Abstract
Background
This study was carried out to clarify the etiology and clinicopathological features of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) arising in patients without chronic viral infection or alcohol abuse.
Methods
HCC patients who underwent resection were divided into three groups: a non-B non-C (NBNC) group (n = 13), who were seronegative for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBs Ag) and anti-hepatitis C antibody (HCV Ab), excluding a history of alcohol abuse; a B group (n = 25), who were seropositive for HBs Ag only; and a C group (n = 116), who were seropositive for HCV Ab only. We analyzed the features of tumor- and host-related factors and the outcome of the NBNC group.
Results
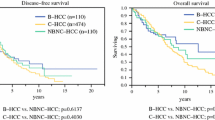
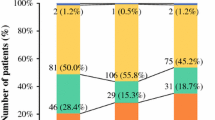
Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis were less severe in the NBNC group than in the other groups. There were no significant differences in tumor-related factors, except for higher serum levels of α-fetoprotein in the NBNC group. Recurrence rates and disease-free survivals were comparable among the three groups. The NBNC group comprised a greater population with one or two recurrent hepatic lesions (P < 0.05), and indocyanine green retention rates and fibrosis scores were preserved after the initial hepatectomy. The NBNC group had higher resection rates for intrahepatic recurrences (75.0%) than the other groups (21.1% and 22.2% in groups B and C, respectively; P < 0.05 and P < 0.05). The survival rate after the initial hepatectomy or detection of the recurrent lesions was significantly better in the NBNC group (both 100% at 5 years) than those in groups B and C (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
NBNC patients maintained good liver function following the initial hepatectomy, and tended to have one or two recurrent lesions. These biological advantages provided NBNC patients more opportunities for repeat resection of intrahepatic recurrences, which may lead to a favorable outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoi, Y., Suzuki, S., Baba, S. et al. Clinicopathological features of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) arising in patients without chronic viral infection or alcohol abuse: a retrospective study of patients undergoing hepatic resection. J Gastroenterol 40, 274–282 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-004-1536-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-004-1536-1