Abstract
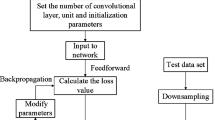
According to the coexistence of fuzziness and randomness of risk factors in engineering early warning, this paper proposes a risk early warning model based on a convolutional neural network, which identifies and analyzes the risk points in engineering through engineering site pictures and provides early warning for engineering risk points in time. The risk warning model fully characterizes the fuzziness and randomness of risk, and the warning results are more objective and in line with the actual situation, which provides a more feasible engineering risk warning method. The experiments prove that the method can accurately warn of project risks, and the warning readiness rate reaches 91.3%.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Seo S, Yoon Y, Lee J, Na J, Lee C (2022) Deep neural network-based optimization framework for safety evacuation route during toxic gas leak incidents. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 218(12):108102
Zhu T, Yin X, Na X, Li B (2020) Research on a novel vehicle rollover risk warning algorithm based on support vector machine model. IEEE Access 8:108324–108334
Zhao J, Ni S, Yang L, Zhang Z, Gong Y, You X (2019) Multiband cooperation for 5g hetnets: a promising network paradigm. IEEE Veh Technol Mag 14(4):85–93
Shen T, Nagai Y, Gao C (2020) Design of building construction safety prediction model based on optimized BP neural network algorithm. Soft Comput 24(11):7839–7850
Zhang L, Zhou G, Han Y, Lin H, Wu Y (2018) Application of internet of things technology and convolutional neural network model in bridge crack detection. IEEE Access 6:39442–39451
Ge C, Rao Y, Ou J, Fan C, Ou J, Fan D (2022) Joint offloading design and bandwidth allocation for ris-aided multiuser mec networks. Phys Commun 53:101752
Leveson NG (2015) A systems approach to risk management through leading safety indicators. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 136:17–34
Meng F (2021) Safety warning model of coal face based on FCM fuzzy clustering and GA-BP neural network. Symmetry 13(6):1082
Xu W, Yang Z, Ng DW-K, Levorato M, Eldar YC, Debbah M (2022) Edge learning for b5g networks with distributed signal processing: Semantic communication, edge computing, and wireless sensing. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 2022:1–10
Zhao J, Li Q, Gong Y, Zhang K (2019) Computation offloading and resource allocation for cloud assisted mobile edge computing in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(8):7944–7956
Zhao J, Sun X, Li Q, Ma X (2020) Edge caching and computation management for real-time internet of vehicles: an online and distributed approach. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 22(4):2183–2197
Liu W, Chen Z, Zheng M (2020) An audio-based fault diagnosis method for quadrotors using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. In: 2020 American Control Conference, ACC 2020, Denver, CO, USA, July 1–3, 2020. IEEE, 2020, pp 1367–1372
Zhang L, Zhou W, Xia J, Gao C, Zhu F, Fan C, Ou J (2022) Dqn-based mobile edge computing for smart internet of vehicle. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2022(1):1–16
Hu X, Zhong C, Zhu Y, Chen X, Zhang Z (2020) Programmable metasurface-based multicast systems: design and analysis. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 38(8):1763–1776
Hu X, Zhong C, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhang Z (2020) Location information aided multiple intelligent reflecting surface systems. IEEE Trans Commun 68(12):7948–7962
Hu X, Wang J, Zhong C (2020) Statistical CSI based design for intelligent reflecting surface assisted MISO systems. Sci China Inf Sci 63(12):222303
Tang S, Xia J, Fan L, Lei X, Xu W, Nallanathan A (2022) A Dilated convolution based CSI feedback compression for massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol
Lu J, Chen L, Xia J, Zhu F, Tang M, Fan C, Ou J (2022) Analytical offloading design for mobile edge computing-based smart internet of vehicle. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2022(1):1–19
He R, Li X, Chen G, Chen G, Liu Y (2020) Generative adversarial network-based semi-supervised learning for real-time risk warning of process industries. Expert Syst Appl 150:113244
Liang Y, Liu Q (2022) Early warning and real-time control of construction safety risk of underground engineering based on building information modeling and internet of things. Neural Comput Appl 34(5):3433–3442
Chen L, Zhao R, He K, Zhao Z, Fan L (2021) Intelligent ubiquitous computing for future uav-enabled mec network systems. Cluster Comput 25:1–11
Lai X, Xia J, Fan L, Duong TQ, Nallanathan A (2022) Outdated access point selection for mobile edge computing with cochannel interference. IEEE Trans Veh Technol
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare(s) that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Chen, Z. Early warning control model and simulation study of engineering safety risk based on a convolutional neural network. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 24587–24594 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-08170-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-08170-9