Abstract
Background
This study is a post-hoc analysis of a subset of patients who participated in our multi-institutional case-control study that evaluated the effects of pitavastatin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with hypercholesterolemia.
Methods
Serum samples of fifteen patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD with dyslipidemia were investigated. Serum markers of lipid metabolism were quantified by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC–MS)/MS. These data were then compared with those of 36 sex- and age-matched healthy controls. In addition, changes in these markers produced by treatment with pitavastatin were evaluated.
Results
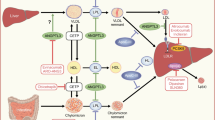
Serum non-cholesterol sterols, reflecting intestinal cholesterol absorption, were significantly lower in the NAFLD patients compared to the controls, and the cholesterol synthesis marker, the ratio of lathosterol to cholesterol, was not significantly different between the two groups. Serum proportions of liver X receptor α (LXRα) ligand oxysterols (ratios to cholesterol) were significantly elevated in the NAFLD patients compared to the controls. The sum of oxysterols relative to cholesterol and the homeostasis model assessment as an index of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were significantly correlated. The marker representing cholesterol synthesis was significantly suppressed by pitavastatin treatment, from 3 months after initiation of the treatment, and the suppression remained significant during the observation period. The markers representing cholesterol absorption were unchanged at 3 months, but had significantly increased at 12 months. Serum oxysterol levels relative to cholesterol maintained high values and did not change significantly during the 12-month period of treatment.
Conclusions:
We speculate that serum LXRα ligand oxysterol levels (relative to cholesterol) could be surrogate markers of insulin resistance, and that high oxysterol levels in the circulation may play an important role in the development of hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance followed by NAFLD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Caldwell SH. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD Single Topic Conference. Hepatology. 2003;37:1202–19.
Kotronen A, Westerbacka J, Bergholm R, Pietilainen KH, Yki-Jarvinen H. Liver fat in the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:3490–7.
Seppala-Lindroos A, Vehkavaara S, Hakkinen AM, Goto T, Westerbacka J, Sovijarvi A, et al. Fat accumulation in the liver is associated with defects in insulin suppression of glucose production and serum free fatty acids independent of obesity in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:3023–8.
Ryysy L, Hakkinen AM, Goto T, Vehkavaara S, Westerbacka J, Halavaara J, et al. Hepatic fat content and insulin action on free fatty acids and glucose metabolism rather than insulin absorption are associated with insulin requirements during insulin therapy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2000;49:749–58.
Dzeletovic S, Breuer O, Lund E, Diczfalusy U. Determination of cholesterol oxidation products in human plasma by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1995;225:73–80.
Gill S, Chow R, Brown AJ. Sterol regulators of cholesterol homeostasis and beyond: the oxysterol hypothesis revisited and revised. Prog Lipid Res. 2008;47:391–404.
Janowski BA, Willy PJ, Devi TR, Falck JR, Mangelsdorf DJ. An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the nuclear receptor LXR alpha. Nature. 1996;383:728–31.
Reschly EJ, Ai N, Welsh WJ, Ekins S, Hagey LR, Krasowski MD. Ligand specificity and evolution of liver X receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;110:83–94.
DeBose-Boyd RA, Ou J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) mRNA in rat hepatoma cells requires endogenous LXR ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:1477–82.
Nakamuta M, Fujino T, Yada R, Yada M, Yasutake K, Yoshimoto T, et al. Impact of cholesterol metabolism and the LXRalpha-SREBP-1c pathway on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Med. 2009;23:603–8.
Higuchi N, Kato M, Shundo Y, Tajiri H, Tanaka M, Yamashita N, et al. Liver X receptor in cooperation with SREBP-1c is a major lipid synthesis regulator in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res. 2008;38:1122–9.
Kotronen A, Seppanen-Laakso T, Westerbacka J, Kiviluoto T, Arola J, Ruskeepaa AL, et al. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)-1 activity and diacylglycerol but not ceramide concentrations are increased in the nonalcoholic human fatty liver. Diabetes. 2009;58:203–8.
Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH. Approaches to measuring cholesterol absorption in humans. Atherosclerosis. 2004;174:197–205.
Miettinen TA, Tilvis RS, Kesaniemi YA. Serum plant sterols and cholesterol precursors reflect cholesterol absorption and synthesis in volunteers of a randomly selected male population. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;131:20–31.
Miettinen TA. Cholesterol production in obesity. Circulation. 1971;44:842–50.
Miettinen TA, Gylling H. Cholesterol absorption efficiency and sterol metabolism in obesity. Atherosclerosis. 2000;153:241–8.
Gylling H, Hallikainen M, Kolehmainen M, Toppinen L, Pihlajamaki J, Mykkanen H, et al. Cholesterol synthesis prevails over absorption in metabolic syndrome. Transl Res. 2007;149:310–6.
Bennion LJ, Grundy SM. Effects of diabetes mellitus on cholesterol metabolism in man. N Engl J Med. 1977;296:1365–71.
Simonen P, Kotronen A, Hallikainen M, Sevastianova K, Makkonen J, Hakkarainen A, et al. Cholesterol synthesis is increased and absorption decreased in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease independent of obesity. J Hepatol. 2011;54:153–9.
