Abstract
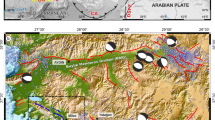
The South Middle Atlas front constitutes a northeast-trending shear zone, located north of the Neogene Missour basin and east of the Taza Guercif basin. This paper analyses the Southern Middle Atlas Fault Zone (SMAFZ) deformation since the Pliocene. The set of structures observed suggests that reverse and thrust faulting along the central part of the SMAFZ are combined with left-lateral slip along N–S striking faults of its south-western termination and right-lateral faulting along E–NE striking faults of the east–northeast termination. Thrusts and oblique thrust-related anticlines of the two lateral ramps partly accommodate north-west directed motion of the African plate. The Thrusts probably resulted from rejuvenation of Jurassic normal faults; they were active during the Upper Miocene–Pliocene and the Pleistocene. The geometries of positive inversion structures and buttressing effects are clearly dependent on the geometry and sedimentology of the original basin-controlling fault system and on the presence of a décollement level. Field mapping is integrated with Landsat imagery and a digital elevation model to investigate the morphotectonic evolution of the south-eastern range front of the Middle Atlas. Geomorphological features provide significant information on the processes that govern lateral propagation of active anticlines. Both suggest that the deformation front may have been active since Pliocene.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait Brahim L, Chotin P, (1989) Genèse et déformation des bassins néogènes du Rif central (Maroc) au cours du rapprochement Europe-Afrique. Geodinamica Acta 3:295–230
Barrier E, Chamot-Rooke N, Giordano G, Morelli A, Brouillet JF (2004) ‘Carte Géodynamique de la Méditerranée’, échelle á l’équateur, projection Mercator. In: CGMW (ed), 2 feuilles
Beauchamp W, Barazangi M, Demnati A, El Alji M (1996) Intracontinental rifting and inversion : Missour Basin and Atlas Mountains, Morocco. AAPG Bull 80:1459–1482
Benammi M, Jeager JJ (1995) Datation des formations continentales du Jbel Rhassoul à l’aide des micro-mammifères. Notes Mem Serv Geol Maroc 155:29–77
Bernini M, Boccaletti M, Moratti G, Papani G (2000) Structural development of the Taza-Guercif Basin as a constraint for Middle Atlas Shear Zone tectonic evolution. Mar Petroleum Geol 17(3):391–408
Boudiaf A, Philip H, Coutelle A, Ritz J-F, (1999) Découverte d’un chevauchement d’âge Quaternaire au sud de la Grande Kabylie (Algérie). Geodinamica Acta 12(2):71–80
Brede R, Hauptmann M, Herbig HG (1992) Plate Tectonics and intracratonic mountain ranges in Morocco. Geologische Rundschau 81(1):127–184
Burbank DW, Anderson RS (2001) Tectonic geomorphology. Blackwell, Oxford pp 1–274
Calvert A, Sandvol E, Seber D, Barazangi M, Roecker S, Mourabit T, Vidal F, Alguacil G, Jabour N, (2000) Geodynamic evolution of the lithosphere and upper mantle beneath the Alboran region of the Western Mediterranean: constraints from travel time tomography. J Geophys Res 10:10871–10898
Charroud M (2002) Evolution géodynamique des Hauts Plateaux (Maroc) et de leurs bordures du Mésozoique au Cenozoique. Thèse d’Etat, Université de Fès: pp 1–314
Colo G (1964) Contribution à l’étude du Jurassique du Moyen Atlas septentrional. Note Mem Serv Geol Maroc, 139 bis:pp 1–226
Delcaillau B (2001) Geomorphic response to growing fault-related folds: example from the foothills of central Taiwan. Geodinamica Acta 14:265–287
Delcaillau B (2004) Reliefs et Tectonique récente - les systèmes géomorphologiques dans les domaines a déformation active. Vuibert, Paris, pp 1–259
De Mets C, Gordon RG, Argus DF, Stein S (1990) Current plate motions. Geophys J Int 101:425–478
Docherty C, Banda E, (1995) Evidence for the eastward migration of the Alboran Sea based on regional subsidence analysis: a case for basin formation by delamination of the subcrustal lithosphere? Tectonics, 14:804–818
Domzig A, Yelles K, Le Roy C, Déverchère J, Bouillin J-P, Bracène R, Mercier B, Lépinay de P, Le Roy P, Calais E, Kherroubi A, Gaullier V, Savoye B, Pauc H (2006) Searching for the Africa–Eurasia Miocene boundary offshore western Algeria (MARADJA’03 cruise). C R Geosci 338 (in press)
