Abstract
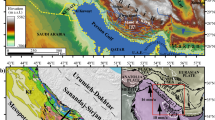
Previous studies suggested an important, but yet poorly-understood, tectonic transition in the Altaids (also termed the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, CAOB) in the Permian. This tectonic transition, clearly documented by published stratigraphic data and provenance analyses, suggested a unified Junger–Turfan basin in northwest China in Permian time and it further indicated that extension dominated Early Permian tectonics in the region, whereas flexural, foreland subsidence controlled Late Permian basin evolution. Our new structural observations, microtectonic analyses, and 40Ar/39Ar geochronological data from southwest of the Turfan basin reveal that in the late Early Permian (266 Ma) a NS-directed contractional deformation operated along the southern border of the unified Junger–Turfan basin, which was probably related to the transition in basin evolution. The contraction gave rise to a NW-striking right-lateral transpressional, rather than simple-shear dextral, ductile shear zone along the southwestern border of the Turfan basin, and to an interference fold pattern together with closely-spaced, concentrated cleavage and thrusts in a constrictional strain regime in the basin interior. After the Late Permian the tectonic evolution of the CAOB changed from Paleozoic continental amalgamation to Mesozoic–Cenozoic intracontinental orogenic reactivation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MB, Vincent SJ (1997) Fault reactivation in the Junger region, northwestern China: the role of basement structures during Mesozoic–Cenozoic compression. J Geol Soc Lond 154:151–155. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.154.1.0151
Allen MB, Windley BF, Zhang C, Zhao ZY, Wang GR (1991) Basin evolution within and adjacent to the Tienshan Range, NW China. J Geol Soc Lond 148:369–378. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.148.2.0369
Allen MB, Windley BF, Zhang C (1992) Paleozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tienshan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics 220:89–115. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(93)90225-9
Allen MB, Sengör AMC, Natal’in BA (1995) Junger, Turfan and Alakol basins as Late Permian to? Early Triassic extensional structures in a sinistral shear zone in the Altaid orogenic collage, Central Asia. J Geol Soc Lond 152:327–338. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.152.2.0327
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resource of Xinjiang (1983) Geological map of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, scale 1:2000000. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resource of Xinjiang (1989) Regional Geology of Xinjiang Province. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–560
Carroll AR, Liang Y, Graham SA, Xiao X, Hendrix MS, Chu J, McKnight CL (1990) Junggar basin, northwest China: trapped late Paleozoic ocean. Tectonophysics 181:1–14. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90004-R
Carroll AR, Brassell SC, Graham SA (1992) Upper Permian lacustrine oil shales, southern Junggar basin, northwest China. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 76:1874–1902
Che ZC, Liu L, Liu HF (1994) Formation and evolution of the middle Tianshan orogenic belt. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–135
Chen Z, Wu N, Zhang D, Hu J, Huang H, Shen G, Wu G, Tang H, Hu Y (1985) Geologic map of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, scale 1:2,000,000. Geologic Publishing House, Beijing 1 sheet
Cunningham D, Owen L, Snee L, Li J-L (2003) Structural framework of a major intracontinental orogenic termination zone: the easternmost Tien Shan, China. J Geol Soc Lond 160:575–590. doi:10.1144/0016-764902-122
Ghosh SK, Khan D, Sengupta S (1995) Interfering folds in constrictional deformation. J Struct Geol 17:1361–1373. doi:10.1016/0191-8141(95)00027-B
Greene TJ, Carroll AR, Wartes M, Graham S, Wooden J (2005) Integrated provenance analysis of complex orogenic terrane: Mesozoic uplift of the Bogda Shan and inception of the Turfan-Hami basin, NW China. J Sediment Res 75:251–267. doi:10.2110/jsr.2005.019
Hames WE, Bowring SA (1994) An empirical evaluation of the argon diffusion geometry in muscovite. Earth Planet Sci Lett 124:161–169. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(94)00079-4
Harrison TM, Ducan I, McDougall I (1985) Diffusion of 40Ar in biotite: temperature, pressure and compositional effects. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:2461–2468. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(85)90246-7
He XP, Hu YX, Zhao ZM, Feng YM (2002) Discovery of the early Permian coral fossils in the upper Carboniferous Qiergusitao formation in the North Tianshan, Xinjiang. Geol Bull China 21:648–652 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hendrix MS, Graham SA, Carroll AR, Sobel ER, McKnight CL, Schulein BJ, Wang ZX (1992) Sedimentary record and climatic implications of recurrent deformation in the Tianshan: evidence from Mesozoic strata of the north Tarim, south Junggar, and Turpan basins, northwest China. Geol Soc Am Bull 104:53–79. doi :10.1130/0016-7606(1992)104<0053:SRACIO>2.3.CO;2
Jahn BM, Griffin WL, Windley BF (2000a) Continental growth in the Phanerozoic: evidence from Central Asia. Tectonophysics 328:viii–x. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00174-8
Jahn BM, Wu FY, Chen B (2000b) Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episode 23(2):82–97
Jiang C, Mu Y, Bai K, Zhao X, Zhang H, Hei A (1999) Chronology, petrology, geochemistry and tectonic environment of granitoids in the Southern Tianshan mountains, western China. Acta Petrol Sin 15:298–308 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lanphere MA, Baadsgaard H (1997) The Fish Canyon Tuff: a standard for geochronology. AGU Abstr Program 78:326
Laurent-Charvet S, Charvet J, Monie P, Shu L (2003) Late Paleozoic strike-slip shear zones in eastern central Asia (NW China): New structural and geochronological data. Tectonics 22. doi:10.1029/2001TC901047
