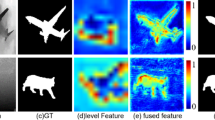
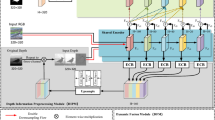
Abstract
Significant improvement has been noticed in salient object detection by multi-modal cross-complementary fusion between Depth and RGB features. The multi-modal feature extracting backbone of existing networks cannot extract complex RGB and color images effectively, which limits the performance of salient object detection in complex and challenging situations. In this paper, a composite backbone network with a mutual attention-based distinguished window is proposed to enhance the salient region and minimize the non-salient region. The distinguished window based on the channel-wise, spatial, mutual, and feature-level attention is inserted in each encoder stage to enhance the saliency features. Finally, a novel self-learning-based decoder, which is capable of utilizing multi-level features is designed to get the accurately dense prediction. The multi-level fusion is guided by deep global localized features. The performance of salient object detection could significantly be enhanced in this way. The extensive comparative and ablation experiments for the proposed framework have been conducted on the seven publicly available datasets for visual saliency. Experimental results have illustrated the effectiveness of the proposed framework and show better performance in comparison with the closely related state-of-the-art methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong S, You T, Kwak S, Han B (2015) In: International conference on machine learning (PMLR), pp. 597–606
Jerripothula KR, Cai J, Yuan J (2016) Image co-segmentation via saliency co-fusion. IEEE Trans Multimedia 18(9):1896–1909
Durand T, Mordan T, Thome N, Cord M (2017) In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR 2017)
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Wang X (2013) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3586–3593
Kompella A, Kulkarni RV (2021) A semi-supervised recurrent neural network for video salient object detection. Neural Comput Appl 33(6):2065–2083
Dong S, Gao Z, Pirbhulal S, Bian GB, Zhang H, Wu W, Li S (2020) Iot-based 3d convolution for video salient object detection. Neural Comput Appl 32(3):735–746
Wang W, Shen J (2017) In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision , pp. 2186–2194
Cheng Y, Fu H, Wei X, Xiao J, Cao X (2014) In: Proceedings of international conference on internet multimedia computing and service (ACM), p. 23
Ju R, Ge L, Geng W, Ren T, Wu G (2014) In: 2014 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (IEEE), pp. 1115–1119
Cong R, Lei J, Zhang C, Huang Q, Cao X, Hou C (2016) Saliency detection for stereoscopic images based on depth confidence analysis and multiple cues fusion. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(6):819–823
Wang N, Gong X (2019) Adaptive fusion for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Access 7:55277–55284
Chen S, Fu Y (2020) In European conference on computer vision (Springer), pp. 520–538
Liu N, Zhang N, Han J (2020) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 13,756–13,765
Fu K, Fan D.P, Ji G.P, Zhao Q (2020) In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3052–3062
Li C, Cong R, Piao Y, Xu Q, Loy CC (2020) In: European conference on computer vision (Springer), pp. 225–241
Zhang J, Fan D.P, Dai Y, Anwar S, Saleh F.S, Zhang T, Barnes N (2020) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 8582–8591
Chen H, Li Y (2019) Three-stream attention-aware network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(6):2825–2835
Fan DP, Lin Z, Zhang Z, Zhu M, Cheng MM (2020) Rethinking rgb-d salient object detection: models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 32(5):2075–2089
Zhu C, Li G, Wang W, Wang R (2017) In: IEEE international conference on computer vision workshop (ICCVW)
Feng D, Barnes N, You S, McCarthy C (2016) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 2343–2350
Song H, Liu Z, Du H, Sun G, Le Meur O, Ren T (2017) Depth-aware salient object detection and segmentation via multiscale discriminative saliency fusion and bootstrap learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(9):4204–4216
Kienzle W, Franz MO, Schölkopf B, Wichmann FA (2009) Center-surround patterns emerge as optimal predictors for human saccade targets. J Vis 9(5):7–7
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 2814–2821
Zhang J, Sclaroff S (2016) Exploiting surroundedness for saliency detection: a boolean map approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(5):889–902
Zhou X, Wang Y, Zhu Q, Xiao C, Lu X (2019) Ssg: superpixel segmentation and grabcut-based salient object segmentation. Vis Comput 35(3):385–398
Alexe B, Deselaers T, Ferrari V (2012) Measuring the objectness of image windows. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(11):2189–2202