du Dresnay R (1975) Influence de l’héritage structural tardi-hercynien et de la tectonique contemporaine de la sédimentation jurassique, dans le sillon marin du Haut Atlas, Maroc. 9e Congr. Int. Sédimentol. Nice 4:103–108
du Dresnay R (1979) Sédiments jurassiques des chaînes atlasiques du Maroc. Symposium “Sédimentation jurassique ouest-européen”, ASF spec. Pub. I:345–365
du Dresnay R (1988) Recent data on geology of the Middle Atlas (Morocco). In: Jacobshagen V (ed) The Atlas system of Morocco. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 293–320
Duringer P, Ais M, Chabi A (1995) Contexte géodynamique et milieu de dépôt du gisement de stévensite (rhassoul) miocène du Maroc : environnement lacustre ou évaporitique? (in French) Bull Soc Geol 2:169–179
El Bakkali S, Gourgaud A, Boudier J-L, Bellon H, Gundogdu N, (1998) Post-collision neogene volcanism of the Eastern Rif (Morocco) : magmatic evolution through time. Lithos, 45:523–543
El Hammichi F, Elmi S, Faure-Muret A, Benshili K (2002) Une plate-forme en distension, témoin de phases pré-accrétion téthysienne en Afrique du Nord pendant le Toarcien-Aalénien, synclinal Iguer Awragh-Afennourir, Moyen Atlas occidental, Maroc. C R Geosci 334(13):1003–1010
Fedan B, Laville E, El Mezgueldi A (1989) Le bassin Jurassique du Moyen Atlas (Maroc): exemple de bassin sur relais de décrochements. (in French) Bull Soc Geol 5:1123–1236
Frizon de Lamotte D, Saint Bezar B, Bracene R, Mercier E (2000) The Two main steps of the Atlas building and geodynamics of the western Mediterranean. Tectonics 19:740–761
Gelati R, Moratti G, Papani G (2000) The Late Cenozoic sedimentary succession of the Taza-Guercif Basin, South Rifian Corridor, Morocco. Mar Petroleum Geol 17(3):343–357
Gillcrist R Coward MP, Mugnier JL (1987) Structural inversion : examples from the Alpine foreland and French Alps. Geodynamica Acta 1:5–34
Gomez F, Barazangi M, Bensaïd M (1996) Active tectonism in the intracontinental Middle Atlas mountains of Morocco : synchronous crustal shortening and extension. J Geol Soc Lond 153:389–402
Gomez F, Beauchamp W, Barazangi M (2000) Role of the Atlas mountains (northwest Africa) within the African-Eurasian plate-boundary zone. Geology 28:775–778
Gutscher M-A, Malod J, Rehault J-P, Contrucci I, Klinghoefer F, Mendes Victor L, Spakman W, (2002) Evidence for active subduction beneath Gibraltar. Geology 30:1071–1074
Harmand C, Moukadiri A, (1986) Synchronisme entre tectonique compressive et volcanisme alcalin: exemple de la province quaternaire du Moyen Atlas (Maroc) (in French) Bull Soc Geol 8(2):595–603
Jacobshagen V, Brede R, Hauptmann RH, Heinitz W, Zylka R (1988) Structure and post-Paleozoic evolution of the central High Atlas.- In: Jacobshagen V (ed) The Atlas system of Morocco. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 245–271
Krijgsman W, Langereis CG (2000) Magnetostratigraphy of Zobzit and Koudiat Zarga sections (Taza-Guercif basin, Morocco): implications for the evolution of the Rifian Corridor. Mar Petroleum Geol 17(3):359–371
Leeder MR, Jakson JA (1993) The interaction between normal faulting and drainage in active extensional basins, with examples from the western United States and central Greece. Basin Res 5:79–102
Lefèvre D (1985) Les formations plio-pléistocènes du bassin de Ksabi (Moyenne Moulouya, Maroc). Thèse 3e cycle, Université Bordeaux I, pp 1–235
Martin J (1981) Le Moyen Atlas central. Etude géomorphologique. Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique du Maroc, 228, 228bis, 445 p., 5 cartes : 1/100 000
Martinez-Diaz J, Hernandez-Enrile JL, (2004) Neotectonics and morphotectonics of the southern Almeria region (Betic Cordillera–Spain) kinematic implications. Int J Earth Sci 93:189–206
Mattauer M, Tapponnier P, Proust F (1977) Sur les mécanismes de formation des chaînes intracontinentales. L’exemple des chaînes atlasiques du Maroc (in French). Bull Soc Geol 7(19):521–526
