Abstract
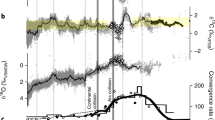
The sulfur isotopic composition of stratigraphically well constrained samples from five evaporitic cycles of the German Zechstein (upper Permian) displays no systematic lateral variation and no significant temporal trend. With an average δ34S value close to 11‰, results confirm the previously determined sulfur isotope minimum for Phanerozoic seawater. Least radiogenic 87Sr/86Sr ratios for these sulfates define a clear temporal variation with a minimum value at 0.707008. A conclusive assessment of this temporal trend in comparison with other data sets for upper Permian seawater is not possible due to substantial differences in (bio)stratigraphic assignments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 January 1998 / Accepted: 11 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kampschulte, A., Buhl, D. & Strauss, H. The sulfur and strontium isotopic compositions of Permian evaporites from the Zechstein basin, northern Germany. Geol Rundsch 87, 192–199 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005310050201
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005310050201