Abstract
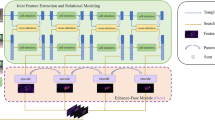
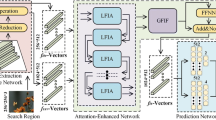
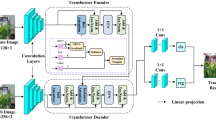
Siamese-based trackers have achieved outstanding tracking performance. However, these trackers in complex scenarios struggle to adequately integrate the valuable target feature information, which results in poor tracking performance. In this paper, a novel shared-encoder dual-pipeline Transformer architecture is proposed to achieve robust visual tracking. The proposed method integrates several main components based on a hybrid attention mechanism, namely the shared encoder, the feature enhancement pipelines with functional complementarity, and the pipeline feature fusion head. The shared encoder is adopted to process template features and provide useful target feature information for the feature enhancement pipeline. The feature enhancement pipeline is responsible for enhancing feature information, establishing feature dependencies between the template and the search region, and employing global information adequately. To further correlate the global information, the pipeline feature fusion head integrates the feature information from the feature enhancement pipelines. Eventually, we propose a robust Siamese-based Repformer tracker, which incorporates a concise tracking prediction network to obtain efficient tracking representations. Experiments show that our tracking method surpasses numerous state-of-the-art trackers on multiple tracking benchmarks, with a running speed of 57.3 fps.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Xu L, Gao M, Liu Z, et al. (2022) Accelerated duality-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. Neural Comput Appl 1–16.
Hu W, Wang Q, Zhang L et al (2023) Siammask: a framework for fast online object tracking and segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(3):3072–3089
Huang H, Liu G, Zhang Y et al (2022) Ensemble siamese networks for object tracking. Neural Comput Appl 34(10):8173–8191
Li S, Zhao S, Cheng B et al (2023) Part-aware framework for robust object tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:750–763
Wang H, Liu J, Su Y et al (2023) Trajectory guided robust visual object tracking with selective remedy. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 33:3425
Zhang J, Yuan T, He Y, et al. (2022) A background-aware correlation filter with adaptive saliency-aware regularization for visual tracking. Neural Comput Appl 1–18.
Zhu XF, Wu XJ, Xu T et al (2021) Complementary discriminative correlation filters based on collaborative representation for visual object tracking. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 31(2):557–568
Chen X, Wang D, Li D, et al. (2022) Efficient visual tracking via hierarchical cross-attention transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.13537
Fu Z, Liu Q, Fu Z, et al. (2021) Stmtrack: template-free visual tracking with space-time memory networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 13774–13783.
Zeng Y, Zeng B, Yin X et al (2022) SiamPCF: siamese point regression with coarse-fine classification network for visual tracking. Appl Intell 52(5):4973–4986
Yu J, Zuo M, Dong L et al (2022) The multi-level classification and regression network for visual tracking via residual channel attention. Digit Signal Process 120:103269
He X, Chen CYC (2022) Learning object-uncertainty policy for visual tracking. Inf Sci 582:60–72
Bolme D S, Beveridge J R, Draper B A, et al. (2010) Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE 2544–2550.
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P et al (2014) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):583–596
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J (2012) Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, October 7-13, 2012, Proceedings, Part IV. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 702–715
Valmadre J, Bertinetto L, Henriques J, et al. (2017) End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 2805–2813.
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, Miksik O, Torr PH (2016) Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 1401–1409.
Danelljan M, Robinson A, Khan FS, Felsberg M (2016) Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham. pp. 472–488.
Danelljan M, Bhat G, Shahbaz KF , Felsberg M (2017) Eco: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 6638–6646.
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, et al. (2015) Convolutional features for correlation filter based visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops 58–66.
Bhat G, Johnander J, Danelljan M, Khan FS, Felsberg M (2018) Unveiling the power of deep tracking. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) pp. 483–498.
Gu F, Lu J, Cai C (2022) RPformer: A robust parallel transformer for visual tracking in complex scenes. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 71:1–14
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. (2016) Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham 850–865.
Li, B., Yan, J., Wu, W., Zhu, Z., & Hu, X. (2018). High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 8971–8980).
Chen X, Yan B, Zhu J, et al. (2021) Transformer tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 8126–8135.
Yan B, Peng H, Fu J, et al. (2021) Learning spatio-temporal transformer for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 10448–10457.
Zhou W, Wen L, Zhang L et al (2021) SiamCAN: real-time visual tracking based on siamese center-aware network. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:3597–3609
Zhang Z, Peng H, Fu J, Li B, Hu W (2020) Ocean: object-aware anchor-free tracking. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision pp. 771–787.
Li Y, Zhu J. (2014) A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham 254–265.
Yuan D, Chang X, Li Z et al (2022) Learning adaptive spatial-temporal context-aware correlation filters for UAV tracking. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl TOMM 18(3):1–18
Yuan D, Chang X, Liu Q, et al. (2023) Active learning for deep visual tracking. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst
Yuan D, Shu X, Liu Q et al (2023) Robust thermal infrared tracking via an adaptively multi-feature fusion model. Neural Comput Appl 35(4):3423–3434
Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, et al. (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision 4310–4318.
Guo, Q., Feng, W., Zhou, C., Huang, R., Wan, L., & Wang, S. (2017). Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1763–1771).
Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wu W, Yan J, Hu W (2018) Distractor-aware siamese networks for visual object tracking. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision pp. 101–117.
