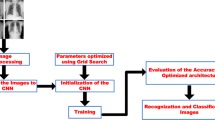
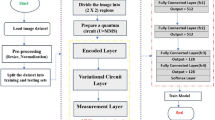
Abstract
Lung diseases are one of the most common diseases around the world. The risk of these diseases are more in under-developed and developing countries, where millions of people are battling with poverty and living in polluted air. Chest X-Ray images are helpful screening tool for lung disease detection. However, disease diagnosis requires expert medical professionals. Furthermore, in developing and under-developed nations, the doctor-to-patient ratio is comparatively poor. Deep learning algorithms have recently demonstrated promise in the analysis of medical images and the discovery of patterns. In this current work, we have proposed a model MLDC (Multi-Lung Disease Classification) to detect common lung diseases. It introduces a MLDC feature extraction model with two different new classifiers, considering ANN (an artificial neural network) and QC (a quantum classifier). In this proposed model, tests are performed on the LDD (Lung Disease Dataset), which includes COVID-19, pneumonia, tuberculosis, and a healthy person’s lung from chest X-ray images. Our proposed model achieves an accuracy of 95.6% for MLDC-ANN and 97.5% for MLDC-QC at a lower computational cost.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Ball RL, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, Ding D, Bagul A, Langlotz CP et al (2018) Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: a retrospective comparison of the chexnext algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med 15(11):1002686
Liu C, Cao Y, Alcantara M (2017) TX-CNN: detecting tuberculosis in chest X-ray images using convolutional neural network, 2314–2318. Cited By :1
Kesim E, Dokur Z, Olmez T (2019) X-ray chest image classification by a small-sized convolutional neural network. In: 2019 scientific meeting on electrical-electronics biomedical engineering and computer science (EBBT), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/EBBT.2019.8742050
Chouhan V, Singh SK, Khamparia A, Gupta D, Tiwari P, Moreira C, Damaševičius R, de Albuquerque VHC (2020) A novel transfer learning based approach for pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020559
Gunraj H, Wang L, Wong A (2020) COVIDNet-CT: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest ct images. Front Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.608525
Maghdid HS, Asaad AT, Ghafoor KZ, Sadiq AS, Mirjalili S, Khan MK (2021) Diagnosing covid-19 pneumonia from x-ray and CT images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms. In: multimodal image exploitation and learning 2021, vol 11734, p 117340. International society for optics and photonics
Ghoshal B, Tucker A (2020) Estimating uncertainty and interpretability in deep learning for coronavirus (COVID-19) detection. arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2003.10769
Wang J-J, Wang L (2022) A cooperative memetic algorithm with feedback for the energy-aware distributed flow-shops with flexible assembly scheduling. Comput Ind Eng 168:108126
Zhao F, Di S, Wang L (2022) A hyperheuristic with q-learning for the multiobjective energy-efficient distributed blocking flow shop scheduling problem. IEEE Transact Cybern
Zhao F, Jiang T, Wang L (2022) A reinforcement learning driven cooperative meta-heuristic algorithm for energy-efficient distributed no-wait flow-shop scheduling with sequence-dependent setup time. IEEE Transact Ind Inf
Cohen JP, Morrison P, Dao L (2020) Covid-19 image data collection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.11597
Kaggle (2020) Kaggle’s chest X-ray images (Pneumonia) dataset. URL: https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia
Arute F, Arya K, Babbush R, Bacon D, Bardin JC, Barends R, Biswas R, Boixo S, Brandao FG, Buell DA et al (2019) Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574(7779):505–510
Nivelkar M, Bhirud S (2022) Modeling of supervised machine learning using mechanism of quantum computing. J Phys Conf Ser 2161:012023 (IOP Publishing)
Dou T, Zhang G, Cui W (2022) Efficient quantum feature extraction for CNN-based learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.01246
Chen G, Chen Q, Long S, Zhu W, Yuan Z, Wu Y (2022) Quantum convolutional neural network for image classification. Pattern Anal Appl, pp 1–13
Choudhuri R, Halder A (2022) Brain mri tumour classification using quantum classical convolutional neural net architecture. Neural Comput Appl, pp 1–12
Cohen JP, Morrison P, Dao L (2020) COVID-19 image data collection. arXiv e-prints, 2003–11597 arXiv:2003.11597 [eess.IV]
Kaggle’s chest X-ray images (Pneumonia) dataset, (2020). https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia. Accessed: 2022-09-30
Tuberculosis (TB) Chest X-ray database. https://www.https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tawsifurrahman/tuberculosis-tb-chest-xray-dataset. Accessed: 2022-09-30
Powers DM (2020) Evaluation: from precision, recall and f-measure to roc, informedness, markedness and correlation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.16061
Actualmed COVID-19 chest X-ray dataset initiative. https://github.com/agchung/Actualmed-COVID-chestxray-dataset
Cohen JP, Morrison P, Dao L (2020) COVID-19 image data collection. arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2003.11597
Narin A, Kaya C, Pamuk Z (2021) Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) using x-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal Appl 24:1207–1220
Loey M, Smarandache F, Khalifa MNE (2020) Within the lack of chest covid-19 x-ray dataset: a novel detection model based on gan and deep transfer learning. Symmetry 12(4):651
Shi F, Wang J, Shi J, Wu Z, Wang Q, Tang Z, He K, Shi Y, Shen D (2021) Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation, and diagnosis for covid-19. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 14:4–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2020.2987975
Oh Y, Park S, Ye JC (2020) Deep learning covid-19 features on cxr using limited training data sets. IEEE Transact Med Imaging 39(8):2688–2700
Khan AI, Shah JL, Bhat MM (2020) Coronet: a deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of covid-19 from chest x-ray images. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 196:105581
Minaee S, Kafieh R, Sonka M, Yazdani S, Soufi GJ (2020) Deep-COVID: Predicting covid-19 from chest x-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med Image Anal 65:101794
Brunese L, Mercaldo F, Reginelli A, Santone A (2020) Explainable deep learning for pulmonary disease and coronavirus covid-19 detection from x-rays. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 196:105608
Ullah Z, Usman M, Gwak J (2023) Mtss-aae: Multi-task semi-supervised adversarial autoencoding for covid-19 detection based on chest x-ray images. Exp Syst Appl 119475
Wang L, Lin ZQ, Wong A (2020) Covid-net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest x-ray images. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12
Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, Valentim CC, Liang H, Baxter SL, McKeown A, Yang G, Wu X, Yan F et al (2018) Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 172(5):1122–1131
Babic D, Jovovic I, Popovic T, Cakic S, Filipovic L (2022) Detecting pneumonia with tensorflow and convolutional neural networks. In: 2022 IEEE international conference on omni-layer intelligent systems (COINS), pp 1–4 . https://doi.org/10.1109/COINS54846.2022.9854948
Rahman T, Khandakar A, Kadir MA, Islam KR, Islam KF, Mazhar R, Hamid T, Islam MT, Kashem S, Mahbub ZB, Ayari MA, Chowdhury MEH (2020) Reliable tuberculosis detection using chest x-ray with deep learning, segmentation and visualization. IEEE Access 8:191586–191601. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3031384
Dey S, Roychoudhury R, Malakar S, Sarkar R (2022) An optimized fuzzy ensemble of convolutional neural networks for detecting tuberculosis from chest x-ray images. Appl Soft Comput 114:108094
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, R., Rao, G.V.E., Banerjea, S. et al. MLDC: multi-lung disease classification using quantum classifier and artificial neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 3803–3816 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09207-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09207-3