Abstract
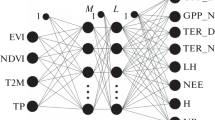
Forest biophysical properties are typically estimated and mapped from remotely sensed data through the application of a vegetation index. This generally does not make full use of the information content of the remotely sensed data, using only the data acquired in a limited number of spectral channels, and may provide a relatively crude spatial representation of the biophysical variable of interest. Using imagery acquired by the NOAA AVHRR, it is shown that a standard neural network may use all the spectral channels available in a remotely sensed data set to derive more accurate estimates of the biophysical properties of tropical forests in Ghana than a series of vegetation indices. Additionally, the spatial representation derived can be refined by fusion with finer spatial resolution imagery, achieved with the application of a further neural network.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foody, G., Boyd, D. Sharpened Mapping of Tropical Forest Biophysical Properties from Coarse Spatial Resolution Satellite Sensor Data. Neural Comput Applic 11, 62–70 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005210200017
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005210200017