Abstract
Background
In rural areas of southern China, where hepatitis E is endemic, residents generally rear pigs in pigsties near their houses. The study was conducted to assess the possibility that hepatitis E virus (HEV) infections in this region are acquired primarily through contact with swine.
Methods
One hundred twenty swine fecal samples collected from pigsties located in eight rural communities of southern China were tested for HEV RNA. The swine HEV isolates were analyzed genetically and were experimentally inoculated into rhesus monkeys to determine the potential risk of cross-species infection.
Results
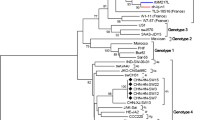
Twenty-nine of the 120 swine fecal samples were positive for HEV RNA. The nucleotide sequences of these swine HEV strains shared 85%–99% identities with the local human genotype 4 isolates and belonged to two subgroups of genotype 4. Importantly, swine HEV strains representing both subgroups induced hepatitis in rhesus monkeys by inoculation with the virus, evidenced by elevated serum alanine transaminase (ALT), viremia, fecal viral shedding, anti-HEV seroconversion, and liver histopathological changes.
Conclusions
Swine may be the principal reservoir for human HEV infection in rural southern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emerson SU, Purcell RH. Hepatitis E virus. Rev Med Virol 2003;13:145–154.
Wang L, Zhuang H. Hepatitis E: An overview and recent advances in vaccine research. World J Gastroenterol 2004;10:2157–2162.
Benowal M, Kumar A, Kar P, Jilani N, Sharma JB. Prevalence and severity of acute viral hepatitis and fulminant hepatitis during pregnancy: a prospective study from north India. Indian J Med Microbiol 2003;21:184–185.
Hussaini SH, Skidmore SJ, Richardson P, Sherratt LM, Cooper BT, O’Grady JG. Severe hepatitis E infection during pregnancy. J Viral Hepatitis 1997;4:51–54.
Lu L, Li CH, Hagedorn CH. Phylogenetic analysis of global hepatitis E virus sequences: genetic diversity, subtypes and zoonosis. Rev Med Virol 2006;16:5–36.
Schlauder GG, Mushahwar IK. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis E virus. J Med Virol 2001;65:282–292.
Meng XJ, Purcell RH, Halbur PG, Lehman JR, Webb DM, Tsareva TS, et al. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:9860–9865.
Hsieh SY, Meng XJ, Wu YH, Liu ST, Tam AW, Lin DY, et al. Identity of a novel swine hepatitis E virus in Taiwan forming a monophyletic group with Taiwan isolates of human hepatitis E virus. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:3828–3834.
Saad MD, Hussein HA, Bashandy MM, Kamel HH, Earhart KC, Fryauff DJ, et al. Hepatitis E virus infection in work horses in Egypt. Infect Genet Evol 2007;7:368–373.
Huang FF, Haqshenas G, Guenette DK, Halbur PG, Schommer SK, Pierson FW, et al. Detection by reverse transcription-PCR and genetic characterization of field isolates of swine hepatitis E virus from pigs in different geographic regions of the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:1326–1332.
Choi IS, Kwon HJ, Shin NR, Yoo HS. Identification of swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) and prevalence of anti-HEV antibodies in swine and human populations in Korea. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:3602–3608.
Zheng YJ, Ge SX, Zhang J, Guo QS, Ng MH, Wang FD, et al. Swine as a principal reservoir of hepatitis E virus that infects humans in eastern China. J Infect Dis 2006;193:1643–1649.
Yazaki Y, Mizuo H, Takahashi M, Nishizawa T, Sasaki N, Gotanda Y, et al. Sporadic acute or fulminant hepatitis E in Hokkaido, Japan, may be food-borne, as suggested by the presence of hepatitis E virus in pig liver as food. J Gen Virol 2003;84:2351–2357.
Banks M, Bendall R, Grierson S, Heath G, Mitchell J, Dalton H. Human and porcine hepatitis E virus strains, United Kingdom. Emerg Infect Dis 2004;10:953–955.
van der Poel WH, Verschoor F, van der Heide R, Herrera MI, Vivo A, Kooreman M, et al. Hepatitis E virus sequences in swine related to sequences in humans, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis 2001;7:970–976.
Meng XJ, Halbur PG, Shapiro MS, Govindarajan S, Bruna JD, Mushahwar IK, et al. Genetic and experimental evidence for cross-species infection by swine hepatitis E virus. J Virol 1998;72:9714–9721.
Arankalle VA, Chobe LP, Chadha MS. Type-IV Indian swine HEV infects rhesus monkeys. J Viral Hepatol 2006;13:742–745.
Wang YC, Zhang HY, Li Z, Gu WJ, Lan HY, Hao W, et al. Detection of sporadic cases of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in China using immunoassays based on recombinant open reading frame 2 and 3 polypeptides from HEV genotype 4. J Clin Microbiol 2001;39:4370–4379.
Li K, Zhuang H, Zhu WF. Partial nucleotide sequencing of hepatitis E viruses detected in sera of patients with hepatitis E from 14 cities in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 2002;115:1058–1063.
Zhuang H, Cao XY, Liu CB, Wang GM. Epidemiology of hepatitis E in China. Gastroenterol Jpn 1991;26:135–138.
Wang YC, Zhang HY, Xia NS, Peng G, Lan HY, Zhuang H, et al. Prevalence, isolation, and partial sequence analysis of hepatitis E virus from domestic animals in China. J Med Virol 2002;67:516–521.
Ning HQ, Niu ZX, Yu RS, Zhang PH, Dong SJ, Li Z. Identification of genotype 3 hepatitis E virus in fecal samples from a pig farm located in a Shanghai suburb. Vet Microbiol 2007;121:125–130.
Li RC, Ge SX, Li YP, Zheng YJ, Nong Y, Guo QS, et al. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus infection, rural southern People’s Republic of China. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:1682–1688.
Ge SX, Guo QS, Li SW, Zhang J, Xia NS. Design and preliminary application of a set of highly sensitive universal RT-PCR primers for detection genotype I/IV hepatitis E virus. Bing Du Xue Bao 2005;21:181–187.
Zhang J, Ge SX, Huang GY, Li SW, He ZQ, Wang YB, et al. Evaluation of antibody-based and nucleic acid-based assays for diagnosis of hepatitis E virus infection in a rhesus monkey model. J Med Virol 2003;71:518–526.
Erker JC, Desai SM, Schlauder GG, Dawson GJ, Mushahwar IK. A hepatitis E virus variant from the United States: molecular characterization and transmission in Cynomolgus macaques. J Gen Virol 1999;80:681–690.
Meng XJ, Halbur PG, Haynes JS, Tsareva TS, Bruna JD, Royer RL, et al. Experimental infection of pigs with the newly identified swine hepatitis E virus (swine HEV), but not with human strains of HEV. Arch Virol 1998;143:1405–1415.
Meng XJ, Wiseman B, Elvinger F, Guenette DK, Toth TE, Engle RE, et al. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis E virus in veterinarians working with swine and in normal blood donors in the United States and other countries. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:117–122.
Olsen B, Axelsson-Olsson D, Thelin A, Weiland O. Unexpected high prevalence of IgG-antibodies to hepatitis E virus in Swedish pig farmers and controls. Scand J Infect Dis 2006;38:55–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Y., Zhu, Y., Liang, J. et al. Swine hepatitis E virus in rural southern China: genetic characterization and experimental infection in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J Gastroenterol 43, 565–570 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2196-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2196-3