Abstract
Although syntectonic sedimentation has been shown to be one of the most important factors involved in thrust belt deformation, previous studies have mostly focused on the influence of just one stage in this context. Two geometric sediment packages that are described as progradation and aggradation are known to lead to different thrust belt deformation subsequences, yet the influence of multistage sedimentary strata remains less well-understood. Interpretation of the latest seismic data shows that the Western Kunlun thrust belt is characterized by classical triangle zone. There are two adjacent sections with different geometrical characteristics, a prograding monocline and a spaced-ramp anticline. We restored these two sections and analyzed the potential geological factors leading to their formation in this study. The results of this analysis provide new insights into a kinematic model for triangle zones and suggest that these two distinct styles formed because of two-stage syntectonic sedimentation. We further discuss the kinematic model of tectonic deformation given the presence of two-stage syntectonic sediments and propose four distinct sedimentary superposition patterns. All of these sequences suggest that deformation is controlled by total syntectonic sediment geometry and imply that early sediment shape exerts the greatest influence. The presence of early prograding sediment promotes the development of the spaced thrust belt, while an early aggrading package enhances the structure of the restricted thrust adjacent to the hinterland.



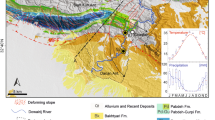
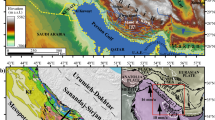
(modified after Wang et al. 2013)







(modified after Duerto and McClay 2009)

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PA (2008) Time scales of tectonic landscapes and their sediment routing systems. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 296:7–28. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP296.2
Bigi S, Di Paolo L, Vadacca L, Gambardella G (2010) Load and unload as interference factors on cyclical behavior and kinematics of Coulomb wedges: insights from sandbox experiments. J Struct Geol 32:28–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2009.06.018
Bonini M (2007) Deformation patterns and structural vergence in brittle–ductile thrust wedges: an additional analogue modelling perspective. J Struct Geol 29:141–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2006.06.012
Calassou S, Larroque C, Malavieille J (1993) Transfer zones of deformation in thrust wedges: an experimental study. Tectonophysics 221:325–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(93)90165-G
Cheng XG, Chen HL, Lin XB, Wu L, Gong JF (2017) Geometry and kinematic evolution of the Hotan-Tiklik segment of the western Kunlun thrust belt: constrained by structural analyses and apatite fission track thermochronology. J Geol 125:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1086/689187
Cooper M (1996) Passive-roof duplexes and pseudo-passive-roof duplexes at mountain fronts: a review. Bull Can Pet Geol 44:410–421
Couzens-Schultz BA, Vendeville BC, Wiltschko DV (2003) Duplex style and triangle zone formation: insights from physical modeling. J Struct Geol 25:1623–1644. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00004-X
Cowgill E (2010) Cenozoic right-slip faulting along the eastern margin of the Pamir salient, northwestern China. Geol Soc Am Bull 122:145–161. https://doi.org/10.1130/B26520.1
Cowgill E, Yin A, Harrison TM, Wang XF (2003) Reconstruction of the Altyn Tagh fault based on U–Pb geochronology: role of back thrusts, mantle sutures, and heterogeneous crustal strength in forming the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 108:2346. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002080
Dickinson WR, Suczek CA (1979) Plate tectonics and sandstone compositions. AAPG Bull 63:2164–2182
Dooley TP, Jackson M, Hudec MR (2007) Initiation and growth of salt-based thrust belts on passive margins: results from physical models. Basin Res 19:165–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.2007.00317.x
Du ZL, Luo JC, Wang BQ, Wei W (2009) The difference of tectonic features in the adjacent area of Kekeya and its causing analysis. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 33:112–116. https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2009.01.016 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Duerto L, McClay K (2009) The role of syntectonic sedimentation in the evolution of doubly vergent thrust wedges and foreland folds. Mar Pet Geol 26:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.07.004
Erickson SG (1995) Mechanics of triangle zones and passive-roof duplexes: implications of finite-element models. Tectonophysics 245:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(94)00251-4
Fan XG, Cheng XG, Chen HL, Wang C, Wang CY (2015) Basin-range coupling structure and deformation features of the eastern Cenozoic foreland basin in SW Tarim. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 39:241–249. https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2015.02.004 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fillon C, Huismans RS, Beek P, Muñoz JA (2013) Syntectonic sedimentation controls on the evolution of the southern Pyrenean fold-and-thrust belt: inferences from coupled tectonic-surface processes models. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 118:5665–5680. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50368
Ford M (2004) Depositional wedge tops: interaction between low basal friction external orogenic wedges and flexural foreland basins. Basin Res 16:361–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.2004.00236.x
