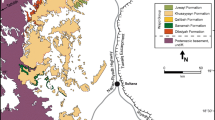
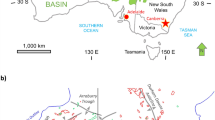
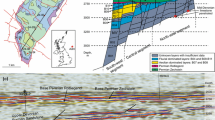
Abstract
We compare the diagenetic evolution of deeply buried Rotliegend (Permian) red bed sandstones at the southern and northern margin of the Central European Basin (CEB) in Germany. Main target is to evaluate the influence of maturation products from hydrocarbon (HC) source rocks during red bed diagenesis. At the southern margin of the CEB, thick coal-bearing Carboniferous source rocks are omnipresent beneath the Rotliegend. They contain dominantly gas-prone terrigenous organic material and some oil source rocks. Hydrocarbons were generated from Late Carboniferous onwards throughout most of basin subsidence. At the northern margin of the CEB, source rocks are almost absent due to deep erosion of Carboniferous rocks and a low TOC of local Lower Carboniferous relics. Early diagenetic processes are comparable at both basin margins. Significant differences in burial diagenetic evolution are spatially correlated to the occurrence of hydrocarbon source rocks. Burial diagenesis at the southern margin of the CEB is characterized especially by bleaching of red beds, major dissolution events, pervasive illite formation, impregnation of pore surfaces with bitumen, and formation of late Fe-rich cements. Almost none of these features were detected at the northern basin margin. Instead, relatively early cements are preserved down to maximum burial depths. This suggests that major diagenetic mineral reactions in deeply buried red bed sandstones are controlled by the presence or absence of maturing hydrocarbon source rocks.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard P, Jahren JS, Harstad AO, Nilsen O, Ramm M (2000) Formation of grain-coating chlorite in sandstones. Laboratory synthesized vs. natural occurrences. Clay Min 35:261–269
Almon WR (1981) Depositional environment and diagenesis of Permian Rotliegendes sandstones in the Dutch sector of the Southern North Sea. In: Longstaffe FJ (ed) Clays and the Resource Geologist. Mineral Assoc Canada Short Course Handbook 7, pp 119–147
Baldschuhn R, Binot F, Fleig S, Kockel F (2001) Geotektonischer Atlas von Nordwest-Deutschland und dem deutschen Nordsee-Sektor. Geol Jb A 153:3–95
Bandlowa T (1990) Lagerstättenbildung in Teilgebieten der Mitteleuropäischen permokarbonischen Erdgasprovinz. Z angew Geol 36(9):336–341
Barclay SA, Worden RH (2000) Geochemical modelling of diagenetic reactions in a sub-arkosic sandstone. Clay Min 35:57–67
Bender F, Hedemann H-A (1983) Zwanzig Jahre erfolgreiche Rotliegend-Exploration in Nordwestdeutschland - weitere Aussichten auch im Präperm? Erdöl-Erdgas 99:39–49
Berthelsen A (1992) From Precambrian to Variscan Europe. In: Blundell D, Freeman R, Mueller S (eds) A continent revealed—the european geotraverse. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 153–164
Bjørlykke K, Ramm M, Saigal GC (1989) Sandstone diagenesis and porosity modification during basin evolution. Geol Rundsch 78(1):243–268
Boigk H, Stahl WJ, Teichmüller M, Teichmüller R (1971) Inkohlung und Erdgas. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 19:101–108
Boles JR, Franks SG (1979) Clay diagenesis in Wilcox sandstones of southwest Texas: implications of smectite diagenesis on sandstone cementation. J Sediment Petrol 49:55–70
Boles JR, Ramseyer K (1987) Diagenetic Carbonate in Miocene Sandstone Reservoir, San Joaquin Basin, California. AAPG Bull 71(12):1475–1487
Brink H-J, Dürschner H, Trappe H (1992) Some aspects of the late and post-Variscan development of the Northwestern German Basin. Tectonophysics 207:65–95
Budzinski H, Judersleben G (1980) Zur Diagenese tonarmer Sandsteine. Z angew Geol 26:302–308
