Abstract
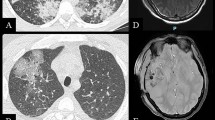
Previously we reported combined chemo-immunotherapy, using interferon (IFN)-α and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and this regimen improved the prognosis. Recently, we experienced an HCC patient who died of severe interstitial pneumonia during the combined IFN-α and 5-FU therapy. This is the first report of the occurrence of interstitial pneumonia during combined IFN-α and 5-FU treatment. A 60-year-old-man was admitted to Osaka University Hospital to receive systemic chemo-immunotherapy for recurrent HCC. In the second week of the chemo-immunotherapy, he showed a decreased level of consciousness, and respiratory insufficiency. Emergency roentgenogram revealed diffuse infiltration in both lungs. Respiratory dysfunction due to interstitial pneumonia was suspected, and steroid pulse therapy was started. However, the patient showed respiratory failure, and he died 32 days after the start of the therapy. Autopsy findings showed atelectasis in the bilateral lungs, which showed elastic hard solidity and a dark red color; esophageal varices were also shown, and there was cirrhosis with a large tumor in the liver. Microscopically, the alveolar wall showed marked fibrous thickness and moderate inflammatory change, which is consistent with acute interstitial pneumonia, and the acute pulmonary change was suspected to have been the cause of death. The association of IFN with the development of interstitial pneumonia has been reported. However, the prognosis of IFN-induced interstitial pneumonia has mostly been favorable when the medication was discontinued. It has been postulated that interstitial pneumonia induced by the combination of IFN and 5-FU may be therapy-resistant. The combination of IFN-α and 5-FU is a useful therapy for patients with advanced HCC, such as that with portal vein invasion or multiple metastatic foci. Thus, interstitial pneumonia in these patients should be carefully managed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, S., Tomita, Y., Hoshida, Y. et al. Interstitial pneumonia induced by combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-α therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 39, 793–797 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-004-1375-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-004-1375-0