Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to visualize the gastric wall layers and to depict the vascular architecture in vitro by using resected porcine stomachs studied with high-spatial resolution magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
Methods
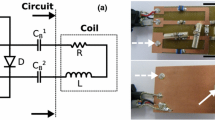
Normal dissected porcine stomach samples (n = 4) were examined with a 3 Tesla MR system using a newly developed surface coil. MR images were obtained by the surface coil as receiver and a head coil as transmitter. High-spatial-resolution spin-echo MR images were obtained with a field of view of 8 × 8 cm, a matrix of 256 × 128 and slice thicknesses of 3 and 5 mm.
Results
T1 and T2-weighted MR images clearly depicted the normal porcine gastric walls as consisting of four distinct layers. In addition, vascular architectures in proper muscle layers were also visualized, which were confirmed by histological examinations to correspond to blood vessels.
Conclusions
High-spatial-resolution MR imaging using a surface coil placed closely to the gastric wall enabled the differentiation of porcine gastric wall layers and the depiction of the blood vessels in proper muscle layer in this experimental study.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akisik FM, Sandrasegaran K, Aisen AM, Lin C, Lall C. Abdominal MR imaging at 3.0T. RadioGraphics. 2007;27:1433–44.
Barth MM, Smith MP, Pedrosa I, Lenkinski RE, Rofski NM. Body MR imaging at 3.0T: understanding the opportunities and challenges. RadioGraphics. 2007;27:1445–64.
Merkle EM, Dale BM. Abdominal MRI at 3.0T: the basic revisited. AJR. 2006;186:1524–32.
Merkle EM, Dale BM, Paulson EK. Abdominal MR imaging at 3T. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006;14:17–26.
Inui K, Nakazawa S, Yoshino J, Yamao K, Yamachika H, Wakabayashi T. Endoscopic MRI: preliminary results of a new technique for visualization and staging of gastrointestinal tumors. Endoscopy. 1995;27:480–5.
Kulling D, Bohning DE, Kay CL, Feldman DR, Cotton PB, Hawes RH. Histological correlates to pig gastrointestinal wall layers imaged in vitro with the magnetic resonance endoscope. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:1568–74.
Feldman DR, Kulling DP, Hawes RH, Kay CL, Muckenfuss VR, Cotton PB, et al. MR endoscopy: preliminary experience in human trials. Radiology. 1997;202:868–70.
Inui K, Nakazawa S, Yoshino J, Ukai H. Endoscopic MRI. Pancreas. 1998;16:413–7.
Kulling D, Feldman DR, Kay CL, Hoffman BJ, Reed CE, Young JWR, et al. Local staging of esophageal cancer using endoscopic magnetic resonance imaging: prospective comparison with endoscopic ultrasound. Endoscopy. 1998;30:745–9.
Stoker J, Van Velthuysen M-L, Van Overhagen H, Van Kempen D, Tilanus HW, Lameris JS. Esophageal carcinoma ex vivo endoluminal magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 1999;34:58–64.
Maldjian C, Smith R, Kilger A, Schnall M, Ginsberg G, Kochman M. Endorectal surface coil MR imaging as a staging technique for rectal carcinoma: a comparison study to rectal endosonography. Abdom Imaging. 2000;25:75–80.
Dave UR, Williams AD, Amin Z, Wilson JA, Gilderdale DJ, Larkman DJ, et al. Esophageal cancer staging with endoscopic MR imaging: pilot study. Radiology. 2004;230:281–6.
Heye T, Kuntz C, Dux M, Encke J, Palmowski M, Autschbach F, et al. New coil concept for endoluminal MR imaging initial results in staging of gastric carcinoma in correlation with histopathology. Eur Radiol. 2006;16:2401–9.
Grenacher L, Heye T, Kuntz C, Palmowski M, Autschbach F, Manz B, et al. Experimental testing of a new coil design for endoluminal MRI applied to the pig stomach. Fortschr Rontgenstr. 2005;177:986–91.
D’amico AV, Schnall M, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Tomaszewski JE, et al. Endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging identifies locally advanced prostate cancer in select patients with clinically localized disease. Urology. 1998;51:449–54.
Greenberg J, Durkin M, Van Drunen M, Aranha GV. Computed tomography or endoscopic ultrasonography in preoperative staging of gastric and esophageal tumors. Surgery. 1994;116:696–701. discussion 701–702.
Meining A, Dittler HJ, Wolf A, Lorenz R, Schusdziarra V, Siewert J-R, et al. You get what you expect? A critical appraisal of imaging methodology in endosonographic cancer staging. Gut. 2002;50:599–603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morita, Y., Kutsumi, H., Yoshinaka, H. et al. Newly developed surface coil for endoluminal MRI, depiction of pig gastric wall layers and vascular architecture in ex vivo study. J Gastroenterol 44, 390–395 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0010-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0010-5