Zhong G, Liu R, Cao J, Su Z (2016) A generalized nonlocal mean framework with object-level cues for saliency detection. Vis Comput 32(5):611–623
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, Liu F (2012) In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (IEEE), pp. 454–461
Qu L, He S, Zhang J, Tian J, Tang Y, Yang Q (2017) Rgbd salient object detection via deep fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(5):2274–2285
Liu Z, Shi S, Duan Q, Zhang W, Zhao P (2019) Salient object detection for rgb-d image by single stream recurrent convolution neural network. Neurocomputing 363:46–57
Imamoglu N, Shimoda W, Zhang C, Fang Y, Kanezaki A, Yanai K, Nishida Y (2018) An integration of bottom-up and top-down salient cues on rgb-d data: saliency from objectness versus non-objectness. SIViP 12(2):307–314
Han J, Chen H, Liu N, Yan C, Li X (2017) Cnns-based rgb-d saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(11):3171–3183
Luo A, Li X, Yang F, Jiao Z, Cheng H, Lyu S (2020) In: European conference on computer vision (Springer), pp. 346–364
Chen H, Li Y (2018) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 3051–3060
Hou Q, Cheng M.M, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr P.H (2017) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 3203–3212
Zhao J.X, Cao Y, Fan D.P, Cheng M.M, Li X.Y, Zhang L (2019) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 3927–3936
Zhu C, Cai X, Huang K, Li T.H, Li G (2019) In: 2019 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME) (IEEE), pp. 199–204
Zhao X, Zhang L, Pang Y, Lu H, Zhang L (2020) In: European conference on computer vision (Springer), pp. 646–662
Chen Z, Cong R, Xu Q, Huang Q (2021) Dpanet: depth potentiality-aware gated attention network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:7012–7024
Ye L, Rochan M, Liu Z, Wang Y (2019) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 10,502–10,511
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 7794–7803
Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K (2007) Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(8):2080–2095
Piao Y, Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Lu H (2019) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision , pp. 7254–7263
Shokri M, Harati A, Taba K (2020) Salient object detection in video using deep non-local neural networks. J Vis Commun Image Represent 68:102–769
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 7132–7141
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhudinov R, Zemel R, Bengio Y (2015) In: International conference on machine learning (PMLR), pp. 2048–2057
Yu S, Zhang B, Xiao J, Lim E.G (2021) In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI) (AAAI Palo Alto, CA, USA)
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) In: International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (Springer), pp. 234–241
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M (2019) In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7479–7489
Peng H, Li B, Xiong W, Hu W, Ji R (2014) In: European conference on computer vision (Springer), pp. 92–109
Zhu C, Li G (2017) In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, pp. 3008–3014
Li N, Ye J, Ji Y, Ling H, Yu J (2014) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 2806–2813
Fan D.P, Cheng M.M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A (2017) In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision , pp. 4548–4557
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H, Li J (2015) Salient object detection: A benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) In: Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE conference on (IEEE), pp. 733–740
Fan D.P, Gong C, Cao Y, Ren B, Cheng M.M, Borji A (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.10421
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T, Lin Z, Gimelshein N, Antiga L et al (2019) Pytorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 32:8026–8037
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition , pp. 1–9
Al Azzeh J, Alhatamleh H, Alqadi ZA, Abuzalata MK (2016) Creating a color map to be used to convert a gray image to color image. Int J Comput Appl 153(2):31–34
Kingma D.P, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Piao Y, Lu H (2020) In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th european conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVIII 16 (Springer), pp. 52–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.K., Srivastava, R. SL-Net: self-learning and mutual attention-based distinguished window for RGBD complex salient object detection. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 595–609 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07772-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07772-7