Abstract
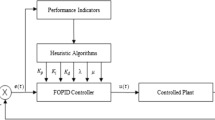
Theoretical and applied studies of fractional-order PI\(^{\lambda }\)D\(^{\mu }\) (FOPID) controller in many scientific and engineering fields have shown many advantages compared to the classical PID control. However, the adjustment of FOPID controller becomes more complicated due to two additional parameters. In this study, the FOPID controller adjustment problem is transformed into a nonconvex optimization problem, and then a new metaheuristic method, named state transition algorithm (STA), is introduced to select the optimal FOPID controller parameters. In the meanwhile, the influence of objective criterion and sample size on the performance of FOPID controller design is analyzed. The dominance of the proposed method, especially for tuning FOPID controller parameters, is attested by several simulation cases and the comparisons of STA with other stochastic global optimization algorithms over the same problems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rai P, Shekher V, Prakash O (2012) Determination of stabilizing parameter of fractional order PID controller using genetic algorithm. Int J Comput Eng Manag 15:24
Sabatier J, Agrawal O, Machado J (2007) Advances in fractional calculus. Springer, Netherlands
Dadras S, Momeni H (2012) Fractional terminal sliding mode control design for a class of dynamical systems with uncertainty. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17(1):367–377
Krishna B (2011) Studies on fractional order differentiators and integrators: a survey. Sig Process 91(3):386–426
Podlubny I (1999) Fractional-order systems and PID controllers. IEEE Trans Autom Control 44(1):208–214
Das S, Pan I, Das S, Gupta A (2012) A novel fractional order fuzzy PID controller and its optimal time domain tuning based on integral performance indices. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25(2):430–442
Koksal E (2013) Fractional-order and active disturbance rejection control of nonlinear two-mass drive system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(2):3806–3813
Wang D, Gao X (2012) H \(\infty\) design with fractional-order PD controllers. Automatica 48(5):974–977
Petráš I (2012) Tuning and implementation methods for fractional-order controllers. Fract Calc Appl Anal 15(2):282–303
Ramezanian H, Balochian S, Zare A (2013) Design of optimal fractional-order PID controllers using particle swarm optimization algorithm for automatic voltage regulator (avr) system. J Control Autom Electr Syst 24(5):601–611
Gao Q, Chen J, Wang L, Xu S, Hou Y (2013) Multiobjective optimization design of a fractional order PID controller for a gun control system. Sci World J 2013(1):907256–907256
Biswas A, Das S, Abraham A, Dasgupta S (2009) Design of fractional-order PID controllers with an improved differential evolution. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22(2):343–350
Özbay H, Bonnet C, Fioravanti A (2012) PID controller design for fractional-order systems with time delays. Syst Control Lett 61(1):18–23
Lee C, Chang F (2010) Fractional-order PID controller optimization via improved electromagnetism-like algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 37(12):8871–8878
Padhee S, Gautam A, Singh Y, Kaur G (2011) A novel evolutionary tuning method for fractional order PID controller. Int J Soft Comput Eng 1(3):1–9
Zhou X, Yang C, Gui W (2012) State transition algorithm. J Ind Manag Optim 8(4):1039–1056
Zhou X, Gao DY, Yang C (2013) A comparative study of state transition algorithm with harmony search and artificial bee colony. Adv Intell Syst Comput 213:651–659
Zhou X, Yang C, Gui W (2014) Nonlinear system identification and control using state transition algorithm. Appl Math Comput 226:169–179
Zhou X, Gao DY, Yang C, Gui W (2016) Discrete state transition algorithm for unconstrained integer optimization problems. Neurocomputing 173:864–874
Zhou X, Gao DY, Simpson AR (2016) Optimal design of water distribution networks by a discrete state transition algorithm. Eng Optim 48(4):603–628
Wang Y, He H, Zhou X, Yang C, Xie Y (2016) Optimization of both operating costs and energy efficiency in the alumina evaporation process by a multi-objective state transition algorithm. Can J Chem Eng 94(1):53–65
Wang G, Yang C, Zhu H, Li Y, Peng X, Gui W (2016) State-transition-algorithm-based resolution for overlapping linear sweep voltammetric peaks with high signal ratio. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 151:61–70
Monje C, Chen Y, Vinagre B, Xue D, Feliu-Batlle V (2010) Fractional-order systems and controls: fundamentals and applications. Springer, Berlin
Qin A, Huang V, Suganthan P (2009) Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13(2):398–417
Liang J, Qin A, Suganthan P, Baskar S (2006) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10(3):281–295
Barbosa RS, Machado JT, Ferreira IM (2004) Tuning of PID controllers based on bodes ideal transfer function. Nonlinear Dyn 38:305–321
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61503416, 61533020, 61533021, 61590921) and Key Exploration Project (Grant No. 7131253) for the funding support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Yang, C., Zhou, X. et al. Fractional-order PID controller tuning using continuous state transition algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 795–804 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2605-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2605-0