Burley SD (1984) Patterns of diagenesis in the Sherwood Sandstone Group (Triassic), United Kingdom. Clay Min 19:403–440
Burley SD (1986) The development and destruction of porosity within Upper Jurassic reservoir sandstones of the Piper and Tartan Fields, Outer Moray Firth, North Sea. Clay Min 21:649–694
Burley SD, Mullis J, Matter A (1989) Timing diagenesis in the Tartan Reservoir (UK North Sea): constraints from combined cathodoluminescence microscopy and fluid inclusion studies. Mar Petrol Geol 6:98–120
Chan MA, Parry WT, Bowman JR (2000) Diagenetic Hematite and Manganese Oxides and Fault-Related Fluid Flow in Jurassic Sandstones, Southeastern Utah. AAPG Bull 84(9):1281–1310
Cookenboo HO, Bustin RM (1999) Pore water evolution in sandstones of the Groundhog Coalfield, northern Bower Basin, British Columbia. Sed Geol 123:129–146
Cord M (1994) Diagenese äolischer Sandsteine im Oberrotliegenden Norddeutschlands. Diss Univ Mainz, pp 1–119
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (1996) The iron oxides. VCH, Weinheim, pp 1–573
Crossey LJ, Surdam RC, Lahann R (1986) Application of organic/inorganic diagenesis to porosity prediction. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:147–155
Curtis CD, Coleman ML (1986) Controls on the precipitation of early diagenetic calcite, dolomite and siderite concretions in complex depositional sequences. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:23–33
Deutrich T (1993) Tonmineral-Diagenese in Rotliegend-Sandsteinen des Norddeutschen Beckens. Diss Univ Mainz, pp 1–179
Drong HJ (1979) Diagenetische Veränderungen in den Rotliegend Sandsteinen im NW-Deutschen Becken. Geol Rundsch 68:1172–1183
Drozdzewski G (1992) Zur Faziesentwicklung im Oberkarbon des Ruhrbeckens, abgeleitet aus Mächtigkeitskarten und lithostratigraphischen Gesamtprofilen. Z angew Geol 38(1):41–48
Edman JD, Surdam RC (1986) Organic-inorganic interactions as a mechanism for porosity enhancement in the Upper Cretaceous Ericson Sandstone, Green River Basin, Wyoming. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:85–109
Eglinton TI, Curtis CD, Rowland SJ (1987) Generation of water-soluble organic acids from kerogen during hydrous pyrolysis: implications for porosity development. Mineral Mag 51:495–503
Faber E, Schmitt M, Stahl WJ (1979) Geochemisch Daten nordwestdeutscher Oberkarbon-, Zechstein- und Buntsandsteingase. Erdöl und Kohle, Erdgas, Petrochemie 32(2):65–70
Foxford KA, Garden IR, Guscott SC, Burley SD, Lewis JJM, Walsh JJ, Watterson J (1996) The field geology of the Moab Fault. In: Huffman AC, Lund WR, Godwin LH (eds). Geology and resources of the Paradox Basin. Utah Geol Assoc Guidebook 25:256–283
Franke D (1990) Der präpermische Untergrund der Mitteleuropäischen Senke - Fakten und Hypothesen. Nds Akad Geowiss Veröfftl 1990(4):19–75
Friedmann I, O’Neil JR (1977) Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interests. In: Fleischer M (ed) Data of geochemistry. USGS Professional Paper 440-KK:KK1–KK12
Frisch U, Kockel F (2004) Der Bremen-Knoten im Strukturnetz Nordwest-Deutschlands. Stratigraphie, Paläogeographie, Strukturgeologie. Berichte, Fachbereich Geowissenschaften, Univ Bremen 223:1–379
Garden IR, Guscott SC, Burley SD, Foxford KA, Walsh JJ, Marshall J (2001) An exhumed palaeo-hydrocarbon migration fairway in a faulted carrier system, Entrada Sandstone of SE Utah, USA. Geofluids 1:195–213
Gast RE (1991) The Perennial Rotliegend Saline Lake in NW Germany. Geol Jb A 119:25–59
Gaupp R (1996) Diagenesis types and their application in diagenesis mapping. Zbl Geol Paläont, Teil 1 1994(11/12):1183–1199
