Abstract
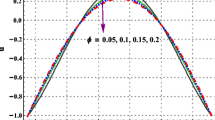
Analysis of the carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluids in a channel with non-parallel stretchable walls is presented. Water is taken as the base fluid for the analysis. The governing partial differential equations governing the flow are transformed to a set of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Solution of the problem is obtained using a numerical scheme as well as an analytical procedure called the differential transform method. Two types of CNTs called the single-walled carbon nanotubes and multi-walled carbon nanotubes are considered for the analysis. To examine the influence of involved parameters on velocity and temperature profiles, graphical analysis is carried out coupled with comprehensive discussions. The expressions for skin friction coefficient and the Nusselt number are formulated, and variations in these two for different values of parameters are presented graphically. Results obtained in this study are compared with some of the already existing results in the literature and found to be in exceptional agreement.





































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. In: Siginer DA, Wang HP (eds) Developments and applications of non-newtonian flows, ASME FED, vol 231/MD-vol 66, pp 99–105
Choi SUS, Zhang ZG, Yu W, Lockwood FE, Grulke EA (2001) Anomalously thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl Phys Lett 79:2252–2254
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transfer 128:240–250
Hamilton RL, Crosser OK (1962) Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 1(3):187–191
Maxwell JC (1904) Electricity and magnetism, 3rd edn. Clarendon, Oxford
Xue Q (2005) Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Phys B 368:302–307
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:2477–2483
Sheikholeslami M, Hatami M, Ganji DD (2014) Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a rotating system in the presence of a magnetic field. J Mol Liq 190:112–120
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R (2014) A study of natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid filled enclosure with elliptic inner cylinder. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 24(8):1906–1927
Nadeem S, Haq RU (2013) Effect of thermal radiation for megnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with convective boundary conditions. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11:32–40
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A (2015) Shape effects of nanosize particles in Cu–H2O nanofluid on entropy generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 81:449–456
Mohyud-Din ST, Khan U, Bin-Mohsin B (2016) Numerical investigation of MHD flow and heat transfer of copper-water nanofluid in a channel with non-parallel walls considering different shapes of nanoparticles. Adv Mech Eng 8(3):1–9
Anwar MI, Sharidan S, Khan I, Salleh MZ (2014) Magnetohydrodynamic flow of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet. Indian J Chem Technol 21:199–204
Khalid A, Khan I, Shafie S (2015) Exact solutions for free convection flow of nanofluids with ramped wall temperature. Eur Phys J Plus 130(57). doi:10.1140/epjp/i2015-15057-9
Mabood F, Khan WA, Ismail AIM (2015) MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a nonlinear stretching sheet: a numerical study. J Magn Magn Mater 374:569–576
Ul Haq R, Nadeem S, Khan ZH, Noor NFM (2015) Convective heat transfer in MHD slip flow over a stretching surface in the presence of carbon nanotubes. Phys B 457:40–47
Rashidi MM, Ganesh NV, Abdul Hakeem AK, Ganga B (2014) Buoyancy effect on MHD flow of nanofluid over a stretching sheet in the presence of thermal radiation. J Mol Liq 198:234–238
Khan U, Mohyud-Din ST, Mohsin BB (2016) Convective heat transfer and thermo-diffusion effects on flow of nanofluid towards a permeable stretching sheet saturated by a porous medium. Aerosp Sci Technol 50:196–203
Jeffery GB (1915) The two-dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Phil Mag 6:455–465
Hamel G (1916) Spiralförmige Bewgungen Zäher Flüssigkeiten. Jahresber Deutsch Math Verein 25:34–60
Motsa SS, Sibanda P, Awad FG, Shateyi S (2010) A new spectral-homotopy analysis method for the MHD Jeffery–Hamel problem. Comput Fluids 39:1219–1225
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD, Ashorynejad HR, Rokni HB (2012) Analytical investigation of Jeffery–Hamel flow with high magnetic field and nanoparticle by Adomian decomposition method. Appl Math Mech Engl Ed 33:25–36
Dorrepaal JM (1993) Slip flow in converging and diverging channels. J Eng Math 27:343–356
Khan U, Ahmed N, Sikander W, Mohyud-Din ST (2015) A study of velocity and temperature slip effects on flow of water based nanofluids in converging and diverging channels. Int J Appl Comput Math 1(4):569–587
Asadullah M, Khan U, Manzoor R, Ahmed N, Mohyud-din ST (2013) MHD flow of a Jeffery fluid in converging and diverging channels. Int J Mod Math Sci 6(2):92–106
Hayat T, Nawaz M, Sajid M (2010) Effect of heat transfer on the flow of a second-grade fluid in divergent/convergent channel. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 64:761–776
Hatami M, Ganji DD (2014) MHD nanofluid flow analysis in divergent and convergent channels using WRMs and numerical method. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 24(5):1191–1203
Khan U, Ahmed N, Sikander W, Mohyud-Din ST (2015) A study of velocity and temperature slip effects on flow of water based nanofluids in converging and diverging channels. Int J Appl Comput Math 1(4):569–587
Khan U, Ahmed N, Mohyud-Din ST (2015) Heat transfer effects on carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls under the effect of velocity slip boundary condition: a numerical study. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-2035-4
Turkyilmazoglu M (2014) Extending the traditional Jeffery–Hamel flow to stretchable convergent/divergent channels. Comput Fluids 100:196–203
Mohyud-Din ST, Khan U, Ahmed N, Hassan SM (2015) Magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer of nanofluids in stretchable convergent/divergent channels. Appl Sci 5:1639–1664
Khan WA, Khan ZH, Rahi M (2014) Fluid flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes along a flat plate with Navier slip boundary. Appl Nanosci. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0242-9
Rashidi MM, Erfani E (2011) The modified differential transform method for Investigating nano boundary-layers over stretching surfaces. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 21(7):864–883
Rashidi MM, Mohimanian Pour SA (2010) Analytic solution of steady three-dimensional problem of condensation film on inclined rotating disk by differential transform method. Math Probl Eng 2010:1–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, U., Ahmed, N., Mohyud-Din, S.T. et al. Flow of carbon nanotubes suspended nanofluid in stretchable non-parallel walls. Neural Comput & Applic 30, 2859–2871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2891-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2891-1