Abstract
Background
The effects of ablation with various settings of powers and times using a newly developed radiofrequency (RF) ablation device, the Habib™ EndoHPB catheter, are not well known. In the present study, we examined the effects of a novel RF ablation catheter using resected fresh pig livers and evaluated the macro- and microscopic effects of RF ablation under various conditions.
Materials and methods
The RF application was performed step by step at 5, 10, 15, and 20 W power and 60, 90, 120 s, respectively. Macroscopic and microscopic findings of the ablation area were evaluated at each setting.
Results
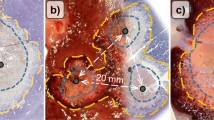
The mean lengths of the short axis of the ablation area at 10 W and 60, 90 and 120 s were 8.0 ± 1.0, 8.3 ± 1.2, and 9.7 ± 0.6 mm, respectively. The mean lengths of the long axis at 10 W power and 60, 90 and 120 s were 20.3 ± 0.6, 21.3 ± 1.6, and 28.3 ± 2.1 mm, respectively. Although the lengths of the short and long axes at 5 and 10 W increased gradually with power, there were no obvious differences in either short or long axis lengths between 15 and 20 W. Of all the settings, only at 5 W and 60 and 90 s did the long axis of the ablation show separate areas around the 2 ring electrodes.
Conclusions
Although other sequelae including hemorrhage, pancreatitis, acute inflammatory changes, perforation and late fibrosis could not be investigated in our ex-vivo pig model, our study clarified the relationship between ablation powers and times and the effects concerning depth and longitudinal spread of ablation. Although the clinical ablation setting at 7–10 W power and 2 min is suitable, ultimately the ablation power and time should be adjusted according to the size of masses using examples from the present results.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SEMS:
-
Self-expandable metallic stent
- RF:
-
Radiofrequency
References
Lai EC, Mok FP, Tan ES, Lo CM, Fan ST, You KT, et al. Endoscopic biliary drainage for severe acute cholangitis. N Engl J Med. 1992;24:1582–6.
Smith AC, Dowsett JF, Russell RC, Hatfield AR, Cotton PB. Randomised trial of endoscopic stenting versus surgical bypass in malignant low bile duct obstruction. Lancet. 1994;344:1655–60.
Fogel EL, Sherman S, Devereaux BM, Lehman GA. Therapeutic biliary endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2001;33:31–8. (review).
Arguedas MR, Heudebert GH, Stinnett AA, Wilcox CM. Biliary stents in malignant obstructive jaundice due to pancreatic carcinoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:898–904.
Isayama H, Komatsu Y, Tsujino T, Ito Y, Tada M, Minagawa N, et al. A prospective randomised study of “covered” versus “uncovered” diamond stents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gut. 2004;53:729–34.
Moss AC, Morris E, Leyden J, MacMathuna P. Malignant distal biliary obstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic and surgical bypass results. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33:213–21.
Kahaleh M, Brock A, Conaway MR, Shami VM, Dumonceau JM, Northup PG, et al. Covered self-expandable metal stents in pancreatic malignancy regardless of resectability: a new concept validated by a decision analysis. Endoscopy. 2007;39:319–24.
Kaassis M, Boyer J, Dumas R, Ponchon T, Coumaros D, Delcenserie R, et al. Plastic or metal stents for malignant stricture of the common bile duct? Results of a randomized prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:178–82.
Bueno JT, Gerdes H, Kurtz RC. Endoscopic management of occluded biliary Wallstents: a cancer center experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:879–84.
Rogart JN, Boghos A, Rossi F, Al-Hashem H, Siddiqui UD, Jamidar P, et al. Analysis of endoscopic management of occluded metal biliary stents at a single tertiary care center. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:676–82.
Ridtitid W, Rerknimitr R, Janchai A, Kongkam P, Treeprasertsuk S, Kullavanijaya P. Outcome of second interventions for occluded metallic stents in patients with malignant biliary obstruction. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:2216–20.
Steel AW, Postgate AJ, Khorsandi S, Nicholls J, Jiao L, Viavianos P, et al. Endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation appears to be safe in the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:149–53.
Khorsandi S. In vivo experiments for the development of a novel bipolar radiofrequency probe (EndoHPB) for the palliation of malignant biliary obstruction. EASL Monothematic Conference. Liver Cancer: from molecular pathogenesis to new therapies (P97). 2008
Zacharoulis D, Khorsandi SE, Vavra P, Dostalik J, Navarra G, Nicholls JP, et al. Pilot study for a new bipolar radiofrequency ablation/aspirator device in the management of primary and secondary liver cancers. Liver Int. 2009;29:824–30.
Conflict of interest
The following author disclosed financial relationships relevant to this publication: Dr. Habib: stockholder and board member of EMcision Ltd UK. The other authors disclose no financial relationship relevant to this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Itoi, T., Isayama, H., Sofuni, A. et al. Evaluation of effects of a novel endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation biliary catheter using an ex-vivo pig liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 19, 543–547 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-011-0465-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-011-0465-7