Gawthorpe R, Hardy S (2002) Extensional fault-propagation folding and base-level change as controls on growth-strata geometries. Sediment Geol 146:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00165-8
Ghiglione MC, Cristallini EO (2007) Have the southernmost Andes been curved since Late Cretaceous time? An analog test for the Patagonian Orocline. Geology 35:13–16. https://doi.org/10.1130/G22770A.1
Grando G, McClay K (2004) Structural evolution of the Frampton growth fold system, Atwater Valley-Southern Green Canyon area, deep water Gulf of Mexico. Mar Pet Geol 21:889–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.12.005
Graveleau F, Malavieille J, Dominguez S (2012) Experimental modelling of orogenic wedges: a review. Tectonophysics 538:1–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.027
Hagke CV, Malz A (2018) Triangle zones—geometry, kinematics, mechanics, and the need for appreciation of uncertainties. Earth Sci Rev 177:24–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.11.003
Hu JZ, Tan YJ, Zhang P, Zhang YQ (2008) Structural features of Cenozoic thrust-fault belts in the piedmont of southwestern Tarim basin. Earth Sci Front 15:222–231. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.02.025 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang GM, Li ZH, Zhou YZ (2017) The different origins between passive-roof duplex in the Fusha area and Piggyback basin in the Wupoer area in southwestern Tarim basin based on numerical modelling study. Acta Geol Sin 91:1674–1693. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.002 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang Z, Huang S, Du H, Li Y, Wang B, Cao Y, Zhang Y (2015) The characteristics of the neotectonic movement and their effects on the formation of gas reservoirs in the marginal depressions of Tarim basin, NW China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 22:503–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.12.028
Jones PB (1996) Triangle zone geometry, terminology and kinematics. Bull Can Pet Geol 44:139–152
Leeder MR (2011) Tectonic sedimentology: sediment systems deciphering global to local tectonics. Sedimentology 58:2–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.2010.01207.x
Li HB, Yang JS, Xu ZQ (2006) The constraint of the Altyn Tagh fault system to the growth and rise of the northern Tibetan plateau. Earth Sci Front 13:59. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.006 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li YJ et al (2016) The Kuqa late Cenozoic fold–thrust belt on the southern flank of the Tian Shan Mountains. Int J Earth Sci 105:1417–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-015-1262-3
Liang H (2013) Structural characteristic and deformation mechanism of Cenozoic fold and thrust belt in eastern section of piedmont of west Kunlun. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou (in Chinese with English abstract)
Martinez A, Malavieille J, Lallemand S, Collot J-Y (2002) Strain partitioning in an accretionary wedge, in oblique convergence: analogue modelling. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France 173:17–24. https://doi.org/10.2113/173.1.17
McClay K, Whitehouse P, Dooley T, Richards M (2004) 3D evolution of fold and thrust belts formed by oblique convergence. Mar Pet Geol 21:857–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.03.009
Mount VS, Martindale KW, Griffith TW, Byrd JO (2011) Basement-involved contractional wedge structural styles: examples from the Hanna basin, Wyoming. In: McClay K, Shaw JH, Suppe J (eds) Thrust fault-related folding: AAPG memoir 94, The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, USA, pp 271–281. https://doi.org/10.1306/13251341M941003
Pei JL, Sun ZM, Li HB, Si JL, Pan JW, Liu J, Liu XG, Zhao Y (2008) Paleocurrent direction of the Late Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of the Tibetan plateau northwestern margin constrained by AMS and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrol Sin 7:1613–1620 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Poblet J, McClay K, Storti F, Muñoz JA (1997) Geometries of syntectonic sediments associated with single-layer detachment folds. J Struct Geol 19:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(96)00113-7
Ramberg H (1981) Gravity, deformation and the earth’s crust: in theory, experiments and geological applications. Academic Press, London
Robinson AC, Yin A, Manning CE, Harrison TM, Zhang S-H, Wang X-F (2004) Tectonic evolution of the northeastern Pamir: constraints from the northern portion of the Cenozoic Kongur Shan extensional system, western China. Geol Soc Am Bull 116:953–973. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25375.1
Simpson GD (2006) Modelling interactions between fold–thrust belt deformation, foreland flexure and surface mass transport. Basin Res 18:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.2006.00287.x
Simpson GD (2010) Formation of accretionary prisms influenced by sediment subduction and supplied by sediments from adjacent continents. Geology 38:131–134. https://doi.org/10.1130/G30461.1
Sobel ER, Schoenbohm LM, Chen J, Thiede R, Stockli DF, Sudo M, Strecker MR (2011) Late Miocene–Pliocene deceleration of dextral slip between Pamir and Tarim: implications for Pamir orogenesis. Earth Planet Sci Lett 304:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.02.012
Sobel ER, Chen J, Schoenbohm LM, Thiede R, Stockli DF, Sudo M, Strecker MR (2013) Oceanic-style subduction controls late Cenozoic deformation of the Northern Pamir orogen. Earth Planet Sci Lett 363:204–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2012.12.009
