Abstract
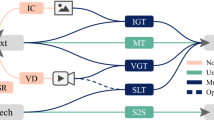
Multimodal machine translation (MMT) is a method that uses visual information to guide text translation. However, recent studies have engendered controversy regarding the extent to which MMT can contribute to the improvement of text-enhanced translation. To explore whether the MMT model can improve translation performance, we use the current Neural Machine Translation (NMT) system for evaluation at Multi30K dataset. Specifically, we judge the performance of the MMT model by comparing the difference between the NMT model and the MMT model. At the same time, we conduct text and multimodal degradation experiments to verify whether vision can play a role. We explored the performance of the NMT model and the MMT model for sentences of different lengths to clarify the pros and cons of the MMT model. We found that the performance of the current NMT model surpasses that of the MMT model, suggesting that the impact of visual features might be less significant. Visual features seem to exert influence primarily when a substantial number of words in the source text are masked.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included are freely available through the following repository: https://github.com/multi30k/dataset.
References
Barrault L, Bougares F, Specia L, Lala C, Elliott D, Frank S (2018) Findings of the third shared task on multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the third conference on machine translation: shared task papers, pp 304–323
Caglayan O, Barrault L, Bougares F (2016) Multimodal attention for neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.03976
Caglayan O, Aransa W, Bardet A, García-Martínez M, Bougares F, Barrault L, Masana M, Herranz L, van de Weijer J (2017) LIUM-CVC submissions for WMT17 multimodal translation task. In: Proceedings of the second conference on machine translation, association for computational linguistics, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 432–439 https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/W17-4746
Caglayan O, Madhyastha P, Specia L, Barrault L (2019) Probing the need for visual context in multimodal machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.08678
Caglayan O, Ive J, Haralampieva V, Madhyastha P, Barrault L, Specia L (2020) Simultaneous machine translation with visual context. In: Proceedings of the 2020 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), association for computational linguistics, Online, pp 2350–236https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.184
Calixto I, Rios M, Aziz W (2019) Latent variable model for multi-modal translation. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, association for computational linguistics, Florence, Italy, pp 6392–640https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1642
Carlsson F, Eisen P, Rekathati F, Sahlgren M (2022) Cross-lingual and multilingual clip. In: Proceedings of the thirteenth language resources and evaluation conference, pp 6848–6854
Chen S, Zeng Y, Cao D, Lu S (2022) Video-guided machine translation via dual-level back-translation. Knowl Based Syst 245:108598
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, et al. (2020) An image is worth \(16\times 16\) words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Elliott D (2018) Adversarial evaluation of multimodal machine translation. In: EMNLP, pp 2974–2978
Elliott D, Frank S, Sima’an K, Specia L (2016) Multi30k: multilingual English–German image descriptions. In: Proceedings of the 5th workshop on vision and language, association for computational linguistics, pp 70–77. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/W16-3210
Elliott D, Frank S, Barrault L, Bougares F, Specia L (2017) Findings of the second shared task on multimodal machine translation and multilingual image description. In: Proceedings of the second conference on machine translation, volume 2: shared task papers, association for computational linguistics, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 215–233. http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W17-4718
Gain B, Bandyopadhyay D, Mukherjee S, Adak C, Ekbal A (2023) Impact of visual context on noisy multimodal NMT: an empirical study for English to Indian languages. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16075
Grönroos SA, Huet B, Kurimo M, Laaksonen J, Merialdo B, Pham P, Sjöberg M, Sulubacak U, Tiedemann J, Troncy R et al (2018) The MeMAD submission to the wmt18 multimodal translation task. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.10802
Gupta D, Kharbanda S, Zhou J, Li W, Pfister H, Wei D (2023) CLIPTrans: transferring visual knowledge with pre-trained models for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 2875–2886
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Helcl J, Libovickỳ J, Variš D (2018) CUNI system for the WMT18 multimodal translation task. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.04697
Huang PY, Liu F, Shiang SR, Oh J, Dyer C (2016) Attention-based multimodal neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the first conference on machine translation, shared task papers, vol 2, pp 639–645
Imankulova A, Kaneko M, Hirasawa T, Komachi M (2020) Toward multimodal simultaneous neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the fifth conference on machine translation, association for computational linguistics, Online, pp 540–549 https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.wmt-1.70