Gaupp R, Solms M (2005) Sedimentological and petrological investigations. In: Palaeo Oil- and Gasfields in the Rotliegend of the North German Basin: effects upon hydrocarbon reservoir quality. DGMK-Forschungsbericht 593–8, pp 1.1–1.44
Gaupp R, Matter A, Platt J, Ramseyer K, Walzebuck JP (1993) Diagenesis and fluid evolution of deeply buried Permian (Rotliegende) Gas Reservoirs, Northwest Germany. AAPG Bull 77(7):1111–1128
Gaupp R, Clauer N, Cord M, Matter A, Ramseyer K, Zwingmann H (1996) Silicification during hydrocarbon migration—evidence from Paleozoic sandstone reservoirs in Northern Germany. Geofluids seminar series, Belfast, pp 25
Gaupp R, Gast R, Forster C (2000) Late Permian Playa Lake Deposits of the Southern Permian Basin (Central Europe). In: Gierlowski-Kordesch EH, Kelts KR (eds) Lake basins through space and time. AAPG Stud Geol 46:75–86
Gaupp R, Baunack C, Pudlo D, Solms M, Trappe H, Schubart-Engelschall J, Samiee R, Littke R, Schwarzer D, Oncken O, Krawczyk CM, Tanner D (2005) Paleo Oil- and Gasfields in the Rotliegend of the North German Basin: effects upon hydrocarbon reservoir quality. DGMK-Forschungsbericht 593–8:1–242
Gerling P, Gulek MC, Kockel F, Lokhorst A, Lott GK, Nicholson RA (1999) NW European Gas Atlas–new implications for the Carboniferous gas plays in the western part of the Southern Permian Basin. In: Fleet AJ, Boldy SAR (eds) Petroleum geology of Northwest Europe. Proceedings of the fifth Conference, pp 799–808
Giles MR, Marshall JD (1986) Constraints on the development of secondary porosity in the subsurface: re-evaluation of processes. Mar Petrol Geol 3:243–255
Glennie KW (1972) Permian Rotliegendes of Northwest Europe interpreted in light of modern desert sedimentation studies. AAPG Bull 56(6):1048–1071
Glennie KW (2001) Exploration activities in the Netherlands and North-West-Europe since Groningen. Geol Mijnbouw/Neth J Geosciences 80(1):33–52
Glennie KW, Mudd G, Nagtegaal PJC (1978) Depositional environment and diagenesis of Permian Rotliegendes sandstones in Leman Bank and Sole Pit areas of the UK southern North Sea. J Geol Soc London 135:25–34
Hancock NJ (1978) Possible causes of Rotliegend sandstone diagenesis in northern W. Germany. J Geol Soc London 135:35–40
Harrison WJ, Thyne GD (1992) Prediction of diagenetic reactions in the presence of organic acids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:565–586
Hedemann H-A (1985) Energierohstoffe im Oberkarbon Nordwestdeutschlands. Erdöl-Erdgas 101(4):106–112
Hedemann H-A, Teichmüller R (1971) Die paläogeographische Entwicklung des Oberkarbons. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 19:129–142
Hedemann H-A, Schuster A, Stancu-Kristoff G, Lösch J (1984) Die Verbreitung der Kohleflöze des Oberkarbons in Nordwestdeutschland und ihre stratigraphische Einstufung. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 32:39–88
Hillier S (1994) Pore-lining chlorites in siliciclastic reservoir sandstones: Electron microprobe, SEM and XRD data, and implications for their origin. Clay Min 29:665–679
Hoefs J (1997) Stable isotope geochemistry, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–201
Hoffmann N, Jödicke H, Fluche B, Jording A, Müller W (1998) Modellvorstellungen zur Verbreitung potentieller präwestfalischer Erdgas-Muttergesteine in Norddeutschland - Ergebnisse neuer magnetotellurischer Messungen. Z angew Geol 44(3):140–158
Hoffmann N, Jödicke H, Horejschi L (2005) Regional distribution of the Lower Carboniferous Culm and Carboniferous Limestone Facies in the North German Basin - Derived from Magnetotelluric Soundings. Z Dt Ges Geowiss 156(2): In press
Hoffmann N, Jödicke H, Gerling P (2001) The distribution of Pre-Westphalian source rocks in the North German Basin—evidence from magnetotelluric and geochemical data. Geol Mijnbouw/Neth J Geosci 80(1):71–84
