Abstract
Background
Erythropoietin (Epo) is the central regulator of red blood cell production and can stimulate proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells. Now, recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEpo) is widely used in patients with renal disease, chronic anemia, and iron deficiency of early childhood. It has been reported that the enhanced erythropoiesis associated with erythropoietin therapy increases intestinal iron absorption, but the molecular mechanisms underlying are unknown. Therefore, we have investigated the effect of rHuEpo on duodenal iron transport protein synthesis in rats.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250 g were randomly divided into two groups: (1) rHuEpo injection group (rHuEpo, 500 IU/day, s.c.), and (2) control group (injection of the same volume of saline). After 3 days injection, blood parameters, serum iron status, and non-heme iron concentrations in the liver and duodenum were examined at the fifth day. The mRNA levels and protein synthesis of duodenal divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), ferroportin 1 (FPN1), and hephaestin (Hp) were measured by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot analysis. Hepatic hepcidin mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR.
Results
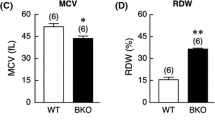
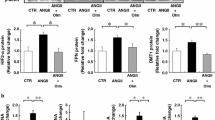
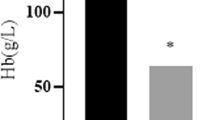
rHuEpo injection significantly stimulated erythropoiesis and decreased serum iron status, non-heme iron concentrations in the liver and duodenum. DMT1 (+IRE) and Hp expression in duodenum were increased significantly. However, DMT1 (−IRE) and FPN1 expression had no apparent change. Hepatic hepcidin mRNA expression was decreased dramatically, reaching an almost undetectable level in rHuEpo-treated rats.
Conclusions
rHuEpo administration improved the duodenal iron absorption by increasing the expression of DMT1 (+IRE) and Hp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krantz SB. Erythropoietin. Blood 1991;77(3):419–434.
Skikne BS, Cook JD. Effect of enhanced erythropoiesis on iron absorption. J Lab Clin Med 1992;120(5):746–751.
Gunshin H, Mackenzie B, Berger UV, Gunshin Y, Romero MF, Boron WF, et al. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature (Lond) 1997;388(6641):482–488.
Tandy S, Williams M, Leggett A, Lopez-Jimenez M, Dedes M, Ramesh B, et al. Nramp2 expression is associated with pH-dependent iron uptake across the apical membrane of human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J Biol Chem 2000;275(2):1023–1029.
Lee PL, Gelbart T, West C, Halloran C, Beutler E. The human Nramp2 gene: characterization of the gene structure, alternative splicing, promoter region and polymorphisms. Blood Cells Mol Dis 1998;24(2):199–215.
Lam-Yuk-Tseung S, Gros P. Distinct targeting and recycling properties of two isoforms of the iron transporter DMT1 (NRAMP2, Slc11A2). Biochemistry 2006;45(7):2294–2301.
Martini LA, Tchack L, Wood RJ. Iron treatment downregulates DMT1 and IREG1 mRNA expression in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 2002;132(4):693–696.
Canonne-Hergaux F, Gruenheid S, Ponka P, Gros P. Cellular and subcellular localization of the Nramp2 iron transporter in the intestinal brush border and regulation by dietary iron. Blood 1999;93(12):4406–4417.
Zoller H, Koch RO, Theurl I, Obrist P, Pietrangelo A, Montosi G, et al. Expression of the duodenal iron transporters divalentmetal transporter 1 and ferroportin 1 in iron deficiency and iron overload. Gastroenterology 2001;120(6):1412–1419.
Yeh KY, Yeh M, Watkins JA, Rodriguez-Paris J, Glass J. Dietary iron induces rapid changes in rat intestinal divalent metal transporter expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;279:G1070–G1079.
Donovan A, Brownlie A, Zhou Y, Shepard J, Pratt SJ, Moynihan J, et al. Positional cloning of zebrafish ferroportin1 identifies a conserved vertebrate iron exporter. Nature (Lond) 2000;403(6771):776–781.
McKie AT, Marciani P, Rolfs A, Brennan K, Wehr K, Barrow D, et al. A novel duodenal iron-regulated transporter, IREG1, implicated in the basolateral transfer of iron to the circulation. Mol Cell 2000;5(2):299–309.
Vulpe CD, Kuo YM, Murphy TL, Cowley L, Askwith C, Libina N, et al. Hephaestin, a ceruloplasmin homologue implicated in intestinal iron transport, is defective in the sla mouse. Nat Genet 1999;21(2):195–199.
Abboud S, Haile DJ. A novel mammalian iron-regulated protein involved in intracellular iron metabolism. J Biol Chem 2000;275(26):19906–19912.
Petrak J, Vyoral D. Hephaestin: a ferroxidase of cellular iron export. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005;37(6):1173–1178.
Sakakibara S, Aoyama Y. Dietary iron-deficiency up-regulates hephaestin mRNA level in small intestine of rats. Life Sci 2002;70(26):3123–3129.
Sun XF, Zhou DB, Zhao YQ. An iron regulator hepcidin is affected by EPO. J Exp Hematol 2006;14(4):778–772.
Nicolas G, Viatte L, Bennoun M, Beaumont C, Kahn A, Vaulont S. Hepcidin, a new iron regulatory peptide. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2002;29(3):327–335.
Viatte L, Lesbordes-Brion JC, Lou DQ, Bennoun M, Nicolas G, Kahn A, et al. Deregulation of proteins involved in iron metabolism in hepcidin-deficient mice. Blood 2005;105(12):4861–4864.
