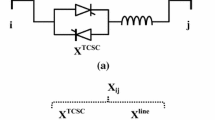
Abstract
Optimal power flow (OPF) is one of the challenging optimization problems in power domain. The complexity of the problem escalates with incorporation of uncertain and intermittent renewable sources into the electrical network. Flexible AC transmission system (FACTS) devices are also becoming more commonplace in modern power system to mitigate growing demand and to relieve congestion from the network. This paper aims to solve the OPF where the generation cost is optimized with incorporation of stochastic wind power and several types of FACTS devices such as static VAR compensator, thyristor-controlled series compensator and thyristor-controlled phase shifter. Case studies with both fixed and uncertain load demands are performed. The stochastic wind energy and load demand are modeled using suitable probability density functions. Optimization objective considers cost of thermal generation, direct cost of scheduled wind power, penalty cost for underestimation and reserve cost for overestimation of the wind power. In addition, both locations and ratings of the FACTS devices are optimized to minimize total generation cost of the system. Success history-based adaptive differential evolution (SHADE), a powerful evolutionary algorithm, is adopted to perform the optimization task. The constraints of OPF problem are handled using superiority of feasible solutions (SF) method. The integration approach of SF method with several popular metaheuristic algorithms has been proposed in this work, and a detailed comparative analysis among various algorithms establishes SHADE algorithm to be the best performer.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesh Kumar A, Premalatha L (2015) Optimal power flow for a deregulated power system using adaptive real coded biogeography-based optimization. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 73:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.05.011
Daryani N, Hagh MT, Teimourzadeh S (2016) Adaptive group search optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimal power flow problem. Appl Soft Comput J 38:1012–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.057
Mahdad B, Srairi K (2016) Security constrained optimal power flow solution using new adaptive partitioning flower pollination algorithm. Appl Soft Comput J 46:501–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.05.027
Chaib AE, Bouchekara HREH, Mehasni R, Abido MA (2016) Optimal power flow with emission and non-smooth cost functions using backtracking search optimization algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 81:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.02.004
Mohamed AAA, Mohamed YS, El-Gaafary AAM, Hemeida AM (2017) Optimal power flow using moth swarm algorithm. Electr Power Syst Res 142:190–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2016.09.025
Biswas PP, Suganthan PN, Mallipeddi R, Amaratunga GAJ (2018) Optimal power flow solutions using differential evolution algorithm integrated with effective constraint handling techniques. Eng Appl Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2017.10.019
Shi L, Wang C, Yao L, Ni Y, Bazargan M (2012) Optimal power flow solution incorporating wind power. IEEE Syst J 6(2):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2011.2162896
Roy R, Jadhav HT (2015) Optimal power flow solution of power system incorporating stochastic wind power using Gbest guided artificial bee colony algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 64:562–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.07.010
Panda A, Tripathy M (2014) Optimal power flow solution of wind integrated power system using modified bacteria foraging algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 54:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.07.018
Panda A, Tripathy M (2015) Security constrained optimal power flow solution of wind-thermal generation system using modified bacteria foraging algorithm. Energy 93:816–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.09.083
Biswas PP, Suganthan PN, Amaratunga GAJ (2017a) Optimal power flow solutions incorporating stochastic wind and solar power. Energy Convers Manag 148:1194–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.06.071
Ongsakul W, Bhasaputra P (2002) Optimal power flow with FACTS devices by hybrid TS/SA approach. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 24(10):851–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-0615(02)00006-6
Basu M (2008) Optimal power flow with FACTS devices using differential evolution. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 30(2):150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2007.06.011
Sonmez Y, Guvenc U, Duman S, Yorukeren N (2012) Optimal power flow incorporating FACTS devices using gravitational search algorithm. In: 2012 International symposium on innovations in intelligent systems and applications, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/INISTA.2012.6246993.
Mahdad B, Srairi K, Bouktir T (2010) Optimal power flow for large-scale power system with shunt FACTS using efficient parallel GA. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 32(5):507–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2009.09.013
Naderi E, Pourakbari-Kasmaei M, Abdi H (2019) An efficient particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve optimal power flow problem integrated with FACTS devices. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.04.012
Berrouk F, Bounaya K (2018) Optimal power flow for multi-FACTS power system using hybrid PSO-PS algorithms. J Control Autom Electr Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-017-0362-7
Mukherjee A, Mukherjee V (2016) Chaotic krill herd algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch considering FACTS devices. Appl Soft Comput J 44:163–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.03.008
Dutta S, Paul S, Roy PK (2018) Optimal allocation of SVC and TCSC using quasi-oppositional chemical reaction optimization for solving multi-objective ORPD problem. J Electr Syst Inf Technol 5(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesit.2016.12.007
Benabid R, Boudour M, Abido MA (2009) Optimal location and setting of SVC and TCSC devices using non-dominated sorting particle swarm optimization. Electr Power Syst Res 79(12):1668–1677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2009.07.004
Sebaa K, Bouhedda M, Tlemçani A, Henini N (2014) Location and tuning of TCPSTs and SVCs based on optimal power flow and an improved cross-entropy approach. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 54:536–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.08.002
Sakr WS, El-Sehiemy RA, Azmy AM (2016) Optimal allocation of TCSCs by adaptive DE algorithm. IET Gener Transm Distrib 10(15):3844–3854. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2016.0362
Ziaee O, Choobineh FF (2017a) Optimal location-allocation of TCSC devices on a transmission network. IEEE Trans Power Syst 32(1):94–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2016.2556424
