Abstract
Background
The introduction of capsule endoscopy (CE) has facilitated the detection of mucosal changes in the small bowel, and such mucosal changes have been noted in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension; these changes are described as portal hypertensive enteropathy. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) on the small bowel mucosal changes detected by CE in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension.
Methods
TIPS was performed in fifteen cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension. All patients underwent CE before and 2 weeks after TIPS. The small bowel mucosal changes were defined as edema, angiodysplasia-like lesions, red spots, and small bowel varices. Changes in the portosystemic pressure gradient (PSG) and CE findings were evaluated.
Results
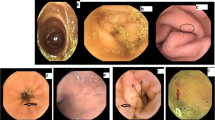
Before TIPS, small bowel edema was detected in all 15 patients, angiodysplasia-like lesions in 7, and red spots in 14 patients. The PSG decreased significantly, from 21.2 ± 2.6 before TIPS to 8.9 ± 3.3 mmHg (p < 0.001) after the procedure. After TIPS, the small bowel edema was attenuated in 8 of the 15 patients. In two patients with angiodysplasia-like lesions and 4 with red spots, these lesions were attenuated after TIPS. The average score for small bowel edema and the grade of red spots were reduced significantly after TIPS (2.3 ± 0.7–1.8 ± 0.6, p < 0.005 and 1.6 ± 0.9–1.3 ± 0.7, p < 0.05, respectively). Small bowel varices were seen in 4 patients before TIPS and all these varices disappeared after TIPS.
Conclusions
In cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension, small bowel edema, red spots, and small bowel varices were attenuated after TIPS. Portal hypertension may be an important factor in the development of small bowel mucosal changes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iddan G, Meron G, Glukhovsky A, Swain P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature. 2000;405:417.
De Palma GD, Rega M, Masone S, Persico F, Siciliano S, Patrone F, et al. Mucosal abnormalities of the small bowel in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: a capsule endoscopy study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:529–34.
Figueiredo P, Almeida N, Lerias C, Lopes S, Gouveia H, Leitao MC, et al. Effect of portal hypertension in the small bowel: an endoscopic approach. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:2144–50.
Abdelaal UM, Morita E, Nouda S, Kuramoto T, Miyaji K, Fukui H, et al. Evaluation of portal hypertensive enteropathy by scoring with capsule endoscopy: is transient elastography of clinical impact? J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010;47:37–44.
Akyuz F, Pinarbasi B, Ermis F, Uyanikoglu A, Demir K, Ozdil S, et al. Is portal hypertensive enteropathy an important additional cause of blood loss in portal hypertensive patients? Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:1497–502.
Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of portal hypertension. Hepatology. 2005;41:386–400.
Garcia-Tsao G. Portal hypertension. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006;22:254–62.
Urata J, Yamashita Y, Tsuchigame T, Hatanaka Y, Matsukawa T, Sumi S, et al. The effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on portal hypertensive gastropathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;13:1061–7.
Mezawa S, Homma H, Ohta H, Masuko E, Doi T, Miyanishi K, et al. Effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt formation on portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric circulation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:1155–9.
Pezzoli A, Fusetti N, Simone L, Zelante A, Cifala V, Carella A, et al. Portal hypertensive enteropathy diagnosed by capsule endoscopy and demonstration of the ileal changes after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:90.
de Franchis R. Updating consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno III Consensus Workshop on definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000;33:846–52.
Delvaux M, Gay G. Capsule endoscopy: technique and indications. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;22:813–37.
Rösch J, Keller FS. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: present status, comparison with endoscopic therapy and shunt surgery, and future prospectives. World J Surg. 2001;25:337–45.
Casado M, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bru C, Banares R, Bandi JC, et al. Clinical events after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: correlation with hemodynamic findings. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:1296–303.
Thalheimer U, Leandro G, Samonakis DN, Triantos CK, Senzolo M, Fung K, et al. TIPS for refractory ascites: a single-centre experience. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:1089–95.
Spina GP, Arcidiacono R, Bosch J, Pagliaro L, Burroughs AK, Santambrogio R, et al. Gastric endoscopic features in portal hypertension: final report of a consensus conference, Milan, Italy, September 19, 1992. J Hepatol. 1994;21:461–7.
Moore KP, Wong F, Gines P, Bernardi M, Ochs A, Salerno F, et al. The management of ascites in cirrhosis: report on the consensus conference of the International Ascites Club. Hepatology. 2003;38:258–66.
Takahashi Y, Fujimori S, Narahara Y, Gudis K, Ensaka Y, Kosugi Y, et al. Small intestinal edema had the strongest correlation with portal venous pressure amongst capsule endoscopy findings. Digestion. 2012;86:48–54.
Higaki N, Matsui H, Imaoka H, Ikeda Y, Murakami H, Hiasa Y, et al. Characteristic endoscopic features of portal hypertensive enteropathy. J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:327–31.
Cubillas R, Rockey DC. Portal hypertensive gastropathy: a review. Liver Int. 2010;30:1094–102.
Vidal V, Joly L, Perreault P, Bouchard L, Lafortune M, Pomier-Layrargues G. Usefulness of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhotic patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29:216–9.
Haskal ZJ, Scott M, Rubin RA, Cope C. Intestinal varices: treatment with the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Radiology. 1994;191:183–7.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita, Y., Narahara, Y., Fujimori, S. et al. Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on changes in the small bowel mucosa of cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol 48, 633–639 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0660-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0660-6