Gomez-Dominguez E, Gisbert JP, Moreno-Monteagudo JA, Garcia-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R. A pilot study of atorvastatin treatment in dyslipemid, non-alcoholic fatty liver patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:1643–7.
Hyogo H, Tazuma S, Arihiro K, Iwamoto K, Nabeshima Y, Inoue M, et al. Efficacy of atorvastatin for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with dyslipidemia. Metabolism. 2008;57:1711–8.
Nelson A, Torres DM, Morgan AE, Fincke C, Harrison SA. A pilot study using simvastatin in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43:990–4.
Hyogo H, Ikegami T, Tokushige K, Hashimoto E, Inui K, Matsuzaki Y, et al. Efficacy of pitavastatin for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with dyslipidemia: an open-label, pilot study. Hepatol Res. 2011;41:1057–65.
Honda A, Yamashita K, Miyazaki H, Shirai M, Ikegami T, Xu G, et al. Highly sensitive analysis of sterol profiles in human serum by LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Lipid Res. 2008;49:2063–73.
Honda A, Yamashita K, Hara T, Ikegami T, Miyazaki T, Shirai M, et al. Highly sensitive quantification of key regulatory oxysterols in biological samples by LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Lipid Res. 2009;50:350–7.
Honda A, Miyazaki T, Ikegami T, Iwamoto J, Yamashita K, Numazawa M, et al. Highly sensitive and specific analysis of sterol profiles in biological samples by HPLC–ESI–MS/MS. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;121:556–64.
Honda A, Yamashita K, Numazawa M, Ikegami T, Doy M, Matsuzaki Y, et al. Highly sensitive quantification of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in human serum by LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:458–64.
Honda A, Yamashita K, Ikegami T, Hara T, Miyazaki T, Hirayama T, et al. Highly sensitive quantification of serum malonate, a possible marker for de novo lipogenesis, by LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Lipid Res. 2009;50(2124):30.
Ghoshal AK, Guo T, Soukhova N, Soldin SJ. Rapid measurement of plasma acylcarnitines by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry without derivatization. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;358:104–12.
Babiker A, Diczfalusy U. Transport of side-chain oxidized oxysterols in the human circulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1392:333–9.
Honda A, Miyazaki T, Ikegami T, Iwamoto J, Maeda T, Hirayama T, et al. Cholesterol 25-hydroxylation activity of CYP3A. J Lipid Res. 2011;52:1509–16.
Cali JJ, Russell DW. Characterization of human sterol 27-hydroxylase. A mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 that catalyzes multiple oxidation reaction in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:7774–8.
Lund EG, Guileyardo JM, Russell DW. cDNA cloning of cholesterol 24-hydroxylase, a mediator of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7238–43.
van der Veen JN, van Dijk TH, Vrins CL, van Meer H, Havinga R, Bijsterveld K, et al. Activation of the liver X receptor stimulates trans-intestinal excretion of plasma cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:19211–9.
Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, Yao X, Hoos LM, Tetzloff G, et al. Niemann–Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science. 2004;303:1201–4.
Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, Yu L, Grishin NV, Schultz J, et al. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 2000;290:1771–5.
Lee MH, Lu K, Hazard S, Yu H, Shulenin S, Hidaka H, et al. Identification of a gene, ABCG5, important in the regulation of dietary cholesterol absorption. Nat Genet. 2001;27:79–83.
Yu L, Hammer RE, Li-Hawkins J, Von Bergmann K, Lutjohann D, Cohen JC, et al. Disruption of Abcg5 and Abcg8 in mice reveals their crucial role in biliary cholesterol secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:16237–42.
Yu L, Li-Hawkins J, Hammer RE, Berge KE, Horton JD, Cohen JC, et al. Overexpression of ABCG5 and ABCG8 promotes biliary cholesterol secretion and reduces fractional absorption of dietary cholesterol. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:671–80.
Hirayama T, Mizokami Y, Honda A, Homma Y, Ikegami T, Saito Y, et al. Serum concentration of 27-hydroxycholesterol predicts the effects of high-cholesterol diet on plasma LDL cholesterol level. Hepatol Res. 2009;39:149–56.
Biddinger SB, Haas JT, Yu BB, Bezy O, Jing E, Zhang W, et al. Hepatic insulin resistance directly promotes formation of cholesterol gallstones. Nat Med. 2008;14:778–82.
Schreuder TC, Marsman HA, Lenicek M, van Werven JR, Nederveen AJ, Jansen PL, et al. The hepatic response to FGF19 is impaired in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;298:G440–5.
Trauner M, Claudel T, Fickert P, Moustafa T, Wagner M. Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism. Dig Dis. 2010;28:220–4.
Yang ZX, Shen W, Sun H. Effects of nuclear receptor FXR on the regulation of liver lipid metabolism in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. 2010;4:741–8.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. This work was presented, in part, at Digestive Disease Week 2011 was held at Chicago, IL, USA.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikegami, T., Hyogo, H., Honda, A. et al. Increased serum liver X receptor ligand oxysterols in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol 47, 1257–1266 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0585-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0585-0