Horsfield B, Yordy KL, Crelling JC (1988) Determining the petroleum-generation potential of coal using organic geochemistry and organic petrology. Org Geochem 13:121–129
Houseknecht DW (1987) Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones. AAPG Bull 71(6):633–642
van Houten FB (1968) Iron oxides in red beds. Geol Soc Am Bull 79:399–416
Humphreys B, Smith SA, Strong GE (1989) Authigenic chlorite in late Triassic sandstones from the Central Graben, North Sea. Clay Min 24:427–444
Irwin H, Curtis C, Coleman M (1977) Isotopic evidence for source of diagenetic carbonates formed during burial of organic-rich sediments. Nature 269:209–213
Katzung G, Krull P (1984) Zur tektonischen Entwicklung Mittel- und Nordwesteuropas während des Jungpaläozoikums. Z angew Geol 30(4):163–173
Kawamura K, Kaplan IR (1987) Dicarbonlic acids generated by thermal alteration of kerogen and humic acids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:3201–3207
van Keer I, Muchez P, Viaene W (1998) Clay mineralogical variations and evolutions in sandstone sequences near a coal seam and shales in the Westphalian of the Campine Basin. Clay Min 33:159–169
Kharaka YK, Law LM, Carothers WW, Goerlitz DF (1986) Role of organic species dissolved in formation waters from sedimentary basins in mineral diagenesis. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:111–122
Kilgore B, Elmore RD (1989) A study of the relationship between hydrocarbon migration and the precipitacion of authigenic magnetic minerals in the Triassic Chugwater Formation, southern Montana. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:1280–1288
Krooss BM, Littke R, Müller B, Frielingsdorf J, Schwochau K, Idiz EF (1995) Generation of nitrogen and methane from sedimentary organic matter: implications on the dynamics of natural gas accumulations. Chem Geol 126:291–318
Lanson B, Beaufort D, Berger G, Baradat J, Lacharpagne J-C (1996) Illitization of diagenetic kaolinite-to-dickite conversion series: Late-stage diagenesis of the Lower Permian Rotliegend sandstone reservoir, offshore of the Netherlands. J Sediment Res 66(3):501–518
Leveille GP, Primmer TJ, Dudley G, Ellis D, Allinson GJ (1997) Diagenetic controls on reservoir quality in Permian Rotliegendes sandstones, Jupiter Fields area, southern North Sea. In: Ziegler K, Turner P, Daines SR (eds) Petroleum geology of the Southern North Sea: Future and Potential. Geol Soc Spec Pub 123:105–122
Liewig N, Clauer N (2000) K-Ar dating of varied microtextural illite in Permian gas reservoirs, northern Germany. Clay Min 35:271–281
Littke R, Leythaeuser (1993) Migration of oil and gas in coals. In: Law BE, Rice DD (eds) Hydrocarbons from coal. AAPG Stud Geol 38:219–236
Littke R, Krooss B, Idiz E, Frielingsdorf J (1995) Molecular nitrogen in natural gas accumulations: generation from sedimentary organic matter at high temperatures. AAPG Bull 79(3):410–430
Littke R, Brauckmann FJ, Radke M, Schaefer RG (1996) Solid bitumen in Rotliegend gas reservoirs in northern Germany: implications for their thermal and filling history. Zbl Geol Paläont, Teil 1 1994(11/12):1275–1292
Lokhorst A (ed) (1998) Northwest European Gas Atlas–composition and isotope ratio of natural gases. NITG-TNO, Haarlem
Lundegard PD, Land LS (1986) Carbon dioxide and organic acids: their role in porosity enhancement and cementation, Paleogene of the Texas Gulf Coast. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:129–146
Macaulay CI, Fallick AE, McLaughlin OM, Haszeldine RS, Pearson MJ (1998) The significance of δ13C of carbonate cements in reservoir sandstones: a regional perspective from the Jurassic of the northern North Sea. Int Ass Sed Spec Pub 26:395–408