Yang K, He Z, Pei W et al (2021) SiamCorners: siamese Corner networks for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Multimedia 24:1956–1967
Yuan D, Chang X, Huang PY, Liu Q, He Z (2020) Self-supervised deep correlation tracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:976–985
Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang F, Xing J, Yan J (2019) Siamrpn++: Evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 4282–4291.
Voigtlaender P, Luiten J, Torr PH, Leibe B (2020) Siam r-cnn: visual tracking by re-detection. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 6578–6588.
Guo D, Wang J, Cui Y, et al. (2020) SiamCAR: Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 6269–6277.
Saribas H, Cevikalp H, Köpüklü O et al (2022) TRAT: tracking by attention using spatio-temporal features. Neurocomputing 492:150–161
Elayaperumal D, Joo YH (2021) Robust visual object tracking using context-based spatial variation via multi-feature fusion. Inf Sci 577:467–482
Bhat G, Danelljan M, Gool LV, Timofte R (2020) Know your surroundings: exploiting scene information for object tracking. In: Proc.European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham pp. 205–221.
Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M (2019) Atom: accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 4660–4669.
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 5998–6008.
Wang Q, Yuan C, Wang J, Zeng W (2018) Learning attentional recurrent neural network for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 21(4):930–942
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S (2020) End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham pp. 213–229.
Liu D, Liu G (2019) A transformer-based variational autoencoder for sentence generation. In: Proc. 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE pp.1–7.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition pp. 770–778.
Ding X, Larson EC (2020) Incorporating uncertainties in student response modeling by loss function regularization. Neurocomputing 409:74–82
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dolla´r P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham pp. 740–755.
Fan H, Lin L, Yang F, Chu P, Deng G, Yu SJ, Bai HX, Xu Y, Liao CY, Ling HB (2019) Lasot: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 5374–5383.
Huang L, Zhao X, Huang K (2021) GOT-10k: a large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43:1562–1577
Loshchilov I, Hutter F (2017) Decoupled weight decay regularization.. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101
Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B (2016) A benchmark and simulator for uav tracking. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham pp. 445–461.
Galoogahi KH, Fagg A, Huang C, Ramanan D, Lucey S (2017) Need for speed: A benchmark for higher frame rate object tracking. In: Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision pp. 1125–1134.
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M (2015) Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37:1834–1848
Kristan M et al. (2018) The sixth visual object tracking vot2018 challenge results. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops
Liang P, Blasch E, Ling H (2015) Encoding color information for visual tracking: algorithms and benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5630–5644
Huang L, Zhao X, Huang K (2020) Globaltrack: A simple and strong baseline for long-term tracking. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 34(07):11037–11044
Bhat G, Danelljan M, Gool LV, Timofte R (2019) Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision pp. 6182–6191.
Nam H, Han B (2016) Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 4293–4302.
Nie J, Wu H, He Z et al (2022) Spreading fine-grained prior knowledge for accurate tracking. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32:6186
Zhang H, Cheng L, Zhang T et al (2022) Target-distractor aware deep tracking with discriminative enhancement learning loss. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32:6267
Lukezic A, Matas J, Kristan M (2020), D3S-A discriminative single shot segmentation tracker. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition pp. 7133–7142.
Zheng L, Tang M, Chen Y, Wang J, Lu H (2020) Learning feature embeddings for discriminant model based tracking. Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis (ECCV) 23(28):759–775
Zhang J, He Y, Wang S (2023) Learning adaptive sparse spatially-regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. IEEE Signal Process Lett 30:11
Ma S, Zhao Z, Hou Z et al (2022) Correlation filters based on multi-expert and game theory for visual object tracking. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 71:1–14
Xu T, Feng ZH, Wu XJ, Kittler J (2019) Learning adaptive discriminative correlation filters via temporal consistency preserving spatial feature selection for robust visual object tracking. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, , pp.5596–5609.
Fan N, Liu Q, Li X et al (2023) Siamese residual network for efficient visual tracking. Inf Sci 624:606
Hu Q, Guo Y, Lin Z et al (2017) Object tracking using multiple features and adaptive model updating. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 66(11):2882–2897
Liu H, Hu Q, Li B et al (2019) Robust long-term tracking via instance-specific proposals. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(4):950–962
Huang B, Xu T, Shen Z et al (2021) SiamATL: online update of siamese tracking network via attentional transfer learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 52:7527
Yao S, Zhang H, Ren W et al (2021) Robust online tracking via contrastive spatio-temporal aware network. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1989–2002
Zhang J, Ma S, Sclaroff S (2014) MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: Proc. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham pp. 188–203.
Yan Y, Guo X, Tang J et al (2021) Learning spatio-temporal correlation filter for visual tracking. Neurocomputing 436:273–282
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve our manuscript. Moreover, this work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China under Grant No. F201123, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52171332 and 52075530, the Green Intelligent Inland Ship Innovation Programme under Grant MC-202002-C01, and the Development Project of Ship Situational Intelligent Awareness System under Grant MC-201920-X01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: FG, JL, CC, QZ, and ZJ; Methodology: FG and JL; Formal analysis and investigation: FG, JL, CC, QZ, and ZJ; Writing—original draft preparation: FG; Writing—review and editing: FG, JL, CC, QZ, and ZJ; Funding acquisition: JL, CC, QZ, and ZJ; Resources: JL, CC, QZ, and ZJ; Supervision: JL and ZJ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, F., Lu, J., Cai, C. et al. Repformer: a robust shared-encoder dual-pipeline transformer for visual tracking. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 20581–20603 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08824-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08824-2