Abstract
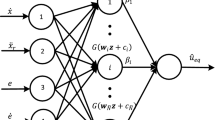
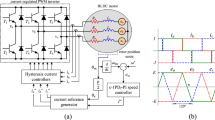
This paper presents an extreme learning machine-based super-twisting repetitive control (ELMSTRC) to improve the tracking accuracy of periodic signal with less chattering. The proposed algorithm is robust against the plant uncertainties caused by mass and viscous friction variations. Moreover, it compensates the nonlinear friction and the backlash by using extreme learning machine based super-twisting algorithm. Firstly, a repetitive control is designed to track the periodic reference and compensate the viscous friction. Then, a stable extreme learning machine-based super-twisting control is constructed to compensate the aperiodic disturbance, nonlinear friction, backlash and plant uncertainties. The stability of ELMSTRC system is analysed based on Lyapunov stability criteria. The proposed algorithm is verified on a brushless DC servo motor with various loading, backlash and friction conditions. The simulation and experimental comparisons highlight the advantages of the proposed algorithm.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue T, Nakano M, Iwai S (1981) High accuracy control of a proton synchrotron magnet power supply. In: Proceedings of 8th world congress IFAC, Kyoto, August 1981, pp 3137–3142
Francis BA, Wonham WM (1975) The internal model principle for linear multivariable regulators. Appl Math Optim 2(2):170–194
Hara S, Yamamoto Y, Omata T, Nakano M (1988) Repetitive control system: a new type servo system for periodic exogenous signals. IEEE Trans Autom Control 33(7):659–666
Chen S, Lai YM, Tan SC, Tse CK (2009) Fast response low harmonic distortion control scheme for voltage source inverters. IET Power Electron 2(5):574–584. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2008.0149
Kurniawan E, Cao Z, Man Z (2014) Design of robust repetitive control with time-varying sampling periods. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 61(6):2834–2841. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2276033
Sayem AHM, Cao Z, Man Z (2017) Model free ESO-based repetitive control for rejecting periodic and aperiodic disturbances. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 64(4):3433–3441. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2606086
Chuei R, Cao Z, Man Z (2017) Super twisting observer based repetitive control for aperiodic disturbance rejection in a brushless DC servo motor. Int J Control Autom Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-016-0415-x
Hamza MF, Yap HJ, Choudhury IA, Chiroma H, Kumbasar T (2018) A survey on advancement of hybrid type 2 fuzzy sliding mode control. Neural Comput Appl 30(2):331–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3144-z
Yuan X, Yang Y, Wang H, Wang Y (2013) Genetic algorithm-based adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for electronic throttle valve. Neural Comput Appl 23(1):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1327-1
Hsu C-F, Kao W-F (2018) Perturbation wavelet neural sliding mode position control for a voice coil motor driver. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3413-5
Levant A (1993) Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control. Int J Control 58(6):1247–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207179308923053
Chuei R, Cao Z, Man Z (2016) Design of super twisting repetitive control. In: 2016 IEEE 11th conference on industrial electronics and applications (ICIEA), 5–7 June 2016, pp 758–762. https://doi.org/10.1109/iciea.2016.7603683
Nordin M, Gutman PO (2002) Controlling mechanical systems with backlash—a survey. Automatica 38(10):1633–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-1098(02)00047-X
Coulomb damping. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coulomb_damping. Accessed 14 Sept 2017
Acho L, Iurian C, Ikhouane F, Rodellar J (2007) Robust-adaptive control of mechanical systems with friction: application to an industrial emulator. In: Proceedings of 2007 American control conference, 9–13 July 2007, pp 5970–5974. https://doi.org/10.1109/acc.2007.4282379
Cai M, Xiang Z (2018) Adaptive finite-time control of a class of non-triangular nonlinear systems with input saturation. Neural Comput Appl 29(7):565–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2540-0
Li Y, Tong S, Li T (2013) Adaptive fuzzy output feedback control of nonlinear uncertain systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis based on modular design. Neural Comput Appl 23(1):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1355-5
Çetin M, Bahtiyar B, Beyhan S (2019) Adaptive uncertainty compensation-based nonlinear model predictive control with real-time applications. Neural Comput Appl 31(2):1029–1043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3068-7
Liu J (2013) Radial basis function (RBF) neural network control for mechanical systems: design, analysis and matlab simulation. Springer, Berlin
Wang H, Xu Z, Do MT, Zheng J, Cao Z, Xie L (2015) Neural-network-based robust control for steer-by-wire systems with uncertain dynamics. Neural Comput Appl 26(7):1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1819-2
Eski İ, Yıldırım Ş (2017) Neural network-based fuzzy inference system for speed control of heavy duty vehicles with electronic throttle control system. Neural Comput Appl 28(1):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2362-0
Yan H, Li Y (2017) Adaptive NN prescribed performance control for nonlinear systems with output dead zone. Neural Comput Appl 28(1):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2043-4
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00994018
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Rong H-J, Zhao G-S (2013) Direct adaptive neural control of nonlinear systems with extreme learning machine. Neural Comput Appl 22(3):577–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0805-1
Yang Y, Wang Y, Yuan X, Chen Y, Tan L (2013) Neural network-based self-learning control for power transmission line deicing robot. Neural Comput Appl 22(5):969–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0789-x
Yang C, Huang K, Cheng H, Li Y, Su C (2017) Haptic Identification by ELM-controlled uncertain manipulator. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern: Syst 47(8):2398–2409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2676022
Hu Y et al (2019) Extreme-learning-machine-based FNTSM control strategy for electronic throttle. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04446-9
Doh TY, Ryoo JR, Chung MJ (2006) Design of a repetitive controller: an application to the track-following servo system of optical disk drives. IEE Proc Control Theory Appl 153(3):323–330
Liu J, Wang X (2011) Advanced sliding mode control for mechanical systems. Springer, Berlin
Levant A (1998) Robust exact differentiation via sliding mode technique. Automatica 34(3):379–384
Manual For Model 220 Industrial Emulator/Servo Trainer (1995), 2.3 edn. Educational Control Products, Bell Canyon, CA
Meng X, Rozycki P, Qiao J, Wilamowski BM (2018) Nonlinear system modeling using RBF networks for industrial application. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 14(3):931–940. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2017.2734686
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuei, R., Cao, Z. Extreme learning machine-based super-twisting repetitive control for aperiodic disturbance, parameter uncertainty, friction, and backlash compensations of a brushless DC servo motor. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 14483–14495 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04965-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04965-w