Agrawal R, Bharadwaj SK, Kothari DP (2018) Population based evolutionary optimization techniques for optimal allocation and sizing of Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor. J Electr Syst Inf Technol 5(3):484–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesit.2017.04.004
Shafik MB, Chen H, Rashed GI, El-Sehiemy RA (2019) Adaptive multi objective parallel seeker optimization algorithm for incorporating TCSC devices into optimal power flow framework. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905266
Taher MA, Kamel S, Jurado F, Ebeed M (2019) Optimal power flow solution incorporating a simplified UPFC model using lightning attachment procedure optimization. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12170
Duman S, Li J, Wu L, Guvenc U (2019) Optimal power flow with stochastic wind power and FACTS devices: a modified hybrid PSOGSA with chaotic maps approach. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04338-y
Elmitwally A, Eladl A (2016) Planning of multi-type FACTS devices in restructured power systems with wind generation. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 77:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.11.023
Aghaebrahimi MR, Golkhandan RK, Ahmadnia S (2016) Localization and sizing of FACTS devices for optimal power flow in a system consisting wind power using HBMO. In: Proceedings of 18th mediterranean electrotechnical conference on intelligent and efficient technologies and services for the citizen, MELECON 2016, April, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/MELCON.2016.7495372
Abdelaziz AY, El-Sharkawy MA, Attia MA, El-Saadany EF (2014) Optimal location of series FACTS to improve the performance of power system with wind penetration. In: IEEE power and energy society general meeting, vol. 2014, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/PESGM.2014.6939190
Ziaee O, Choobineh F (2017b) Optimal location-allocation of TCSCs and transmission switch placement under high penetration of wind power. IEEE Trans Power Syst 32(4):3006–3014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2016.2628053
Tanabe R, Fukunaga A (2013) Success-history based parameter adaptation for differential evolution. In: 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation CEC 2013, no 3, pp 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2013.6557555
Biswas PP, Mallipeddi R, Suganthan PN, GAJ Amaratunga (2018) Optimal reconfiguration and distributed generator allocation in distribution network using an advanced adaptive differential evolution. In: 2017 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence, SSCI 2017—Proceedings, vol 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2017.8280824
Biswas PP, Suganthan P, Amaratunga GAJ (2017b) Optimal placement of wind turbines in a windfarm using L-SHADE algorithm. IEEE Congr Evol Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2017.7969299
Biswas PP, Awad NH, Suganthan P, Ali MZ, Amaratunga GAJ (2017) Minimizing THD of multilevel inverters with optimal values of DC voltages and switching angles using LSHADE-EpSin algorithm. IEEE Congr Evol Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2017.7969298
Biswas PP, Suganthan PN, Amaratunga GAJ (2017c) Minimizing harmonic distortion in power system with optimal design of hybrid active power filter using differential evolution. Appl Soft Comput J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.08.031
Biswas PP (2019) Evolutionary algorithms for solving power system optimization problems. Nanyang Technological University
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution: a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. Technical report, TR06, Erciyes Univ.
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: MHS'95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, IEEE, pp 39-43
Yang XS (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32894-7_27
Nayyar A (2018) Advances in swarm intelligence for optimizing problems in computer science, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Alsac O, Stott B (1974) Optimal load flow with steady-state security. IEEE Trans Power Appar Syst 93(3):745–751. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAS.1974.293972
Biswas PP, Suganthan PN, Qu BY, Amaratunga GAJ (2018) Multiobjective economic-environmental power dispatch with stochastic wind-solar-small hydro power. Energy 150:1039–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.002
Cai LJ, Erlich I, Stamtsis GC (2004) Optimal choice and allocation of FACTS devices in deregulated electricity market using genetic algorithms. In: 2004 IEEE PES power systems conference and exposition, vol 1, no c, pp 201–207. https://doi.org/10.1109/PSCE.2004.1397562.
Abaci K, Yamacli V (2016) Differential search algorithm for solving multi-objective optimal power flow problem. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 79:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.12.021
Zimmerman RD, Murillo-Sánchez CE, Thomas RJ Matpower. http://www.pserc.cornell.edu/matpower
Mallipeddi R, Suganthan PN (2010) Ensemble of constraint handling techniques. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 14(4):561–579. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2009.2033582
Mallipeddi R, Suganthan PN, Pan QK, Tasgetiren MF (2011) Differential evolution algorithm with ensemble of parameters and mutation strategies. Appl Soft Comput J 11(2):1679–1696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2010.04.024
Tanabe R, Fukunaga AS (2014) Improving the search performance of SHADE using linear population size reduction. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation CEC 2014, pp 1658–1665. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2014.6900380.
Bhattacharyya B, Kumar S (2016) Loadability enhancement with FACTS devices using gravitational search algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 78:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.11.114
Mohseni-Bonab SM, Rabiee A, Mohammadi-Ivatloo B (2016) Voltage stability constrained multi-objective optimal reactive power dispatch under load and wind power uncertainties: a stochastic approach. Renew Energy 85:598–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.07.021
Biswas PP, Suganthan PN, Mallipeddi R, Amaratunga GAJ (2019) Optimal reactive power dispatch with uncertainties in load demand and renewable energy sources adopting scenario-based approach. Appl Soft Comput 75:616–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.11.042
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, P.P., Arora, P., Mallipeddi, R. et al. Optimal placement and sizing of FACTS devices for optimal power flow in a wind power integrated electrical network. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 6753–6774 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05453-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05453-x