Meghraoui M, Morel JL, Andrieux J, Dahmani M, (1996) Neotectonique de la chaîne Tello-Rifaine et de la Mer d’Alboran: une zone complexe de convergence continent-continent. (in French) Bull Soc Geol 167:143–159
Morel JL (1989) Etat de contrainte et cinématique de la chaine rifaine (Marc) du Tortonien à l’actuel. Geodinamica Acta 3(4):283–294
Morel JL, Zouine EM Poisson A (1993) Relations entre la subsidence des bassins moulouyens et la création des reliefs atlasiques (Maroc): un exemple d’inversion tectonique depuis le Néogène. (in French) Bull Soc Geol164(1):79–91
Negrado AM, Bird P, Sanz de Galdeano C, Buforn E (2002) Neotectonic modelling of the Ibero-Maghrebian region. J Geophys Res 107 B11 2292. DOI 10.1029/2001JB000743
Ouattani F, Addoum B, Mercier E, Frizon de Lamotte D, Andrieux J, (1995) Geometry and kinematics of the South Atlas Front, Algeria and Tunisia. Tectonophysics 249:223–248
Piqué A, Aït Brahim L, El Azzouzi M, Maury R, Bellon H, Semroud B, Laville E (1998) Le poinçon maghrébin : contraintes structurales et géochimiques. C R Geoscience 326:575–581
Platt JP, Vissers RLM, (1989) Extensional collapse of thickened continental lithosphere: a working hypothesis for the Alboran Sea and Gibraltar arc. Geology 17:540–543
Saadi M, Bensaïd M, Dahmani M (1984) Carte géologique du Rif, Al Hoceima. Notes Mem Serv Geol Maroc, 302
Sani F, Zizi M, Bally A (2000) The Neogene-Quaternary evolution of the Guercif Basin (Morocco) reconstructed from seismic line interpretation. Mar Petroleum Geol 17(3):343–357
Sanz de Galdeano C, (1990) Geologic evolution of the Betic Cordilleras in the western Mediterranean, Miocene to present. Tectonophysics 172:107–119
Schumm SA (1986) Alluvial river response to active tectonics. In: Active tectonics. National Academy Press, Washington, pp 80–94
Schumm SA, Dumont JF, Holbrook JM (2000) Active tectonics and alluvial rivers. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 1–276
Teixell A, Arboleya M-L, Julivert M Charroud M (2002) Tectonic shortening and topography in the central High Atlas of Morocco. Tectonics 22(5):1–13
Torres-Roldan RL, Poli G, Peccerillo A, (1986) An early Miocene arc-tholeitic magmatic dike event from the Alboran Sea: evidence for precollision subduction and back-arc crustal extension in the westernmost Mediterranean. Geologische Rundschau, 75:219–234
Vially R, Letouzey J, Benard F, Haddad H, Desforges G, Askir H, Boudjema A (1994) Basin inversion along the North African margin: The Saharan Atlas (Algeria). In: Roure F (eds) Peri tethys platforms. Technip, Paris, pp 79–118
Viseras C, Fernandez J (1994) Channel migration patterns and related sequences in some alluvial fans systems. Sediment Geol 88:201–217
Wells SG, Bullard TF, Menges CM, Drake PG, Karas PA, Kelson KI, Ritter JB, Wesling JR (1988) Regional variations in tectonic geomorphology along a segmented convergent plate boundary, Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Geomorphology 1(3):239–265
Yelles-Chaouche A, Boudiaf A, Djellit H, Bracene R, (2006) La tectonique de la région nord-algérienne. C R Geosci 338 (in press)
Zizi M (1996) Triassic–Jurassic extension and Alpine inversion in the northern Morocco. In: Ziegler PA, Horvath F (eds) Peri-Tethys Memoir. 2: Structure and prospects of the Alpine basins and forelands. Mem Mus Natu Hist Nat 170:87–101
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the French Moroccan Cooperation Program (PAI, Action intégrée MA 219 ST 00). The authors are grateful to Dr. Stackebrandt and the anonymous reviewer for their comments that helped to refine the paper. The authors are also grateful to Dr. A.K. Shrivastava for helping in the translation of the manuscript and to Prof. P.L. Gibbard, Cambridge University, for his comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laville, E., Delcaillau, B., Charroud, M. et al. The Plio-Pleistocene evolution of the Southern Middle Atlas Fault Zone (SMAFZ) front of Morocco. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 96, 497–515 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0113-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0113-7