Machel HG (2001) Bacterial and thermodynamic sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings—old and new insights. Sed Geol 140:143–175
Marx J, Huebscher H-D, Hoth K, Korich D, Kramer W (1995) Vulkanostratigraphie und Geochemie der Eruptivkomplexe. In: Plein E (ed) Norddeutsches Rotliegendbecken, Rotliegend-Monographie Teil II. Cour Forsch-Inst Senckenberg 183:54–83
Matlack KS, Houseknecht DW, Applin KR (1989) Emplacement of clay into sand by infiltration. J Sediment Petrol 59:77–87
McBride EF (1963) A classification of common sandstones. J Sediment Petrol 33(3):664–669
McCann T (1996) Per-Permian of the north-east German Basin. Geol J 31:159–177
Meshri ID (1986) On the reactivity of carbonic and organic acids and the generation of secondary porosity. In: Gautier DL (ed) Roles of organic matter in sediment diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 38:123–128
Metcalfe R, Rochelle CA, Savage D, Higgo JW (1994) Fluid-Rock interactions during continental red bed diagenesis: implications for theoretical models of mineralization in sedimentary basins. In: Parnell J (ed) Geofluids: origin, migration and evolution of fluids in sedimentary basins. Geol Soc Spec Pub 78:301–324
Morad S, Bergan M, Knarud R, Nystuen JP (1990) Albitization of detrital plagioclase in Triassic reservoir sandstones from the Snorre Field, Norwegian North Sea. J Sediment Petrol 60:411–425
Muchez P, Viaene W, Dusar M (1992) Diagenetic control on secondary porosity in flood plain deposits: an example of the Lower Triassic of northeastern Belgium. Sed Geol 78:285–298
Müller EP (1990) Genetische Modelle der Bildung von Erdgaslagerstätten im Rotliegenden. Nds Akad Geowiss Veröfftl 4:77–90
Neunzert GH (1997) Simulation der Beckensubsidenz, der Temperaturgeschichte, der Reifung organischen Materials, und der Genese, Migration und Akkumulation von Methan und Stickstoff in Nordwestdeutschland auf der Basis seismischer Interpretationen. Ber Forschungszentrum Jülich 3521:1–173
Neunzert GH, Gaupp R, Littke R (1996) Absenkungs- und Temperaturgeschichte paläozoischer und mesozoischer Formationen im Nordwestdeutschen Becken. Z dt geol Ges 147(2):183–208
Parnell J (1994) Hydrocarbons and other fluids: paragenesis, interactions and exploration potential inferred from petrographic studies. In: Parnell J (ed) Geofluids: origin, migration and evolution of fluids in sedimentary basins. Geol Soc Spec Pub 78:275–291
Parnell J, Eakin P (1987) The replacement of sandstones by uraniferous hydrocarbons: significance for petroleum migration. Mineral Mag 51:505–515
Parnell J, Carey P, Monson B (1996) Fluid inclusion constraints on temperatures of petroleum migration from authigenic quartz in bitumen veins. Chem Geol 129:217–226
Parry WT, Chan MA, Beitler B (2004) Chemical bleaching indicates episodes of fluid flow in deformation bands in sandstone. AAPG Bull 88(2):175–191
Philipp W, Reinicke KM (1982) Zur Entstehung und Erschließung der Gasprovinz Osthannover. Erdöl-Erdgas 98:85–90
Platt J (1991) The diagenesis of early Permian Rotliegend deposits from northwest Germany. Diss Univ Bern, pp 1–367
Platt J (1993) Controls on clay mineral distribution and chemistry in the early Permian Rotliegend of Germany. Clay Min 28:393–416
Platt J (1994) Geochemical evolution of pore waters in the Rotliegend (Early Permian) of northern Germany. Mar Petrol Geol 11:66–78
Plein E (1978) Rotliegend-Ablagerungen im Norddeutschen Becken. Z dt geol Ges 129:71–97
Plein E (ed) (1995) Norddeutsches Rotliegendbecken, Rotliegend-Monographie Teil II. Cour Forsch-Inst Senckenberg, Frankfurt a.M. Stratigraphie von Deutschland I 183:1–193