Storti F, McClay K (1995) Influence of syntectonic sedimentation on thrust wedges in analogue models. Geology 23:999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023%3c0999:IOSSOT%3e2.3.CO;2
Storti F, Poblet J (1997) Growth stratal architectures associated to decollement folds and fault-propagation folds. Inferences on fold kinematics. Tectonophysics 282:353–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00230-8
Suppe J, Chou GT, Hook SC (1992) Rates of folding and faulting determined from growth strata. In: McClay KR (eds) Thrust tectonics. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3066-0_9
Teson E, Teixell A (2008) Sequence of thrusting and syntectonic sedimentation in the eastern Sub-Atlas thrust belt (Dades and Mgoun valleys, Morocco). Int J Earth Sci 97:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0151-1
Wang CY (2014) The deformation controlling factors of fold-and-thrust belt in SW Tarim Basin: physical analogue modeling study. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang CY, Chen HL, Cheng XG, Li K (2013) Evaluating the role of syn-thrusting sedimentation and interaction with frictional detachment in the structural evolution of the SW Tarim basin, NW China: insights from analogue modeling. Tectonophysics 608:642–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.08.016
Wang C, Cheng XG, Chen HL, Li K, Fan XG, Wang CY (2016) From folding to transpressional faulting: the Cenozoic Fusha structural belt in front of the Western Kunlun Orogen, northwestern Tibetan Plateau. Int J Earth Sci 105:1621–1636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1305-4
Wei HH, Meng QR, Ding L, Li ZY (2013) Tertiary evolution of the western Tarim basin, northwest China: a tectono-sedimentary response to northward indentation of the Pamir salient. Tectonics 32:558–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/tect.20046
Wu JE, McClay KR (2011) Two-dimensional analog modeling of fold and thrust belts: dynamic interactions with syncontractional sedimentation and erosion. In: McClay K, Shaw JH, Suppe J (eds) Thrust fault-related folding: AAPG memoir 94. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, USA, pp 301–333. https://doi.org/10.1306/13251343M9450
Wu XF, Liu S, Wang X, Yang SF, Gu XM (2004) Analysis on structural sections in the Cenozoic Pamir-Western Kunlun foreland fold-and thrust belt Chinese. J Geol 39:260–271. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.02.013 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiang K (2006) Transpressional structural systems and their petroleum geological significance in southwestern margin of Tarim Basin. J Palaeogeogr 8:233–240. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2006.02.009 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao WJ, Han FL, Windley BF, Yuan C, Zhou H, Li JL (2003) Multiple accretionary orogenesis and episodic growth of continents: insights from the Western Kunlun Range, central Asia. Int Geol Rev 45:303–328. https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.45.4.303
Xie HW, Wang CY, Wang ZB, Cheng XG, Du ZL, Shi J, Chen HL, Li K (2012) The effect of spatial distribution of basement detachment on deformation in a fold and thrust belt: an analogue modeling approach an example of west Kunlun fold-and-thrust belt. Geol J China Univ 18:701–710. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.04.010 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao Z, He G, Zheng X, Dong C, Cao Z, Yang S, Gu Y (2017) A geometric model of faulted detachment folding with pure shear and its application in the Tarim Basin, NW China. Front Earth Sci 11:416–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0591-2
Zapata TR, Allmendinger RW (1996) Thrust-front zone of the Precordillera, Argentina: a thick-skinned triangle zone. AAPG Bull 80:359–381
Zhang MN (2015) Temporal and spatial differences and is mechanism of the frontal thrust belt of the West Kunlun Mountains in the NE Pamir. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang W, Qi JF, Lei GL, Wei W, Zeng YZ (2011) Analysis of structure model and formation mechanism of Fusha structure zone in south-western depression of Tarim Basin. J Southwest Pet Univ (Sci Technol Ed) 33:42–48. https://doi.org/10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2011.01.008 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao GP, Liu SG, Deng B, Li ZW, Wang XJ, Wan YB, Li JX (2015) Correlationship between deformation and various shortening velocities of fold-and-thrust belt: evidence from sandbox modeling. Geol Rev 61:935–947. https://doi.org/10.16509/j.georeview.2015.04.020 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng XL, He GY, Yao ZW (2016) Structural characteristics and geometric models of the Yasongdi Fault Belt, the Bachu Uplift. Earth Sci Front 4:025. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.2016.04.021 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project No. 41572202. We would like to thank the Korla Branch Research Institution of BGP Inc. for allowing the publication of the seismic lines shown in this paper. We also thank Rick Groshong, Wenjiao Xiao and another anonymous reviewer for their valuable comments and insightful suggestions, which have significantly improved the scientific impact of this paper. Journal Editor-in-Chief Prof. Wolf-Christian Dullo is warmly thanked for his support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Qi, J., Ni, Q. et al. The influence of syntectonic sedimentation on thrust belt deformation: a kinematic model example from the triangle zone within the Western Kunlun thrust belt. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 108, 1121–1136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-019-01697-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-019-01697-8