Li JY, Xiao WJ, Wang KZ, Sun GH, Gao LM (2003) Neoproterozoic to Paleozoic tectonostratgraphy, magmatic activities and tectonic evolution of eastern Xinjiang, NW China. In: Mao JW, Goldfarb R, Seltman R, Wang D, Xiao WJ, Hart C (eds) Tectonic evolution and metallogeny of the Chinese Altay and Tianshan. IAGOD guidebook Series 10: CERCAMS/NHM London, pp 31–74
Lin S, Williams PF (1992) The origin of ridge-in-groove slickenside striae and associated steps in an S–C mylonite. J Struct Geol 14:315–321. doi:10.1016/0191-8141(92)90089-F
Ludwig KR (2003) Isoplot/EX, rev. 3.00, a geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel. Berkeley Geochronol Cent Spec Publ 4:71
McDougall I, Harrison TM (1999) Geochronology and thermochronology by the 40Ar/39Ar method. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–269
Passchier CW, Trouw RAJ (2005) Micro-tectonics, 2nd revised and enlarged edition. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–306
Sengör AMC, Natal’in A, Burtman VS (1993) Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature 364:299–307. doi:10.1038/364299a0
Wang B, Su LS, Cluzel D, Faure M, Charvet J (2007a) Geochemical constraints on Carboniferous volcanic rocks of the Yili block (Xinjiang, NW China): Implication for the tectonic evolution of Western Tianshan. J Asian Earth Sci 29:148–159. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.02.008
Wang HL, Xu XY, He SP, Chen JL (2007b) Geological map of Tianshan and it adjacent region, Scale 1/1,000,000. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Wang ZX, Wu J, Lu X, Zhang J, Liu C (1990) Polycyclic tectonic evolution and metallogeny of the Tianshan mountain. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–217
Wartes MA, Carroll AR, Greene TJ (2002) Permian sedimentary record of the Turpan-Hami basin and adjacent regions, northwest China: constraints on post-amalgamation tectonic evolution. GSA Bull 114:131–152
Windley BF, Allen MB, Zhang C, Zhao Z, Wang G (1990) Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tienshan range, central Asia. Geology 18:128–131. doi :10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0128:PAACRO>2.3.CO;2
Windley BF, Alexeiev DV, Xiao WJ, Kröner A, Badarch G (2007) Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J Geol Soc Lond 164:31–47. doi:10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Xiao X, Tang Y, Feng Y, Zhu B, Li J, Zhao M (1992) Tectonic evolution of northern Xinjiang and its adjacent regions. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Xiao WJ, Zhang L, Qin KZ, Sun S, Li JL (2004a) Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): implications for the continental growth of central Asia. Am J Sci 304:370–395. doi:10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Badarch G, Sun S, Qin KZ, Wang ZH (2004b) Paleozoic accretionary and convergent tectonic of the southern Altaids: implications for the growth of Central Asia. J Geol Soc Lond 161:339–342
Xu XW, Ma TL, Sun LQ, Cai XP (2003) Characteristics and dynamic origin of the large-scale Jiaoluotage ductile compressional zone in the eastern Tianshan Mountains, China. J Struct Geol 25:1901–1915. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00017-8
Yang TN, Wang XP (2006) Geochronology, petrochemistry and tectonic implications of earlier Devonian plutons in Kumish area, Xinjiang. Acta Petrol Miner 25:401–411 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang XK, Su CQ, Chen H, Zhang HJ, Yan HQ, Li XF, Liu JQ (2006a) Discovery of the Permian volcanic rocks in the Bindaban-Houxia, Tianshan Mountain, and its geological significance. Geol Bull China 25:969–976 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang TN, Li JY, Sun GH, Wang YB (2006b) Earlier Devonian active continental arc in central Tianshan: evidence of geochemical analyses and zircon SHRIMP dating on mylonitized granitic rocks. Acta Petrol Sin 22:41–48 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang TN, Wang Y, Li JY, Sun GH (2007) Vertical and horizontal strain partitioning of the Central Tianshan (NW China): evidence from structures and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology. J Struct Geol 29:1605–1621. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2007.08.002
Yang TN, Li JY, Sun GH, Wang YB (2008) Meso-proterozoic continental arc type granite in the Central Tianshan mountains (NW China): zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and geochemical analyses. Acta Geol Sin 82:117–125 (English edition)
Zheng YD, Wang T, Ma M, Davis GA (2004) Maximum effective moment criterion and the origin of low-angle normal faults. J Struct Geol 26:271–285. doi:10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00079-8
Zhou D, Graham SA, Chang EZ, Wang B, Hacker B (2001) Paleozoic tectonic amalgamation of the Chinese Tianshan: evidence from a transect along the Dushanzi-Kuqa Highway. In: Hendrix MS, Gregory AD (eds) Paleozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution of central and eastern Asia: from continental assembly to intracontinental deformation. Geol Soc Am Memoir 194: 23–46
Zhu YF, Zhang LF, Gu LB, Guo X, Zhou J (2005) Zircon SHRIMP geochronology and trace elements of Carboniferous volcanic rocks from eastern Tianshan. Chin Sci Bull 50:2004–2014 (in Chinese)
Zhu YF, Zhou J, Zeng YS (2007) The Tianger (Bindaban) shear zone hosted gold deposit, west Tianshan, NW China: petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Ore Geol Rev 32:337–365. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.10.006
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the State Key Research Development Program of China (973. No.2007CB411306 and 2001CB409810). M. B. Allen and Shoufa Lin provided helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. Special thanks are given to Professor. F. B. Windley for his help with the English text and grammar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T.N., Li, J.Y., Wang, Y. et al. Late Early Permian (266 Ma) N–S compressional deformation of the Turfan basin, NW China: the cause of the change in basin pattern. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 98, 1311–1324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-008-0396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-008-0396-y