
Acknowledgements
We have no funds and grants in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
HI and SY: concept, design and writing of article. ST, MY, HH, HF, YS, MY, HT, TN, YS, KM, KK, KI: Date Procedures. KS, SI: Pathologist. MO, YE, TK, MY, AN, KC, TS, TS, KF, TO: Obserever. YI: Director of this study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors do not have any financial of conflicts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiba, H., Sumida, Y., Tanaka, S. et al. The novel cutoff points for the FIB4 index categorized by age increase the diagnostic accuracy in NAFLD: a multi-center study. J Gastroenterol 53, 1216–1224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-018-1474-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-018-1474-y