Abstract
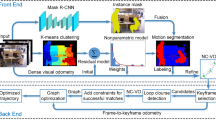
The traditional visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) systems have a high dependence on static world assumption, which makes them easy to fail to track in dynamic environments. In this paper, we propose a real-time dynamic visual SLAM system (RTDSLAM) based on ORB-SLAM3 to realize accurate pose estimation of the camera in indoor dynamic environments. We regard the static objects in the environments as a complete virtual rigid body and add two motion removal modules to handle the dynamic feature points without the aid of the camera’s ego motion. The geometry-based motion removal module utilizes the point correlations and the structural invariance of rigid body to detect sparse dynamic feature points between two keyframes, and the clustering of depth images helps find the complete dynamic regions. Meanwhile, the template-based motion removal module uses template matching to fast track the known moving objects between ordinary frames. The dynamic feature points located on moving objects are removed and only static feature points are reserved for pose estimation. We evaluate our system on public TUM and Bonn datasets, and the comparison with state-of-the-art dynamic visual SLAM systems shows our advantages both in runtime and the accuracy of pose estimation. Besides, the test in real-world scenes shows the effectiveness of our system in dynamic environments.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Popović G, Cvišić I, Écorchard G et al (2022) Human localization in robotized warehouses based on stereo odometry and ground-marker fusion. Rob Comput Integr Manuf 73:102241
Davison AJ, Reid ID, Molton ND et al (2007) MonoSLAM: real-time single camera SLAM. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(6):1052–1067
Campos C, Elvira R, Rodríguez JJG et al (2021) ORB-SLAM3: an accurate open-source library for visual, visual-inertial, and multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans Rob 37(6):1874–1890
Engel J, Koltun V, Cremers D (2018) Direct sparse odometry. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(3):611–625
Qin T, Li P, Shen S (2018) VINS-Mono: a robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Trans Rob 34(4):1004–1020
Fischler MA, Bolles RC (1981) Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun ACM 24(6):381–395
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(12):2481–2495
Bochkovskiy A, Wang C-Y, Liao H-YM (2020) Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, pp 2961–2969
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) Algorithm AS 136: a k-means clustering algorithm. J R Stat Soc 28(1):100–108
Sun Y, Liu M, Meng M et al (2017) Improving RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments: a motion removal approach. Rob Auton Syst 89:110–122
Tan W, Liu H, Dong Z, et al (2013) Robust monocular SLAM in dynamic environments. In: 2013 IEEE international symposium on mixed and augmented reality (ISMAR), Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2013, pp 209–218
Sun Y, Liu M, Meng MQ-H (2018) Motion removal for reliable RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments. Rob Auton Syst 108:115–128
Bahraini MS, Bozorg M, Rad AB (2018) SLAM in dynamic environments via ML-RANSAC. Mechatronics 49:105–118
Rousseeuw PJ (1984) Least median of squares regression. J Am Stat Assoc 79(388):871–880
Yu C, Liu Z, Liu X-J, et al (2018) DS-SLAM: A semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments. In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, pp 1168–1174
Mur-Artal R, Tardós JD (2017) Orb-slam2: an open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans Rob 33(5):1255–1262
Ji T, Wang C, Xie L (2021) Towards real-time semantic RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments. In: 2021 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Xi'an, China, pp 11175–11181
Zhong YH, Hu SS, Huang G et al (2022) WF-SLAM: a robust VSLAM for dynamic scenarios via weighted features. IEEE Sens J 22(11):10818–10827
Yang S, Fan G, Bai L et al (2020) SGC-VSLAM: a semantic and geometric constraints VSLAM for dynamic indoor environments. Sensors 20(8):2432
Ma P, Bai Y, Zhu J et al (2019) DSOD: DSO in dynamic environments. IEEE Access 7:178300–178309
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2018) Yolov3: an incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767
Saputra MRU, Markham A, Trigoni N (2019) Visual SLAM and structure from motion in dynamic environments: a survey. ACM Comput Surv 51(2):1–36
Sheng C, Pan SG, Gao W et al (2020) Dynamic-DSO: direct sparse odometry using objects semantic information for dynamic environments. Appl Sci-Basel 10(4):1467
Soares JCV, Gattass M, Meggiolaro MA (2019) Visual SLAM in human populated environments: exploring the trade-off between accuracy and speed of YOLO and Mask R-CNN. In: 2019 19th international conference on advanced robotics (ICAR), Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2019, pp 135–140
Wu W, Guo L, Gao H et al (2022) YOLO-SLAM: a semantic SLAM system towards dynamic environment with geometric constraint. Neural Comput Appl 34(8):6011–6026
Ding Z, Huang R, Hu B (2019) Robust indoor slam based on pedestrian recognition by using rgb-d camera. In: 2019 Chinese automation congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, pp 292–297
Bescos B, Facil JM, Civera J et al (2018) DynaSLAM: tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Rob Autom Lett 3(4):4076–4083
Li P, Zhang G, Zhou J, et al (2019) Study on slam algorithm based on object detection in dynamic scene. In: 2019 international conference on advanced mechatronic systems (ICAMechS), Kusatsu, Japan, 2019, pp 363–367
Dai W, Zhang Y, Li P et al (2020) RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using point correlations. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(1):373–389
Barber CB, Dobkin DP, Huhdanpaa H (1996) The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Trans Math Softw 22(4):469–483
Liu G, Zeng W, Feng B et al (2019) DMS-SLAM: a general visual SLAM system for dynamic scenes with multiple sensors. Sensors 19(17):3714
Xie W, Liu PX, Zheng M (2021) Moving object segmentation and detection for robust RGBD-SLAM in dynamic environments. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 70:1–8
Korman S, Reichman D, Tsur G, et al (2013) Fast-match: fast affine template matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2331–2338
Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, et al (2012) A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 2012, pp 573–580
Palazzolo E, Behley J, Lottes P, et al (2019) ReFusion: 3D reconstruction in dynamic environments for RGB-D cameras exploiting residuals. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), 2019, pp 7855–7862
Scona R, Jaimez M, Petillot YR, et al (2018) Staticfusion: background reconstruction for dense rgb-d slam in dynamic environments. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2018, pp 3849–3856
Li S, Lee D (2017) RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using static point weighting. IEEE Rob Autom Lett 2(4):2263–2270
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515010095, 2021A1515010506), the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Royal Society of Edinburgh (51911530245), the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant (51675186)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, author- ship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Yao, X., Ma, N. et al. Real-time motion removal based on point correlations for RGB-D SLAM in indoor dynamic environments. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 8707–8722 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07879-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07879-x