Rieken R (1988) Lösungs-Zusammensetzung und Migrationsprozesse von Paläo-Fluidsystemen in Sedimentgesteinen des Norddeutschen Beckens (Mikrothermometrie, Laser-Raman-Spektroskopie und Isotopen-Geochemie). Göttinger Arb Geol Paläont 37:1–116
Rosenbaum J, Sheppard SM (1986) An isotopic study of siderites, dolomites and ankerites at high temperatures. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:1147–1150
Rowe J, Burley SD (1997) Faulting and porosity modification in the Sherwood Sandstone at Alderley Edge, northeastern Cheshire: an exhumed example of fault-related diagenesis. In: Meadows NS et al (eds) Petroleum geology of the Irish Sea and adjacent areas. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 124:325–352
Saigal GC, Bjørlykke K, Larter S (1992) The effects of oil emplacement on diagenetic processes—examples from the Fulmar Reservoir Sandstones, Central North Sea. AAPG Bull 76(7):1024–1033
Schmidt V, McDonald DA (1979) The role of secondary porosity in the course of sandstone diagenesis. In: Scholle PA, Schluger PR (eds) Aspects of diagenesis. SEPM Spec Pub 26, pp 175–207
Schröder L, Plein E, Bachmann GH, Gast RE, Gebhardt U, Graf R, Helmuth HJ, Pasternak M, Porth H, Süssmuth S (1995) Stratigraphische Neugliederung des Rotliegend im Norddeutschen Becken. Geol Jb A 148:3–21
Schumacher D (1996) Hydrocarbon-induced alteration of soils and sediments. In: Schumacher D, Abrams MA (eds) Hydrocarbon migration and its near-surface expression. AAPG Mem 66:71–89
Schwarzer D, Littke R (2005) Petroleum systems modelling. In: Palaeo Oil- and Gasfields in the Rotliegend of the North German Basin: effects upon hydrocarbon reservoir quality. DGMK-Forschungsbericht 593–8:3.1–3.58
Schwarzkopf T (1990) Relationship between petroleum generation, migration and sandstone diagenesis, Middle Jurassic, Gifhorn Trough, N Germany. Mar Petrol Geol 7:153–169
Sedat B (1992) Petrographie und Diagenese von Sandsteinen im Nordwestdeutschen Oberkarbon. DGMK-Forschungsbericht 384-7:1–143
Seemann U (1982) Depositional facies, diagenetic clay minerals and reservoir quality of Rotliegend sediments in the Southern Permian Basin (North Sea): a review. Clay Min 17:55–67
Seewald JS (2001) Model for the origin of carboxylic acids in basinal brines. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65(21):3779–3789
Seewald JS (2003) Organic-inorganic interactions in petroleum-producing sedimentary basins. Nature 426:327–333
Shebl MA, Surdam RC (1996) Redox reactions in hydrocarbon clastic reservoirs: experimental validation of this mechanism for porosity enhancement. Chem Geol 132:103–117
Spötl C, Houseknecht DW, Riciputi LR (2000) High-temperature quartz cement and the role of stylolites in a deep gas reservoir, Spiro Sandstone, Arkoma Basin, USA. In: Worden R, Morad S (eds). Quartz cementation in sandstones. Blackwell, Oxford, Int Ass Sed Spec Pub 29, pp 281–297
Stahl WJ (1968) Zur Herkunft nordwestdeutscher Erdgase. Erdöl und Kohle, Erdgas, Petrochemie 21:514–518
Stancu-Kristoff G, Stehn O (1984) Ein großregionaler Schnitt durch das nordwestdeutsche Oberkarbon-Becken vom Ruhrgebiet bis in die Nordsee. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 32:35–38
Strack Ä, Freudenberg U (1984) Schichtmächtigkeiten und Kohleninhalte im Westfal des Niederrheinisch-Westfälischen Steinkohlenreviers. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 32:243–256
Surdam RC, Boese SW, Crossey LJ (1984) The geochemistry of secondary porosity. In: Mcdonald DA, Surdam RC (eds). Clastic diagenesis. AAPG Mem 37:127–149
Surdam RC, Jiao ZS, MacGowan DB (1993) Redox reactions involving hydrocarbons and mineral oxidants: a mechanism for significant porosity enhancement in sandstones. AAPG Bull 77(9):1509–1518
