Abstract
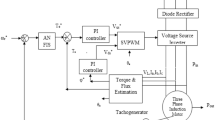
In this paper, a five-level cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverters topology is applied on induction motor control known as direct torque control (DTC) strategy. More inverter states can be generated by a five-level inverter which improves voltage selection capability. This paper also introduces two different control methods to select the appropriate output voltage vector for reducing the torque and flux error to zero. The first is based on the conventional DTC scheme using a pair of hysteresis comparators and look up table to select the output voltage vector for controlling the torque and flux. The second is based on a new fuzzy logic controller using Sugeno as the inference method to select the output voltage vector by replacing the hysteresis comparators and lookup table in the conventional DTC, to which the results show more reduction in torque ripple and feasibility of smooth stator current. By using Matlab/Simulink, it is verified that using five-level inverter in DTC drive can reduce the torque ripple in comparison with conventional DTC, and further torque ripple reduction is obtained by applying fuzzy logic controller. The simulation results have also verified that using a fuzzy controller instead of a hysteresis controller has resulted in reduction in the flux ripples significantly as well as reduces the total harmonic distortion of the stator current to below 4 %.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hassan AA, Shehata EG (2012) High performance direct torque control schemes for an IPMSM drive. Electric Power Syst Res 89:171–182
Takahashi I, Noguchi T (1986) A new quick-response and high-efficiency control strategy of an induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl IA–22(5):820–827
Toufouti R, Meziane S, Benalla H (1997) Direct torque control for induction motor using fuzzy logic. Power Electronics 12.3
Abad G, Rodriguez MA, Poza J (2008) Two-level VSC based predictive direct torque control of the doubly fed induction machine with reduced torque and flux ripples at low constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(3):1050–1061
Casadei D, Serra G, Tani A (1998) Improvement of direct torque control performance by using a discrete svm technique. In: 29th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference (PESC 98) record, vol 2, pp 997–1003
Buja GS, Kazmierkowski MP (2004) Direct torque control of PWM inverter-fed AC motors—a survey. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(4):744–757
Vas P (1990) Vector control of AC machines. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Idris NRN, Yatim AHM (2004) Direct torque control of induction machines with constant switching frequency and reduced torque ripple. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(4):758–767
Sheng-wei G, Yan C (2010) Torque ripple minimization strategy for direct torque control of induction motors. In: 3rd international conference on intelligent networks and intelligent systems (ICINIS), pp 148–151
Casadei D, Serra G, Tani A (1997) Analytical investigation of torque and flux ripple in DTC schemes for induction motors. In: 23rd international conference on industrial electronics, control and instrumentation (IECON 97), vol 2, pp 552–556
Habetler TG, Profumo F, Pastorelli M, Tolbert LM (1992) Direct torque control of induction machines using space vector modulation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 28(5):1045–1053
Colak I, Kabalci E, Bayindir R (2011) Review of multilevel voltage source inverter topologies and control schemes. Energy Convers Manag 52(2):1114–1128
Mir SA, Zinger DS, Elbuluk ME (1994) Fuzzy controller for inverter fed induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 30(1):78–84
Casadei D, Serra G, Tani A, Zarri L, Profumo F Constant frequency operation of a DTC induction motor drive for electric vehicle. In: Proceedings of the ICEM conference, vol 3, pp 224–229
Mir SA, Elbuluk ME, Zinger D (1994) Fuzzy implementation of direct self-control of induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 30(3):729–735
Bird I, Zelaya De La Parra H (1997) Fuzzy logic torque ripple reduction for DTC based AC drives. Electron Iett 33(17):1501–1502
Mir S, Elbuluk ME (1995) Precision torque control in inverter-fed induction machines using fuzzy logic. In: 26th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference (PESC ’95) record, vol 1, pp 396–401
Rahmani R, Mahmodian MS, Mekhilef S, Shojaei AA (2012) Fuzzy logic controller optimized by particle swarm optimization for DC motor speed control. In: IEEE student conference on research and development (SCOReD), pp 109–113
Pati S, Samantray S, Patel NC (2013) A novel adaptive fuzzy controller for performance improvement of direct torque controlled induction generator employed for wind power applications. In: Annual international conference on emerging research areas and international conference on microelectronics, communications and renewable energy (AICERA/ICMiCR), pp 1–6
Lekhchine S, Bahi T, Soufi Y (2014) Indirect rotor field oriented control based on fuzzy logic controlled double star induction machine. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 57:206–211
Nayak M, Singh S (2013) Fuzzy logic control of induction motor drive for performance improvement. Doctoral dissertation. National Institute of Technology Rourkela
Nabae A, Takahashi I, Akagi H (1981) A new neutral-point-clamped PWM inverter. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 23(5):518–523
Rodriguez J, Lai JS, Peng FZ (2002) Multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 49(4):724–738
Casadei D, Profumo F, Serra G, Tani A (2002) FOC and DTC: two viable schemes for induction motors torque control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 17(5):779–787
del Toro X, Jayne M, Witting P, Arias A, Romeral J (2004) Direct torque control of an induction motor using a three-level inverter and fuzzy logic. In: IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, vol 2, pp 923–927
Tan Z, Li Y, Li M (2001) A direct torque control of induction motor based on three-level NPC inverter. In: IEEE 32nd annual Power electronics specialists conference (PESC), vol 3, pp 1435–1439
Baker RH, Lawrence BH (1975) Electric power converter. US Patent 3,867,643, 18 Feb 1975
Vahedi H, Al-Haddad K, Ounejjar Y, Addoweesh K (2013) Crossover switches cell (CSC): a new multilevel inverter topology with maximum voltage levels and minimum DC sources. In: 39th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society (IECON 2013), pp 54–59
Vahedi H, Rahmani S, Al-Haddad K (2013) Pinned mid-points multilevel inverter (PMP): three-phase topology with high voltage levels and one bidirectional switch. In: 39th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society (IECON 2013), pp 102–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmani, R., Langeroudi, N.M.A., Yousefi, R. et al. Fuzzy logic controller and cascade inverter for direct torque control of IM. Neural Comput & Applic 25, 879–888 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1561-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1561-9