Li L, Tayir T, Han Y, Tao X, Velásquez JD (2023) Multimodality information fusion for automated machine translation. Inf Fusion 91:352–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.018
Libovický J, Helcl J (2017) Attention strategies for multi-source sequence-to-sequence learning. In: Barzilay R, Kan MY (eds) Proceedings of the 55th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (vol 2: short papers), association for computational linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, pp 196–20https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P17-2031
Lin H, Meng F, Su J, Yin Y, Yang Z, Ge Y, Zhou J, Luo J (2020) Dynamic context-guided capsule network for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 1320–1329
Liu P, Cao H, Zhao T (2021) Gumbel-attention for multi-modal machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.08862
Long Q, Wang M, Li L (2021) Generative imagination elevates machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2021 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies, association for computational linguistics, Online, pp 5738–574https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.naacl-main.457
Madhyastha PS, Wang J, Specia L (2017) Sheffield multimt: using object posterior predictions for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the second conference on machine translation, pp 470–476
Peng R, Zeng Y, Zhao J (2022) Distill the image to nowhere: inversion knowledge distillation for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, association for computational linguistics, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, pp 2379–2390 https://aclanthology.org/2022.emnlp-main.152
Radford A, Kim JW, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, Sastry G, Askell A, Mishkin P, Clark J et al (2021) Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR, pp 8748–8763
Raffel C, Shazeer N, Roberts A, Lee K, Narang S, Matena M, Zhou Y, Li W, Liu PJ (2020) Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J Mach Learn Res 21(1):5485–5551
Shaw P, Uszkoreit J, Vaswani A (2018) Self-attention with relative position representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.02155
Song Y, Chen S, Jin Q, Luo W, Xie J, Huang F (2021) Enhancing neural machine translation with dual-side multimodal awareness. IEEE Trans Multimedia 24:3013–3024
Specia L, Frank S, Sima’An K, Elliott D (2016) A shared task on multimodal machine translation and crosslingual image description. In: Proceedings of the first conference on machine translation, shared task papers, vol 2, pp 543–553
Tamura H, Hirasawa T, Kaneko M, Komachi M (2020) TMU Japanese-English multimodal machine translation system for wat 2020. In: Proceedings of the 7th workshop on Asian translation, pp 80–91
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Advances in neural information processing system, vol 30
Wang X, Wu J, Chen J, Li L, Wang YF, Wang WY (2019) VaTeX: a large-scale, high-quality multilingual dataset for video-and-language research. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 4581–4591
Wu Z, Kong L, Bi W, Li X, Kao B (2021a) Good for misconceived reasons: an empirical revisiting on the need for visual context in multimodal machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.14462
Wu Z, Kong L, Bi W, Li X, Kao B (2021b) Good for misconceived reasons: an empirical revisiting on the need for visual context in multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 59th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics and the 11th international joint conference on natural language processing (Volume 1: long papers), association for computational linguistics, Online, pp 6153–616 https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.480
Yang P, Chen B, Zhang P, Sun X (2020) Visual agreement regularized training for multi-modal machine translation. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 34:9418–9425
Yang Z, Hirasawa T, Komachi M, Okazaki N (2022) Why videos do not guide translations in video-guided machine translation? An empirical evaluation of video-guided machine translation dataset. J Inform Process 30:388–396
Yao S, Wan X (2020) Multimodal transformer for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 4346–4350
Yin Y, Meng F, Su J, Zhou C, Yang Z, Zhou J, Luo J (2020) A novel graph-based multi-modal fusion encoder for neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.08742
Young P, Lai A, Hodosh M, Hockenmaier J (2014) From image descriptions to visual denotations: new similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist 2:67–78
Zhao Y, Komachi M, Kajiwara T, Chu C (2020) Double attention-based multimodal neural machine translation with semantic image regions. In: Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference of the European association for machine translation, pp 105–114
Zhao Y, Komachi M, Kajiwara T, Chu C (2022) Region-attentive multimodal neural machine translation. Neurocomputing 476:1–13
Zhou M, Cheng R, Lee YJ, Yu Z (2018) A visual attention grounding neural model for multimodal machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, association for computational linguistics, Brussels, Belgium, pp 3643–365https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D18-1400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, S., Duan, K., Ma, W. et al. Dose multimodal machine translation can improve translation performance?. Neural Comput & Applic (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09705-y