Abstract
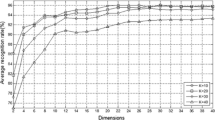
Two-dimensional locality preserving projections (2DLPP) was recently proposed to extract features directly from image matrices based on locality preserving criterion. A significant drawback of 2DLPP is that it only works on one direction (left or right) to reduce the dimensionality of the image matrices and thus too many coefficients are needed for image representation in low-dimensional subspace. In this paper, we propose a novel method called two-dimensional bilinear preserving projections (2DBPP) for image feature extraction. We generalized the image-based (2D-based) feature extraction techniques into bilinear cases, in which 2DLPP is a special case of our proposed method. In order to obtain the bilinear projections, we proposed an iteration method by solving the corresponding generalized eigen-equations. Moreover, analyses show that 2DBPP has stronger locality preserving abilities than 2DLPP. By using the label information and defining different local neighborhood graphs, the proposed framework is further extended to supervised case. Experiments on three databases show that 2DBPP and its supervised extension are superior to some other image-based state-of-the-art techniques.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turk M, Pentland AP (1991) Face recognition using eigenfaces. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 586–591
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriengman DJ (1997) Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720
He X, Niyogi P (2003) Locality preserving projections. In: Proceedings of the 16th conference neural information processing systems
He XF, Yan S, Hu Y, Niyogi P, Zhang HJ (2005) Face recognition using Laplacianfaces. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(3):328–340
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Zhang H-J (2007) Graph embedding: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(1):40–51
Lai Z, Wan M, Jin Z (2011) Locality preserving embedding for face and handwriting digital recognition. Neural Comput Appl 20(4):565–573
Lai Z, Zhao C, Chen Y, Jin Z (2011) Maximal local interclass embedding with application to face recognition. Mach Vis Appl 22(4):619–627
Lai Z, Zhao C, Wan M (2012) Fisher difference discriminant analysis: determining the effective discriminant subspace dimensions for face recognition. Neural Process Lett 35(3):203–220
Yang J, Zhang D, Frangi AF, Yang JY (2004) Two-dimensional PCA: a new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(1):131–137
Sun N, Wang H, Ji Z, Zou C, Zhao L (2008) An efficient algorithm for Kernel two-dimensional principal component analysis. Neural Comput Appl 17(1):46–59
Ye J (2005) Generalized low rank approximations of matrices. Mach Learn 61(1):167–191
Li M, Yuan B (2005) 2D-LDA: a statistical linear discriminant analysis for image matrix. Pattern Recogn Lett 26(5):527–532
Nagabhushan P, Guru DS, Shekar BH (2006) (2D)2FLD: an efficient approach for appearance based object recognition. Neurocomputing 69:934–940
Niu B, Yang Q, Shiu SCK, Pal SK (2008) Two-dimensional Laplacianfaces method for face recognition. Pattern Recogn 41(10):3237–3243
Hu D, Feng G, Zhou Z (2007) Two-dimensional locality preserving projections (2DLPP) with its application to palmprint recognition. Pattern Recogn 40(1):339–342
Chen S, Zhao H, Kong M, Luo B (2007) 2DLPP: a two-dimensional extension of locality preserving projections. Neurocomputing 70(4–6):912–921
Wan M, Lai Z, Shao J, Jin Z (2009) Two-dimensional local graph embedding discriminant analysis (2DLGEDA) with its application to face and palm biometrics. Neurocomputing 73:193–203
Xu Y, Feng G, Zhao Y (2009) One improvement to two-dimensional locality preserving projection method for use with face recognition. Neurocomputing 73:245–249
Lai Z, Wong WK, Jin Z, Yang J, Xu Y (2012) Sparse approximation to the eigen subspace for discrimination. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2217154
Lai Z, Jin Z, Yang J (2011) Sparse two dimensional local discriminant projections for feature extraction. Neurocomputing 74(4):629–637
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2003) The CMU pose, illuminlation, and expression database”. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(12):1615–1618
Zhang D (2004) Palmprint authentication. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Tan, Z. & Zhan, Y. Two-dimensional bilinear preserving projections for image feature extraction and classification. Neural Comput & Applic 24, 901–909 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1311-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1311-9