Anderson GJ, Frazer DM, Wilkins SJ, Becker EM, Millard KN, Murphy TL, et al. Relationship between intestinal iron-transporter expression, hepatic hepcidin levels and the control of iron absorption. Biochem Soc Trans 2002;30(4):724–726.
Frazer DM, Inglis HR, Wilkins SJ, Millard KN, Steele TM, McLaren GD, et al. Delayed hepcidin response explains the lag period in iron absorption following a stimulus to increase erythropoiesis. Gut 2004;53(10):1509–1515.
Ke Y, Chang YZ, Duan XL, Du JR, Zhu L, Wang K, et al. Age-dependent and iron-independent expression of two mRNA isoforms of divalent metal transporter 1 in rat brain. Neurobiol Aging 2005;26(5):739–748.
Liu YQ, Duan XL, Chang YZ, Wang HT, Qian ZM. Molecular analysis of increased iron status in moderately exercised rats. Mol Cell Biochem 2006;282(1–2):117–123.
Ke Y, Chen YY, Chang YZ, Duan XL, Ho KP, Jiang de H, et al. Post-transcriptional expression of DMT1 in the heart of rat. J Cell Physiol 2003;196(1):124–130.
Qian ZM, Xiao DS, Tang PL, Yao FYD, Liao QK. The increased expression of transferrin receptor on the membrane of erythroblast in strenuous exercised rats. J Appl Physiol 1999;87:523–529.
Qian ZM, Xiao DS, Ke Y, Liao QK. Increased nitric oxide is one of the causes of changes of iron metabolism in strenuously exercised rats. Am J Physiol 2001;280:R739–R743.
Chang YZ, Qian ZM, Wang K, Zhu L, Yang XD, Du JR, et al. Effects of development and iron status on ceruloplasmin expression in rat brain. J Cell Physiol 2005;204(2):623–631.
Weiss G, Houston T, Kastner S, Johrer K, Grunewald K, Brock JH. Regulation of cellular iron metabolism by erythropoietin: activation of iron-regulatory protein and upregulation of transferrin receptor expression in erythroid cells. Blood 1997;89(2):680–687.
Frazer DM, Anderson GJ. The orchestration of body iron intake: how and where do enterocytes receive their cues? Blood Cells Mol Dis 2003;30:288–297.
Pantopoulos K. Iron metabolism and the IRE/IRP regulatory system: an update. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004;1012:1–13.
Zoller H, Theurl I, Koch R, Kaser A, Weiss G. Mechanisms of iron mediated regulation of the duodenal iron transporters divalent metal transporter 1 and ferroportin 1. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2002;29(3):488–497.
Trinder D, Oates PS, Thomas C, Sadleir J, Morgan EH. Localisation of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) to the microvillus membrane of rat duodenal enterocytes in iron deficiency, but to hepatocytes in iron overload. Gut 2000;46(2):270–276.
Wardrop SL, Richardson DR. Interferon-gamma and lipopolysaccharide regulate the expression of Nramp2 and increase the uptake of iron from low relative molecular mass complexes by macrophages. Eur J Biochem 2000;267(22):6586–6593.
Yamaji S, Sharp P, Ramesh B, Srai SK. Inhibition of iron transport across human intestinal epithelial cells by hepcidin. Blood 2004;104(7):2178–2180.
Mena NP, Esparza AL, Nunez MT. Regulation of transepithelial transport of iron by hepcidin. Biol Res 2006;39(1):191–193.
Chen H, Su T, Attieh ZK, Fox TC, McKie AT, Anderson GJ, et al. Systemic regulation of Hephaestin and Ireg1 revealed in studies of genetic and nutritional iron deficiency. Blood 2003;102(5):1893–1899.
Frazer DM, Wilkins SJ, Becker EM, Murphy TL, Vulpe CD, McKie AT, et al. A rapid decrease in the expression of DMT1 and Dcytb but not Ireg1 or hephaestin explains the mucosal block phenomenon of iron absorption. Gut 2003;52(3):340–346.
Hinoi T, Gesina G, Akyol A, Kuick R, Hanash S, Giordano TJ, et al. CDX2-regulated expression of iron transport protein hephaestin in intestinal and colonic epithelium. Gastroenterology 2005;128(4):946–961.
Delaby C, Pilard N, Goncalves AS, Beaumont C, Canonne-Hergaux F. Presence of the iron exporter ferroportin at the plasma membrane of macrophages is enhanced by iron loading and down-regulated by hepcidin. Blood 2005;106(12):3979–3984.
Nemeth E, Tuttle MS, Powelson J, Vaughn MB, Donovan A, Ward DM, et al. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004;306(5704):2090–2093.
Yeh KY, Yeh M, Glass J. Hepcidin regulation of ferroportin 1 expression in the liver and intestine of the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2004;286(3):G385–G394.
Canonne-Hergaux F, Donovan A, Delaby C, Wang HJ, Gros P. Comparative studies of duodenal and macrophage ferroportin proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006;290(1):G156–G163.
Frazer DM, Anderson GJ. The orchestration of body iron intake: how and where do enterocytes receive their cues? Blood Cells Mol Dis 2003;30:288–297.
Vokurka M, Krijt J, Sulc K, Necas E. Hepcidin mRNA levels in mouse liver respond to inhibition of erythropoiesis. Physiol Res 2006;55(6):667–674.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, WN., Chang, YZ., Wang, SM. et al. Effect of erythropoietin on hepcidin, DMT1 with IRE, and hephaestin gene expression in duodenum of rats. J Gastroenterol 43, 136–143 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-007-2138-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-007-2138-5