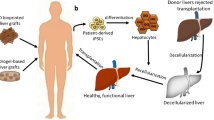
Abstract
In recent years there has been a particular focus on research regarding tissue engineering targeting the liver, especially in terms of what types of cells and extracellular matrices should be organized and in what type of environments to create an artificial liver, i.e., a life-saving organ. The ideal is to use healthy human liver cells as a source of cells for such research, but there is an extreme shortage of human-donor livers that can be used for cell isolation. Therefore, we are presently working on the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into liver cells as well as reversibly immortalized human liver cell lines that can be cultured in large quantities and at low cost. We are also working on the development of a bioartificial liver (BAL) using such cells as a source. Herein, we introduce our findings on the current status of BAL development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langer R, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260:920–6.
Vacanti JP, Vacanti CA. The history and scope of tissue engineering. In: Lanza RP, Langer R, Vacanti J, editors. Principles of tissue engineering. San Diego: Academic Press; 2000. p. 3–7.
Kobayashi N, Fujiwara T, Westerman KA, Inoue Y, Sakaguchi M, Noguchi H, et al. Prevention of acute liver failure in rats with reversibly immortalized human hepatocytes. Science. 2000;287:1258–62.
Okitsu T, Kobayashi N, Jun HS, Shin S, Kim SJ, Han J, et al. Transplantation of reversibly immortalized insulin-secreting human hepatocytes controls diabetes in pancreatectomized pigs. Diabetes. 2004;53:105–12.
Totsugawa T, Yong C, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, Noguchi H, et al. Survival of liver failure pigs by transplantation of reversibly immortalized human hepatocytes with tamoxifen-mediated self-recombination. J Hepatol. 2007;47:74–82.
Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Chen Y, Yamatsuji T, Tanaka N, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to hepatocytes using deleted variant of HGF and poly-amino-urethane-coated nonwoven polytetrafluoroethylene fabric. Cell Transplant. 2006;15:335–41.
Chen Y, Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Yamatsuji T, Shirakawa Y, et al. Instant hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells using activin A and a deleted variant of HGF. Cell Transplant. 2006;15:865–71.
Soto-Gutierrez A, Kobayashi N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Navarro-Alvarez N, Zhao D, Okitsu T, et al. Reversal of mouse hepatic failure using an implanted liver-assist device containing ES cell-derived hepatocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1412–9.
Navarro-Alvarez N, Soto-Gutierrez A, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Fox IJ, Tanaka N, Kobayashi N. Stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2006;11:659–664.
Watanabe T, Shibata N, Westerman KA, Okitsu T, Allain JE, Sakaguchi M, et al. Establishment of immortalized human hepatic stellate scavenger cells to develop bioartificial livers. Transplantation. 2003;75:1873–80.
Noguchi H, Kobayashi N, Westerman KA, Sakaguchi M, Okitsu T, Totsugawa T, et al. Controlled expansion of human endothelial cell populations by Cre/loxP-based reversible immortalization. Hum Gene Ther. 2002;13:321–34.
Maruyama M, Kobayashi N, Westerman KA, Sakaguchi M, Allain JE, Totsugawa T, et al. Establishment of a highly differentiated immortalized human cholangiocyte cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation. 2004;77:446–51.
Matsumura T, Takesue M, Westerman KA, Okitsu T, Sakaguchi M, Fukazawa T, et al. Establishment of an immortalized human-liver endothelial cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation. 2004;77:1357–65.
Sternberg N, Hamilton D. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. I. Recombination between loxP sites. J Mol Biol. 1981;150:467–86.
Narushima M, Kobayashi N, Okitsu T, Tanaka Y, Li SA, Chen Y. A human beta-cell line for transplantation therapy to control type 1 diabetes. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1274–82.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–7.
Rambhatla L, Chiu CP, Kundu P, Peng Y, Carpenter MK. Generation of hepatocyte-like cells from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2003;12:1–11.
Xu C, Inokuma MS, Denham J, Golds K, Kundu P, Gold JD, et al. Feeder-free growth of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:971–4.
Tanaka K, Kobayashi N, Soto-Gutierrez A, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Navarro-Alvarez N, Chen Y, et al. Prolonged survival of mice with acute liver failure with transplantation of monkey hepatocytes cultured with an antiapoptotic pentapeptide V5. Transplantation. 2006;81:427–37.
Ikeda H, Kobayashi N, Tanaka Y, Nakaji S, Yong C, Okitsu T, et al. A newly developed bioartificial pancreas successfully controls blood glucose in totally pancreatectomized diabetic pigs. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:1799–809.
Soto-Gutierrez A, Navarro-Alvarez N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, Tanaka K, Chen Y, Misawa H, et al. Construction and transplantation of an engineered hepatic tissue using a polyaminourethane-coated nonwoven polytetrafluoroethylene fabric. Transplantation. 2007;83:129–137.
Kobayashi N, Okitsu T, Nakaji S, Tanaka N. Hybrid bioartificial liver: establishing a reversibly immortalized human hepatocyte line and developing a bioartificial liver for practical use. J Artif Organs. 2003;6:236–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, N. Life support of artificial liver: development of a bioartificial liver to treat liver failure. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16, 113–117 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-008-0022-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-008-0022-1