Teichmüller M (1955) Anzeichen mariner Beeinflussung bei der Kohle aus Flöz Katharina der Zeche Frierich Heinrich. N Jb Geol Paläont, Mh 1955:193–201
Teichmüller M (1974) Entstehung und Veränderung bituminöser Substanzen in Kohlen in Beziehung zur Entstehung und Umwandlung des Erdöl. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 24:65–112
Teichmüller M, Teichmüller R, Bartenstein H (1984) Inkohlung und Erdgas–eine neue Inkohlungskarte der Karbon-Oberfläche in Nordwestdeutschland. Fortschr Geol Rheinld u Westf 32(1):11–34
Torrent J, Schwertmann U (1987) Influence of hematite on the color of red beds. J Sediment Petrol 57(4):682–686
Walker TR (1967) Formation of red beds in modern and ancient deserts. Geol Soc Am Bull 78:353–368
Walker TR (1976) Diagenetic origin of continental red beds. In: Falke H (ed) The continental Permian in central, west and south Europe. NATO ASI series C 22:240–282
Wilkinson M, Haszeldine RS (2002) Fibrous illite in oilfield sandstones—a nucleation kinetic theory of growth. Terra Nova 14(1):56–60
Wilkinson JJ, Lonergan L, Fairs T, Herrington RJ (1998) Fluid inclusion constraints on conditions and timing of hydrocarbon migration and quartz cementation in Brent Group reservoir sandstones, Columba Terrace, northern North Sea. In: Parnell J (ed) Dating and duration of fluid flow and fluid-rock interaction. Geol Soc Spec Pub 144:69–89
Zachara JM, Fredrickson JK, Li S, Kennedy DW, Smith SC, Gassman PL (1998) Bacterial reduction of crystalline Fe3+ oxides in single phase suspensions and subsurface materials. Amer Mineral 83:1426–1443
Ziegler PA (1978) North-Western Europe: tectonics and basin developement. Geol Mijnbouw 57:589–626
Ziegler A (1990) Geological Atlas of Western and Central Europe, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–239
Zwingmann H, Clauer N, Gaupp R (1998) Timing and fluid flow in a sandstone reservoir of the north German Rotliegend (Permian) by K-Ar dating of related hydrothermal illite. In: Parnell J (ed) Dating and duration of fluid flow and fluid-rock interaction. Geol Soc Spec Pub 144:91–106
Zwingmann H, Clauer N, Gaupp R (1999) Structure-related geochemical (REE) and isotopic (K-Ar, Rb-Sr, δ18O) characteristics of clay minerals from Rotliegend sandstone reservoirs (Permian, northern Germany). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(18):2805–2823
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to DFG for funding this project, which is part of the DFG research program 1135 (Dynamics of Sedimentary Systems under varying Stress Conditions by example of the Central European Basin System), DGMK project 577. This is publication no. GEOTECH-96 of the program GEOTECHNOLOGIEN of BMBF and DFG. We thank ExxonMobil Production Deutschland GmbH and Gaz de France for kindly providing us with core and data material from three deep wells in Schleswig-Holstein and for the permission to publish our results. We gratefully acknowledge the analytical assistance of Andreas Kronz (Göttingen, EMP), Jens Götze (Freiberg, cathodoluminscence), Günther Völksch (Jena, SEM) and Michael Joachimski (Erlangen, carbonate isotopes). Rebecca Tenorio kindly revised the English manuscript. Special thanks are due to Robert Ondrak (Potsdam), who carefully reviewed an earlier version of the manuscript, and to two anonymous reviewers. Their constructive comments and suggestions helped to improve this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schöner, R., Gaupp, R. Contrasting red bed diagenesis: the southern and northern margin of the Central European Basin. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 94, 897–916 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0004-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0004-3